(Press-News.org) An international team of astrophysicists led by the Stellar Astrophysics Group of the University of Alicante (UA), the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), and the University of Valparaíso (Chile) has discovered a massive cluster of stars of intermediate age in the direction of the Scutum constellation. This object, which has been named Valparaíso 1, lies some seven thousand light years away from the Sun, and contains at least fifteen thousand stars. To detect it, observations have been combined from ESA's Gaia satellite, and various ground-based telescopes, including the Isaac Newton Telescope at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory (Garafía, La Palma, Canary Islands). The result has been published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS).
Open clusters are groups of stars which were born together, and move together, bound by gravity. This makes them natural laboratories for studying the physics and the lives of stars. The more stars there are in a cluster, the more useful it is, because the larger sample gives a better chance to find stars in less frequent evolutionary phases.
This is why astronomers are searching for the most massive clusters in our Galaxy, those with over ten thousand stars. Until twenty years ago it was thought that these are formed only in distant galaxies with exotic properties, but thanks to these searches now we know a dozen very young massive clusters (less than 25 million years old), and a few very old ones (thousands of millions of years old), which are descendants of former young clusters. But there are hardly any massive clusters known with intermediate ages, and it was not clear whether these do not exist, or whether they had not yet been found.
The newly discovered cluster, which they have called Valparaíso 1, is at some seven thousand light years from the sun, and contains at least fifteen thousand stars. Its unexpected discovery, in a well-explored part of the sky, suggests than many other massive clusters might be hidden in the very dense star fields, which observers find when looking towards the centre of our Galaxy.
"Valparaíso 1 contains dozens of stars sufficiently bright to be observable through an amateur telescope, but they are lost in the middle of a crowd of stars which don't belong to the cluster, but which are in front of it or behind it, and which disguise the structure of the cluster", explains Ignacio Negueruela, a researcher at the University of Alicante and the first author of the article.
"Previous searches tried to locate open clusters, but Valparaíso 1 does not look like a cluster similar to those which we usually find, and that is why it was not discovered before", says Ricardo Dorda, an IAC researcher who is a co-author of the article.
The cluster was detectable thanks to the Gaia satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), a space telescope which gives extremely accurate positions and distances of stars quite far away, and with this information we can measure the tiny motions across the sky shown by the stars over the years. Combining all of the information, we can detect clusters as groups of stars, which are at the same distance from us, and move together, groups of stars easier to detect using physics than just by looking at them on the sky. When the researchers had located this cluster, they used telescopes at the Las Campanas Observatory (in Chile) and the Isaac Newton Telescope (INT) at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory (Garafía, La Palma, Canary Islands) to derive the physical properties of its stars.
INFORMATION:
Article: I. Negueruela, A-N. Chené, H. M. Tabernero, R. Dorda, J. Borissova, A. Marco, R. Kurtev, "A massive open cluster hiding in full sight". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, April 24, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stab1117
Tsukuba, Japan - It is estimated that during a heart attack, one billion cells in the heart are lost. In the wake of the heart attack, the lost tissue is replaced by scar tissue, which can lead to heart failure, arrhythmia and death. In a new study, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have shown how cells in the scar tissue can be converted to heart muscle cells, effectively regenerating the injured heart.
The injured heart of humans and rodents alike does not have the capacity to regenerate after injury. Therefore, the only way for the heart to heal the wound is to build a scar tissue in the injured area. A longstanding goal in the field has been to find a way to reprogram fibroblasts, ...
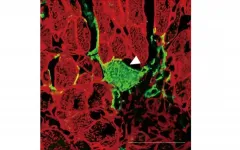
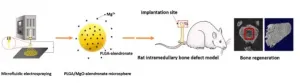
Bone-regenerating treatments are in high demand due to the ageing population. Increasingly, the orthopaedic biomaterials used to support these treatments are designed to be "immunomodulatory", i.e., guide the body's inflammatory response. They do this by encouraging macrophages - a type of white blood cell that surrounds and kills microorganisms - to adopt new roles based on signals and stimuli in their microenvironment. This approach has proved effective for developing new bone and for encouraging existing bone to accept artificial implants.
