(Press-News.org) Researchers at Linköping University in Sweden have developed an app to help women achieve a healthy weight gain and lifestyle during a pregnancy. The results from an evaluation of the app have now been published in two scientific articles. Using the app contributed to a better diet. Pregnant women with overweight or obesity who received the app also gained less weight during pregnancy.
"Pregnancy is a phase in life when many people try to do what is best for themselves and their baby. We think it's important to be able to offer a tool that has a sound base in research. Our vision is that the app will help both those working in maternity care and pregnant women, by providing support for a healthy lifestyle", says Marie Löf, professor at the Department of Health, Medicine and Caring Sciences at Linköping University, who has led the research.
Weight gain during pregnancy is normal. The definition of appropriate weight gain, or recommended weight gain, depends on the weight status prior to pregnancy. There may be negative consequences if a woman gains too much or too little weight.
"Gaining too much weight during pregnancy increases the risk of pre-eclampsia and gestational diabetes, and of subsequent overweight in both mother and child. At the same time, gaining less weight than recommended is associated with an increased risk of preterm birth and low birth weight", says Johanna Sandborg, doctoral student at Karolinska Institutet affiliated with Linköping University. She is first author for both of the articles that have been published in the journal JMIR mHealth and uHealth.
The researchers emphasise that the app aims to support pregnant women in achieving a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy. It provides an exercise guide, help to keep track of dietary habits and physical activity, support in changing habits, recipes and information. It has been developed by a team consisting of nutritionists, dieticians, midwives, physicians, physiotherapists, behavioural scientists, and systems developers.
In order to evaluate the effectiveness of using the app, the researchers have conducted a study in which just over 300 pregnant women in Östergötland took part. Half of them received standard care within the maternity care system (the control group), and the other half also had access to the app (the intervention group). Previous similar studies of smartphone apps have most often focused on pregnant women with overweight and obesity, in other words, those with a high body mass index (BMI). In this case, however, women from all BMI categories were included. All participants registered their physical activity and food consumption (using the Riksmaten FLEX tool from the National Food Agency, Sweden) at 14 weeks of pregnancy and approximately six months later. The researchers also measured the women's weight, height and body fat percentage on both occasions.
"The diet in the group that used the HealthyMoms app was slightly better towards the end of the pregnancy than that of the control group. Another result is that the women with overweight or obesity before pregnancy in the intervention group gained on average 1.7 kg less than those in the control group. We regard it as very positive that our app can lead to an effect similar to that seen in studies evaluating interventions that require more personnel and resources", says Marie Löf.
The researchers interviewed 19 of the women who had had access to the app. In these interviews, the participants expressed that the app contained a good combination of useful tools, and that they trusted the content since the app came from a credible source.
"We now have an evidence-based, validated tool that we can use in the healthcare system, benefitting both pregnant women and personnel", says Marie Löf.
The researchers are working on how to spread the HealthyMoms app to a broader group, and to offer it in more languages than Swedish. They are working with co-workers who speak Somali and Arabic not only to translate the information, but also to adapt the app for different groups.
INFORMATION:
Others at Linköping University who have played major roles in the project are Pontus Henriksson, Eva Flinke and Emmie Söderström. Sources of funding for the research include FORTE - the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, and the Strategic Research Area Health Care Science (SFO-V) at Karolinska Institutet and Umeå University.
The article: "Effectiveness of a Smartphone App to Promote Healthy Weight Gain, Diet, and Physical Activity During Pregnancy (HealthyMoms): Randomized Controlled Trial", Johanna Sandborg, Emmie Söderström, Pontus Henriksson, Marcus Bendtsen, Maria Henström, Marja H Leppänen, Ralph Maddison, Jairo H Migueles, Marie Blomberg and Marie Löf, (2021), JMIR mHealth and uHealth, published online 11 March 2021, doi: 10.2196/26091
https://mhealth.jmir.org/2021/3/e26091
The article: "Participants' Engagement and Satisfaction With a Smartphone App Intended to Support Healthy Weight Gain, Diet, and Physical Activity During Pregnancy: Qualitative Study Within the HealthyMoms Trial", Johanna Sandborg, Pontus Henriksson, Erica Larsen, Anna-Karin Lindqvist, Stina Rutberg, Emmie Söderström, Ralph Maddison and Marie Löf, (2021), JMIR mHealth and uHealth, published online 5 March 2021, doi: 10.2196/26159
https://mhealth.jmir.org/2021/3/e26159
Good acoustics in the workspace improve work efficiency and productivity, which is one of the reasons why acoustic materials matter. The acoustic insulation market is already expected to hit 15 billion USD by 2022 as construction firms and industry pay more attention to sound environments. Researchers at Aalto University, in collaboration with Finnish acoustics company Lumir, have now studied how these common elements around us could become more eco-friendly, with the help of cellulose fibres.
'Models for acoustic absorption are based on tests done with synthetic fibres, and ...
