(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO (June 2, 2021) -- Scientists from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio have discovered a mechanism by which SARS-CoV-2 exploits changes in metal ion concentrations to disguise itself in the body. Varying concentrations of metal ions -- positively charged atoms such as magnesium, manganese and calcium -- are observed in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
"This is a newly described metal-dependent mechanism by which these ions help the virus to evade immune surveillance," said END
Metal ions help COVID-19 virus to disguise itself
Positively charged atoms steady the machinery that the virus uses to trick the system
2021-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
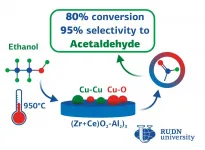
RUDN University chemists created cheap catalysts for ethanol conversion
2021-06-02
RUDN University chemists proposed a new way to synthesize catalysts for the conversion of ethyl alcohol. The obtained materials are promising catalysts for the selective conversion of ethanol, which is an important stage in the development of an alternative technology for obtaining valuable chemical synthesis products based on plant raw materials. The results of the study are published in Catalysis Today.
Ethanol fuel is ethyl alcohol, it is produced from plant material by fermentation of industrial or agricultural waste biomass. It is used as a more environmentally ...
Laser physics: Two-stage particle-beam booster
2021-06-02
In collaborative international effort, laser physicists at LMU have built the first hybrid plasma accelerator.
Particle accelerators have made crucial contributions to some of the most spectacular scientific discoveries of modern times, and greatly augmented our knowledge of the structure of matter. Now a team of laser physicists led by Prof. Stefan Karsch at the Ludwig-Maximilian University (LMU) in Munich and the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics, in cooperation with scientists based at the Helmholtz Centre in Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR), the Laboratoire d'Optique Appliquée in Paris (LOA), Strathclyde University in Glasgow and the DESY Electron Synchrotron in Hamburg, have now achieved a significant ...
Current global environmental law and policy are failing, experts say
2021-06-02
Amsterdam, June 2, 2021 - On the eve of the 50th anniversary of the 1972 Stockholm conference that created the United Nations Environmental Programme, it is clear that the global environmental situation has only deteriorated. In "Our Earth Matters: Pathways to a Better Common Environmental Future," an extended special issue of Environmental Policy and Law (EPL), leading scholars from more than five continents call for an honest introspection of what has been attained over the last 50 years relating to regulatory processes and laws and explore future trajectories with new ideas and frameworks for environmental governance in the 21st century.
"Our objective is to fire the imaginations of scholars and decision-makers to re-examine current approaches and to explore the future, ...
New study reveals how smoking during puberty can cause negative consequences in offspring
2021-06-02
Smoking in early puberty in boys may have negative consequences for their future generations of offspring, a study from the University of Bergen (UiB) shows.
By continued analysis of data gathered in the large international RHINESSA, RHINE and ECRHS studies, researchers have found that the health of future generations depends on actions and decisions made by young people today. This is particularly relevant for boys in early puberty and mothers/grandmothers both pre-pregnancy and during pregnancy, the study shows.
The paper "Prenatal and prepubertal exposures to tobacco smoke in ...
Anyone can get super-hearing
2021-06-02
Humans can observe what and where something happens around them with their hearing, as long as sound frequencies lie between 20 Hz and 20 000 Hz. Researchers at Aalto University have now developed a new audio technique that enables people to also hear ultrasonic sources that generate sound at frequencies above 20,000 Hz with simultaneous perception of their direction. The results have been published in Scientific Reports on 2 June 2021.
'In our study, we used bats in their natural habitat as sources of ultrasonic sound. With our new technique, we can now hear the directions-of-arrival of bat sounds, which means we can track bats in flight and hear where they are - we're ...
Astronomers discover a massive star cluster, of intermediate age, in the constellation Scutum
2021-06-02
An international team of astrophysicists led by the Stellar Astrophysics Group of the University of Alicante (UA), the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), and the University of Valparaíso (Chile) has discovered a massive cluster of stars of intermediate age in the direction of the Scutum constellation. This object, which has been named Valparaíso 1, lies some seven thousand light years away from the Sun, and contains at least fifteen thousand stars. To detect it, observations have been combined from ESA's Gaia satellite, and various ground-based telescopes, ...
Converting scar tissue to heart muscle after a heart attack
2021-06-02
Tsukuba, Japan - It is estimated that during a heart attack, one billion cells in the heart are lost. In the wake of the heart attack, the lost tissue is replaced by scar tissue, which can lead to heart failure, arrhythmia and death. In a new study, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have shown how cells in the scar tissue can be converted to heart muscle cells, effectively regenerating the injured heart.
The injured heart of humans and rodents alike does not have the capacity to regenerate after injury. Therefore, the only way for the heart to heal the wound is to build a scar tissue in the injured area. A longstanding goal in the field has been to find a way to reprogram fibroblasts, ...
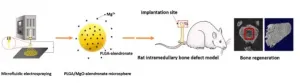
Magnesium ions injected directly into compromised bone accelerate bone regeneration
2021-06-02
Bone-regenerating treatments are in high demand due to the ageing population. Increasingly, the orthopaedic biomaterials used to support these treatments are designed to be "immunomodulatory", i.e., guide the body's inflammatory response. They do this by encouraging macrophages - a type of white blood cell that surrounds and kills microorganisms - to adopt new roles based on signals and stimuli in their microenvironment. This approach has proved effective for developing new bone and for encouraging existing bone to accept artificial implants.
Magnesium is a mineral that not only helps to maintain normal nerve and ...
Central Oregon bat survey shows value and scale-up potential of citizen science
2021-06-02
BEND, Ore. - Bat researchers say a project in Central Oregon shows citizen science's strong potential for helping ecologists learn more about one of the least understood groups of mammals.
Volunteers listened for the rare spotted bat, Euderma maculatum, within study grids in a 24,000-square-kilometer area in and around the Deschutes and Ochoco national forests. They completed a total of 61 surveys and heard the bat 25 times.
Bat encounters help fill in holes in basic information regarding species abundance and distribution - gaps that impede conservation - and the ...
Low-wage earners spent less time at home during early pandemic lockdown
2021-06-02
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. - Fine-grained location data gleaned from mobile phones shows that people living in less affluent neighborhoods spent less time at home during the early lockdown and first several months of the coronavirus pandemic.
Researchers tracked data from millions of mobile phone users in the largest U.S. metropolitan areas. Their findings contribute to a growing body of research suggesting that low-wage earners -- a vulnerable group already at greater risk for contracting COVID-19 -- could not afford to comply with stay-at-home orders or worked in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
Study: Anxiety, gloom often accompany intellectual deficits
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
Increasing the number of coronary interventions in patients with acute myocardial infarction does not appear to reduce death rates
Tackling uplift resistance in tall infrastructures sustainably
Novel wireless origami-inspired smart cushioning device for safer logistics
Hidden genetic mismatch, which triples the risk of a life-threatening immune attack after cord blood transplantation
Physical function is a crucial predictor of survival after heart failure
Striking genomic architecture discovered in embryonic reproductive cells before they start developing into sperm and eggs
Screening improves early detection of colorectal cancer
New data on spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) – a common cause of heart attacks in younger women
How root growth is stimulated by nitrate: Researchers decipher signalling chain
Scientists reveal our best- and worst-case scenarios for a warming Antarctica
Cleaner fish show intelligence typical of mammals
AABNet and partners launch landmark guide on the conservation of African livestock genetic resources and sustainable breeding strategies
[Press-News.org] Metal ions help COVID-19 virus to disguise itselfPositively charged atoms steady the machinery that the virus uses to trick the system