(Press-News.org) Bone-regenerating treatments are in high demand due to the ageing population. Increasingly, the orthopaedic biomaterials used to support these treatments are designed to be "immunomodulatory", i.e., guide the body's inflammatory response. They do this by encouraging macrophages - a type of white blood cell that surrounds and kills microorganisms - to adopt new roles based on signals and stimuli in their microenvironment. This approach has proved effective for developing new bone and for encouraging existing bone to accept artificial implants.
Magnesium is a mineral that not only helps to maintain normal nerve and muscle function, importantly, it also supports a healthy immune system and helps bones to retain their strength. Typically, it is given to orthopaedic patients as an oral supplement.
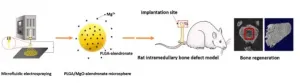
In a recent study published in the KeAi journal Bioactive Materials, a group of researchers from Hong Kong and mainland China, trialed a new immunomodulatory approach which replaces that magnesium supplement with an injection - directly into the compromised bone - of custom-made, polymer microspheres that control the release of magnesium ions.
According to one of the study's authors, Kelvin Yeung, Professor in Orthopaedics and Traumatology at the University of Hong Kong, the team tested the hypothesis by using two different animal models. "In one, we injected the microspheres containing the magnesium (Mg) ions. In the other, we injected microspheres without the Mg loading. In the two weeks following the injections, faster bone regeneration rates were observed in the first group."
Professor Young believes that one of the benefits of magnesium is that it encourages the immune system and skeletal system to work in tandem to support in situ healing.
He explains: "The biomaterial development for bone repair usually involves the direct activation of osteoprogenitor cells - stem cells located in the bone that play a key role in bone repair and growth. However, the "conversation" that takes place between the skeletal and immune systems during the bone healing process has often been overlooked."
Professor Yeung points to the fact that the healthy functioning of immune cells significantly impacts bone regeneration and remodelling. "In this study, we have drawn on the properties of biomaterials that can tailor the plasticity of macrophages. For instance, our custom-made, magnesium-loaded microspheres created a favourable, anti-inflammatory, osteoimmune environment."
He adds: "Bioactive metal ions working as minerals has huge potential in bone or other musculoskeletal tissue regenerations. We hope our results can convince scientists to explore the potentials of these ions beyond bone healing."
INFORMATION:
Contact the paper's authors: Zhengjie Lin, linzhengjie1218@163.com | Kelvin W.K. Yeung, wkkyeung@hku.hk
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
BEND, Ore. - Bat researchers say a project in Central Oregon shows citizen science's strong potential for helping ecologists learn more about one of the least understood groups of mammals.
Volunteers listened for the rare spotted bat, Euderma maculatum, within study grids in a 24,000-square-kilometer area in and around the Deschutes and Ochoco national forests. They completed a total of 61 surveys and heard the bat 25 times.
Bat encounters help fill in holes in basic information regarding species abundance and distribution - gaps that impede conservation - and the ...
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. - Fine-grained location data gleaned from mobile phones shows that people living in less affluent neighborhoods spent less time at home during the early lockdown and first several months of the coronavirus pandemic.
Researchers tracked data from millions of mobile phone users in the largest U.S. metropolitan areas. Their findings contribute to a growing body of research suggesting that low-wage earners -- a vulnerable group already at greater risk for contracting COVID-19 -- could not afford to comply with stay-at-home orders or worked in ...
Global oceans absorb about 25% of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burned. Electricity-eating bacteria known as photoferrotrophs could provide a boost to this essential process, according to new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Scientists led by Arpita Bose, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, found that bacteria found in brackish sediments can "eat" electricity and, in the process, absorb and lock away climate-warming carbon dioxide. This unusual skill was previously thought to be almost exclusive to freshwater bacteria, but may be common ...
WASHINGTON--A new study finds people who consume two servings of fruit per day have 36 percent lower odds of developing type 2 diabetes than those who consume less than half a serving. The research was published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Diabetes is a disease where people have too much sugar in their bloodstream, and it is a huge public health burden. Approximately 463 million adults worldwide were living with diabetes in 2019, and by 2045 this number is expected to rise to 700 million. An estimated 374 million people are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, the most common form of the disease. A healthy diet and lifestyle can play a major role in lowering a person's diabetes risk.
"We ...
A new study led by researchers at Washington State University has identified a protein that could be the key to improving treatment outcomes after a heart attack.
Published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, the research suggests that protein kinase A (PKA) plays a role in heart muscle cell necrosis, a major type of cell death that commonly occurs after reperfusion therapy, the treatment used to unblock arteries and restore blood flow after a heart attack.
"Our study has found that turning off a gene that controls this protein activity increased necrotic cell death and led to more heart injury and worse heart function following heart attack in a rodent model," said study author Zhaokang Cheng, an assistant professor in the WSU College ...
As early as the Neolithic period (circa 3900 BC), the domestication of animals likely led to the development of diseases including measles and smallpox. Since then, zoonotic disease has led to other major transnational outbreaks including HIV, Ebola, SARS, MERS, and H1N1 swine flu, among others. Currently, more than half of all existing human pathogens, and almost three-quarters of emerging infectious diseases, are zoonotic in nature.
COVID-19 is the latest and most impactful zoonotic event of the modern era, but it will certainly not be the last.
Given the breadth of these impacts and the fact that other zoonotic pandemics are highly likely - a matter of when and not if - the key public health ethics question that emerges is about whether it is ethically appropriate for governments ...
Doctors have hoped that antibiotics could benefit patients with chronic lung diseases, but a new study has found no benefit for patients with life-threatening idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in preventing hospitalization or death.
While there were no statistical benefits for patients with the lung-scarring disease, the new research will prevent unnecessary antibiotic use that could contribute to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance. The nationwide clinical trial - believed to be the largest idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis trial ever conducted - also collected biological samples that will advance the understanding and treatment of the mysterious and ultimately fatal illness.
"We were certainly disappointed in the results. But we remain hopeful that in further downstream ...
(Carlisle, Pa.) -- A new study published in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine finds critical links between job loss and physical inactivity in young adults during the U.S. Great Recession of 2008-09 that can be crucial to understanding the role of adverse economic shocks on physical activity during the COVID-19 pandemic. It is the first study to examine how job losses during the Great Recession affected the physical activity of young adults in the United States.
The study by Dickinson College economist Shamma Alam and Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health economist Bijetri Bose looked at Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) data for young adults age 18 to 27--a phase of development associated with maturation and significant ...
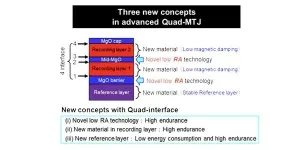
Professor Tetsuo Endoh's Group at Tohoku University's Center for Innovative Integrated Electronics has announced a new magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) quad-technology that provides better endurance and reliable data retention - over 10 years - beyond the 1X nm generation.
This novel Quad technology meets the design requirements for the state-of-the-art X nm complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) node and will pave the way for ultra-low-power consumption for Internet of Things (IoT) edge-devices in mobile communication, the automotive industry, consumer electronics, ...
Researchers from Telethon Kids Institute and Curtin University in Perth and Tulane University in New Orleans have developed sophisticated data modelling that could help eradicate malaria in Haiti.
Haiti is the poorest country in the Caribbean - beset by natural disasters - and is one of the few countries in the region that have not mostly wiped out the mosquito-borne disease.
Telethon Kids Institute researcher Associate Professor Ewan Cameron led the team, using a range of different health data to create a complete picture of where malaria infections are taking place in Haiti. This information has been used to directly inform Haiti's national response to malaria.
The team's findings ...