RUDN University chemists created cheap catalysts for ethanol conversion
2021-06-02
(Press-News.org) RUDN University chemists proposed a new way to synthesize catalysts for the conversion of ethyl alcohol. The obtained materials are promising catalysts for the selective conversion of ethanol, which is an important stage in the development of an alternative technology for obtaining valuable chemical synthesis products based on plant raw materials. The results of the study are published in Catalysis Today.
Ethanol fuel is ethyl alcohol, it is produced from plant material by fermentation of industrial or agricultural waste biomass. It is used as a more environmentally friendly fuel compared to gasoline. But this is not its sole use -- ethanol can be converted into acetaldehyde, diethyl ether and other chemicals that are in demand in the industry. Highly efficient catalysts are required to trigger such chemical reactions. However, existing catalysts contain precious metals, and therefore they are too expensive to use. RUDN University chemists proposed new catalysts based on aluminium and zirconium, modified with copper.
"The best-known catalysts for ethanol conversion are based on oxides promoted by noble metals. However, they are quite expensive. A more affordable option is catalysts with copper as the active phase, but so far, the best option has not been found among them. Improvements are required to use these catalysts to ensure both high conversion and selectivity of the reaction -- that is, to leave as little ethanol as possible unprocessed and at the same time to obtain the necessary substances, and not by-products", Anna Zhukova, associated professor, PhD, from the Department of Physical and Colloidal Chemistry of RUDN University
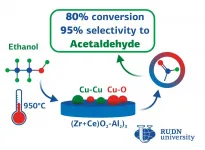
RUDN chemists combined two approaches to improve the efficiency of catalysts for acetaldehyde synthesis. First, they combined oxides of several metals in nanocomposites: aluminium, cerium, and zirconium. The researchers synthesized five types of powders with different oxides ratios. Five of them was prepared at a relatively low temperature of 180°C, and another five was heated to 950°C. This made it possible to form different structures in the materials. The calcined samples had a large diameter and pore volume.
The second idea was to add copper. All the powders were soaked in an aqueous solution of copper nitrate, dried at room temperature, and exposed to a flow of hydrogen at 400°C. After that, the finished catalysts were tested in the ethanol vapor dehydrogenation reaction. Chemists placed them in a thin layer on a porous filter, and then fed alcohol vapors in the helium flow. The reaction was carried out at temperatures from 240°C to 360°C.
"All obtained systems demonstrated ? high alcohol conversion and selectivity to acetaldehyde. The copper containing catalysts with 5% aluminium oxide produced significant amounts of acetaldehyde with selectivity above 80 % at 3600C. We found that the mixed composition of the oxides creates conditions for the formation of active centres on the surface of the catalyst from copper ions with different charges. The best option is to use a mixture of oxides with a small content of aluminium in the synthesis of the catalyst and calcinate them at 950°C", Anna Zhukova from RUDN University
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-02
In collaborative international effort, laser physicists at LMU have built the first hybrid plasma accelerator.
Particle accelerators have made crucial contributions to some of the most spectacular scientific discoveries of modern times, and greatly augmented our knowledge of the structure of matter. Now a team of laser physicists led by Prof. Stefan Karsch at the Ludwig-Maximilian University (LMU) in Munich and the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics, in cooperation with scientists based at the Helmholtz Centre in Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR), the Laboratoire d'Optique Appliquée in Paris (LOA), Strathclyde University in Glasgow and the DESY Electron Synchrotron in Hamburg, have now achieved a significant ...
2021-06-02
Amsterdam, June 2, 2021 - On the eve of the 50th anniversary of the 1972 Stockholm conference that created the United Nations Environmental Programme, it is clear that the global environmental situation has only deteriorated. In "Our Earth Matters: Pathways to a Better Common Environmental Future," an extended special issue of Environmental Policy and Law (EPL), leading scholars from more than five continents call for an honest introspection of what has been attained over the last 50 years relating to regulatory processes and laws and explore future trajectories with new ideas and frameworks for environmental governance in the 21st century.
"Our objective is to fire the imaginations of scholars and decision-makers to re-examine current approaches and to explore the future, ...