An international research team determined that ancestors of modern domestic horses and the Przewalski horse moved from the territory of Eurasia (Russian Urals, Siberia, Chukotka, and eastern China) to North America (Yukon, Alaska, continental USA) from one continent on another at least twice. It happened during the Late Pleistocene (2.5 million years ago - 11.7 thousand years ago). The analysis results are published in the journal. The findings and description of horse genomes are published in the journal Molecular Ecology.
"We found out that the Beringian Land Bridge, or the area known as Beringia, influenced genetic ...
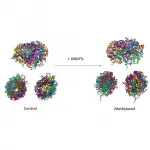
All the cells of an organism share the same DNA sequence, but their functions, shapes or even lifespans vary greatly. This happens because each cell "reads" different chapters of the genome, thus producing alternative sets of proteins and embarking on different paths. Epigenetic regulation--DNA methylation is one of the most common mechanisms--is responsible for the activation or inactivation of a given gene in a specific cell, defining a secondary cell-specific genetic code.
Researchers led by Dr. Modesto Orozco, head of the Molecular Modelling and Bioinformatics lab at IRB Barcelona, have described how methylation has a protein-independent regulatory role by increasing the stiffness of DNA, which affects the 3D structure ...
Autistic people's ability to accurately identify facial expressions is affected by the speed at which the expression is produced and its intensity, according to new research at the University of Birmingham.
In particular, autistic people tend to be less able to accurately identify anger from facial expressions produced at a normal 'real world' speed. The researchers also found that for people with a related disorder, alexithymia, all expressions appeared more intensely emotional.
The question of how people with autism recognise and relate to emotional expression has been debated by scientists for more than three decades and it's only in the past 10 years ...
The gut and the brain communicate with each other in order to adapt satiety and blood sugar levels during food consumption. The vagus nerve is an important communicator between these two organs. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Metabolism Research in Cologne, the Cluster of Excellence for Ageing Research CECAD at the University of Cologne and the University Hospital Cologne now took a closer look at the functions of the different nerve cells in the control centre of the vagus nerve, and discovered something very surprising: although the nerve cells are located in the same control center, they innervate different regions of the gut and also differentially control satiety and blood sugar levels. This discovery could play an important role in the development of future ...
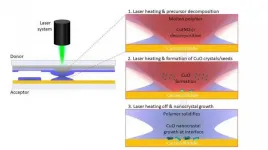
In the journal Nature Communications, an interdisciplinary team from the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces presents for the first time a laser-driven technology that enables them to create nanoparticles such as copper, cobalt and nickel oxides. At the usual printing speed, photoelectrodes are produced in this way, for example, for a wide range of applications such as the generation of green hydrogen.
Previous methods produce such nanomaterials only with high energy input in classical reaction vessels and in many hours. With the laser-driven technology developed at the institute, the scientists can deposit small amounts of material on a surface and simultaneously perform chemical synthesis in a very short time using high temperatures from the laser. 'When I discovered ...
A facial expression or the sound of a voice can say a lot about a person's emotional state; and how much they reveal depends on the intensity of the feeling. But is it really true that the stronger an emotion, the more intelligible it is? An international research team comprised of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Empirical Aesthetics, New York University, and the Max Planck NYU Center for Language, Music, and Emotion (CLaME) has now discovered a paradoxical relationship between the intensity of emotional expressions and how they are perceived.
Emotions ...
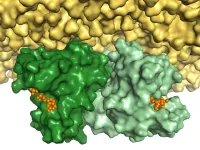
Researchers from Bochum and Osnabrück have gained new insights into the structure of the Ras protein, which acts as a molecular switch for cell growth and is involved in the development of cancer. With the help of fluorescence markings, they have demonstrated that the protein is deposited in a pair at the cell membrane, and with the very structure that they predicted in theory back in 2012. The team from the Bochum Center for Protein Diagnostics (PRODI) hopes that these findings will open up a new approach for the development of cancer medications. The researchers from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and Osnabrück University ...
Prenuptial agreements, or "prenups," can be difficult to talk about. But a recent study offers insights into how people can discuss this often taboo subject. One approach? Use metaphors.
"Many people view prenups as being negative, and argue that they indicate a lack of faith in the marriage from the outset," says Lynsey Romo, corresponding author of the study and an associate professor of communication at North Carolina State University. "By the same token, we know from other research that open communication about financial issues contributes to successful relationships.
"And yet there is virtually no academic research on prenups. So how do people talk about prenups? How do they make sense of them? That's what we wanted ...
SAN ANTONIO (June 2, 2021) -- Scientists from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio have discovered a mechanism by which SARS-CoV-2 exploits changes in metal ion concentrations to disguise itself in the body. Varying concentrations of metal ions -- positively charged atoms such as magnesium, manganese and calcium -- are observed in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
"This is a newly described metal-dependent mechanism by which these ions help the virus to evade immune surveillance," said END ...