(Press-News.org) SMU Office of Research & Tech Transfer - Short selling often gets a bad rap because it is a type of trade that bets against the success of a firm. In essence, short selling allows investors to borrow stock from a broker to sell into the market with the hope of buying the stock back at a cheaper price, thus, profiting on the difference between the sell and buy prices. Because of this practice, short selling is sometimes seen as a controversial tactic.
Furthermore, speculative short selling attacks are concerning as it can put downward pressure on the entire stock market. It is for this reason that governments and regulators have stepped in to curtail or ban short selling during times of market stress such as the Global Financial Crisis or more recently, at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Contrary to the negativity surrounding short selling, SMU Associate Professor Rencheng Wang told the Office of Research and Tech Transfer: "Quite honestly, there are many benefits of short selling. Short selling can drive market liquidity, price stocks more efficiently, mitigate market bubbles, as well as provide a check on upward market manipulations."
"Because of monetary gains, short sellers are motivated to detect and expose negative news such as poor firm performance that investors have yet to be informed, or unethical and opportunistic behaviours taken by managers at the cost of investors. In other words, short sellers are like detectives of the capital markets," Professor Wang adds.
Given that there are still so many unanswered questions about the positive benefits of short selling, Professor Wang and his collaborators decided to probe deeper into the issue. Specifically, Professor Wang wanted to understand how short selling affects the behaviours of the firm's managers and large shareholders.
Short sale regulation
The regulation on short selling had remained relatively intact since its introduction over 60 years ago. It was believed that the short sale rule had become increasingly susceptible to abuse and was inconsistent with market developments, which led the SEC (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission) to adopt a modified version of the proposed Rule 202T in 2005.
As part of the review of the short sale rule, the SEC introduced a pilot programme for a select group of securities, of which represented a third of the securities listed on the Russell 3000 index. Rule 202T referred to a temporary exemption from Rule 202 of Regulation SHO (short selling regulation) that suspended any short sale price test for the select group of securities.
The purpose of this pilot programme was to enable the SEC to study the effects of unrestricted short selling on, among other things, market volatility, price efficiency, and market liquidity.
The research
Given this scenario, Professor Wang was able to take advantage of this temporary rule exemption by designing a quasi-experiment to compare the performance and behaviours of the designated group of securities (pilot firms) with the rest of the securities (control firms) on the Russell 3000 index.
Professor Wang elaborated: "Our intent of conducting this research was not merely to observe the impact of Rule 202T on short selling. Rather, we expect the firm's managers, whom we call insiders, to adjust their behaviours to reflect the increased threat of short selling."
The sample included 974 pilot firms and 1,935 control firms listed on the Russell 300 index. The research included a total of 55,002 firm quarters in the pre-period of Rule 202T (January 2002 - April 2005) to post-period of Rule 202T (May 2005 - July 2007).
In conveying the research findings, Professor Wang was pleased to inform the Office of Research and Tech Transfer: "We saw a reduction of 11 percent in opportunistic insider sales in the pilot firms, which means that short selling has a disciplinary effect on the behaviours of the insiders. And the threat of short selling was more pronounced in deterring insiders whose firms have higher litigation risks, greater reputation concerns and have more insiders with large stock-related holdings."
He added: "When we extended our research to the securities listed on the Chinese (Shanghai and Shenzhen) and Hong Kong Stock Exchanges, we also saw a similar pattern - short sellers can deter unethical insiders from engaging in high volume opportunistic sell offs in stock exchanges that differ in culture, market development, and legal environments - from the New York Stock Exchange to other exchanges in Asia. Thus, we provide new evidence to highlight the importance of short sellers in capital market development and governance reforms across different institutional environments."
Professor Wang's paper on short selling can be found here.
INFORMATION:
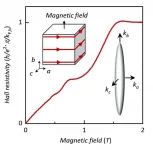
The quantum Hall effect traditionally only plays a role in two-dimensional electron systems. Recently, however, a three-dimensional version of the quantum Hall effect was described in the Dirac semimetal ZrTe5. It has been suggested that this version results from a magnetic field-induced Fermi surface instability that transforms the original three-dimensional electron system into a stack of two-dimensional electron systems. Now scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids in Dresden, at the Technical University of Dresden, at the Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York, at the Helmholtz Center Dresden-Rossendorf, the Max Planck Institute ...