2021-06-02
Smoking in early puberty in boys may have negative consequences for their future generations of offspring, a study from the University of Bergen (UiB) shows.
By continued analysis of data gathered in the large international RHINESSA, RHINE and ECRHS studies, researchers have found that the health of future generations depends on actions and decisions made by young people today. This is particularly relevant for boys in early puberty and mothers/grandmothers both pre-pregnancy and during pregnancy, the study shows.
The paper "Prenatal and prepubertal exposures to tobacco smoke in ...
2021-06-02
Humans can observe what and where something happens around them with their hearing, as long as sound frequencies lie between 20 Hz and 20 000 Hz. Researchers at Aalto University have now developed a new audio technique that enables people to also hear ultrasonic sources that generate sound at frequencies above 20,000 Hz with simultaneous perception of their direction. The results have been published in Scientific Reports on 2 June 2021.
'In our study, we used bats in their natural habitat as sources of ultrasonic sound. With our new technique, we can now hear the directions-of-arrival of bat sounds, which means we can track bats in flight and hear where they are - we're ...
2021-06-02
An international team of astrophysicists led by the Stellar Astrophysics Group of the University of Alicante (UA), the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), and the University of Valparaíso (Chile) has discovered a massive cluster of stars of intermediate age in the direction of the Scutum constellation. This object, which has been named Valparaíso 1, lies some seven thousand light years away from the Sun, and contains at least fifteen thousand stars. To detect it, observations have been combined from ESA's Gaia satellite, and various ground-based telescopes, ...
2021-06-02
Tsukuba, Japan - It is estimated that during a heart attack, one billion cells in the heart are lost. In the wake of the heart attack, the lost tissue is replaced by scar tissue, which can lead to heart failure, arrhythmia and death. In a new study, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have shown how cells in the scar tissue can be converted to heart muscle cells, effectively regenerating the injured heart.
The injured heart of humans and rodents alike does not have the capacity to regenerate after injury. Therefore, the only way for the heart to heal the wound is to build a scar tissue in the injured area. A longstanding goal in the field has been to find a way to reprogram fibroblasts, ...
2021-06-02
Bone-regenerating treatments are in high demand due to the ageing population. Increasingly, the orthopaedic biomaterials used to support these treatments are designed to be "immunomodulatory", i.e., guide the body's inflammatory response. They do this by encouraging macrophages - a type of white blood cell that surrounds and kills microorganisms - to adopt new roles based on signals and stimuli in their microenvironment. This approach has proved effective for developing new bone and for encouraging existing bone to accept artificial implants.
Magnesium is a mineral that not only helps to maintain normal nerve and ...
2021-06-02
BEND, Ore. - Bat researchers say a project in Central Oregon shows citizen science's strong potential for helping ecologists learn more about one of the least understood groups of mammals.
Volunteers listened for the rare spotted bat, Euderma maculatum, within study grids in a 24,000-square-kilometer area in and around the Deschutes and Ochoco national forests. They completed a total of 61 surveys and heard the bat 25 times.
Bat encounters help fill in holes in basic information regarding species abundance and distribution - gaps that impede conservation - and the ...
2021-06-02
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. - Fine-grained location data gleaned from mobile phones shows that people living in less affluent neighborhoods spent less time at home during the early lockdown and first several months of the coronavirus pandemic.
Researchers tracked data from millions of mobile phone users in the largest U.S. metropolitan areas. Their findings contribute to a growing body of research suggesting that low-wage earners -- a vulnerable group already at greater risk for contracting COVID-19 -- could not afford to comply with stay-at-home orders or worked in ...
2021-06-02
Global oceans absorb about 25% of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burned. Electricity-eating bacteria known as photoferrotrophs could provide a boost to this essential process, according to new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Scientists led by Arpita Bose, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, found that bacteria found in brackish sediments can "eat" electricity and, in the process, absorb and lock away climate-warming carbon dioxide. This unusual skill was previously thought to be almost exclusive to freshwater bacteria, but may be common ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] RUDN University chemists created cheap catalysts for ethanol conversion