Magnesium is a mineral that not only helps to maintain normal nerve and ...
BEND, Ore. - Bat researchers say a project in Central Oregon shows citizen science's strong potential for helping ecologists learn more about one of the least understood groups of mammals.
Volunteers listened for the rare spotted bat, Euderma maculatum, within study grids in a 24,000-square-kilometer area in and around the Deschutes and Ochoco national forests. They completed a total of 61 surveys and heard the bat 25 times.
Bat encounters help fill in holes in basic information regarding species abundance and distribution - gaps that impede conservation - and the ...
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. - Fine-grained location data gleaned from mobile phones shows that people living in less affluent neighborhoods spent less time at home during the early lockdown and first several months of the coronavirus pandemic.
Researchers tracked data from millions of mobile phone users in the largest U.S. metropolitan areas. Their findings contribute to a growing body of research suggesting that low-wage earners -- a vulnerable group already at greater risk for contracting COVID-19 -- could not afford to comply with stay-at-home orders or worked in ...
Global oceans absorb about 25% of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burned. Electricity-eating bacteria known as photoferrotrophs could provide a boost to this essential process, according to new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Scientists led by Arpita Bose, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, found that bacteria found in brackish sediments can "eat" electricity and, in the process, absorb and lock away climate-warming carbon dioxide. This unusual skill was previously thought to be almost exclusive to freshwater bacteria, but may be common ...
WASHINGTON--A new study finds people who consume two servings of fruit per day have 36 percent lower odds of developing type 2 diabetes than those who consume less than half a serving. The research was published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Diabetes is a disease where people have too much sugar in their bloodstream, and it is a huge public health burden. Approximately 463 million adults worldwide were living with diabetes in 2019, and by 2045 this number is expected to rise to 700 million. An estimated 374 million people are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, the most common form of the disease. A healthy diet and lifestyle can play a major role in lowering a person's diabetes risk.
"We ...
A new study led by researchers at Washington State University has identified a protein that could be the key to improving treatment outcomes after a heart attack.
Published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, the research suggests that protein kinase A (PKA) plays a role in heart muscle cell necrosis, a major type of cell death that commonly occurs after reperfusion therapy, the treatment used to unblock arteries and restore blood flow after a heart attack.
"Our study has found that turning off a gene that controls this protein activity increased necrotic cell death and led to more heart injury and worse heart function following heart attack in a rodent model," said study author Zhaokang Cheng, an assistant professor in the WSU College ...
As early as the Neolithic period (circa 3900 BC), the domestication of animals likely led to the development of diseases including measles and smallpox. Since then, zoonotic disease has led to other major transnational outbreaks including HIV, Ebola, SARS, MERS, and H1N1 swine flu, among others. Currently, more than half of all existing human pathogens, and almost three-quarters of emerging infectious diseases, are zoonotic in nature.
COVID-19 is the latest and most impactful zoonotic event of the modern era, but it will certainly not be the last.
Given the breadth of these impacts and the fact that other zoonotic pandemics are highly likely - a matter of when and not if - the key public health ethics question that emerges is about whether it is ethically appropriate for governments ...
Doctors have hoped that antibiotics could benefit patients with chronic lung diseases, but a new study has found no benefit for patients with life-threatening idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in preventing hospitalization or death.
While there were no statistical benefits for patients with the lung-scarring disease, the new research will prevent unnecessary antibiotic use that could contribute to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance. The nationwide clinical trial - believed to be the largest idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis trial ever conducted - also collected biological samples that will advance the understanding and treatment of the mysterious and ultimately fatal illness.
"We were certainly disappointed in the results. But we remain hopeful that in further downstream ...
(Carlisle, Pa.) -- A new study published in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine finds critical links between job loss and physical inactivity in young adults during the U.S. Great Recession of 2008-09 that can be crucial to understanding the role of adverse economic shocks on physical activity during the COVID-19 pandemic. It is the first study to examine how job losses during the Great Recession affected the physical activity of young adults in the United States.
The study by Dickinson College economist Shamma Alam and Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health economist Bijetri Bose looked at Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) data for young adults age 18 to 27--a phase of development associated with maturation and significant ...