Boulder, Colo., USA: GSA's dynamic online journal, Geosphere, posts articles online regularly. Locations and topics studied this month include the Moine thrust zone in northwestern Scotland; the Eastern California shear zone; implementation of "OpenTopography"; the finite evolution of "mole tracks"; the southern central Andes; the work of International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP) Expedition 351; and the Fairweather fault, Alaska, USA. You can find these articles at https://geosphere.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent.
Detrital-zircon analyses, provenance, and ...
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- As its name suggests, dark matter -- material which makes up about 85% of the mass in the universe -- emits no light, eluding easy detection. Its properties, too, remain fairly obscure.
Now, a theoretical particle physicist at the University of California, Riverside, and colleagues have published a research paper in the Journal of High Energy Physics that shows how theories positing the existence a new type of force could help explain dark matter's properties.
"We live in an ocean of dark matter, yet we know very little about what it could be," said Flip Tanedo, an assistant professor of physics and astronomy and the paper's senior author. "It is one of the most vexing known unknowns in nature. ...
It's long been known that people living with HIV experience a loss of white matter in their brains. As opposed to "gray matter," which is composed of the cell bodies of neurons, white matter is made up of a fatty substance called myelin that coats neurons, offering protection and helping them transmit signals quickly and efficiently. A reduction in white matter is associated with motor and cognitive impairment.
Earlier work by a team from the University of Pennsylvania and Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) found that antiretroviral therapy (ART)--the lifesaving suite ...
There is a long-held belief that having your pet sleep on the bed is a bad idea. Aside from taking up space, noisy scratching, or triggering allergies, the most common assertion averred that your furry companion would disrupt your sleep.
A new study published in the journal Sleep Health tells a different story. Researchers at Concordia's Pediatric Public Health Psychology Lab (PPHP) found that the sleep quality of the surprisingly high number of children who share a bed with their pets is indistinguishable from those who sleep alone.
"Sleeping with your pet does not appear to be disruptive," ...
Do firms respond to tougher competition by searching for completely new technological solutions (exploration), or do they work to defend their position by improving current technologies (exploitation)?
Competition from increased import penetration generally results in tight profit margins, low prices, and strong efficiency pressures, immediately affecting firms' bottom lines in the form of reduced profits and increased bankruptcy risk.
A firm's R&D strategy is one of the fundamental determinants of success or failure when responding to competitive threats. To ensure both short-term performance and long-term survival, firms have two basic R&D options: explore new knowledge or exploit existing knowledge bases. ...
A new study by a team of University of Rochester psychologists and other researchers in the Collaborative Initiative on Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (CIFASD) finds that partners of mothers-to-be can directly influence a pregnant woman's likelihood of drinking alcohol and feeling depressed, which affects their babies' development.
The study, which appeared in Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research, highlights the importance of engaging partners in intervention and prevention efforts to help pregnant women avoid drinking alcohol. A baby's prenatal alcohol ...
Nano-sized particles have been engineered in a new way to improve detection of tumors within the body and in biopsy tissue, a research team in Sweden reports. The advance could enable identifying early stage tumors with lower doses of radiation.
In order to enhance visual contrast of living tissues, state-of-the-art imaging relies on agents such as fluorescent dyes and biomolecules. Advances in nanoparticle research have expanded the array of promising contrast agents for more targeted diagnostics, and now a research team from KTH Royal Institute of Technology has raised the bar further yet. They are combining optical and X-ray fluorescence contrast agents into a single enhancer for both modes.
Muhammet ...
Researchers from Sinai Health have published a study providing an ultra-detailed look at the organization of a living human cell, providing a new tool that can help scientists around the world better understand what happens during disease.
The new study, out today in the journal END ...
In the universe's earliest moments, particles existed in an unimaginably hot plasma, whose behaviour was governed by deeply complex webs of interaction between individual particles. Today, researchers can recreate these exotic conditions through high-energy collisions between heavy ions, whose products can tell us much about how hot, strongly-interacting matter behaves. Yet without extensive, highly coordinated collaborations between researchers across many different backgrounds, studies like this simply wouldn't be possible. This Topical Issue of EPJ A draws together a large collection of papers inspired by the theory of hot matter and relativistic heavy-ion collisions (THOR) European Cooperation ...