(Press-News.org) Researchers from Sinai Health have published a study providing an ultra-detailed look at the organization of a living human cell, providing a new tool that can help scientists around the world better understand what happens during disease.
The new study, out today in the journal END
Sinai Health scientists provide detailed map to understanding human cells
2021-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
THOR: Driving collaboration in heavy-ion collision research
2021-06-02
In the universe's earliest moments, particles existed in an unimaginably hot plasma, whose behaviour was governed by deeply complex webs of interaction between individual particles. Today, researchers can recreate these exotic conditions through high-energy collisions between heavy ions, whose products can tell us much about how hot, strongly-interacting matter behaves. Yet without extensive, highly coordinated collaborations between researchers across many different backgrounds, studies like this simply wouldn't be possible. This Topical Issue of EPJ A draws together a large collection of papers inspired by the theory of hot matter and relativistic heavy-ion collisions (THOR) European Cooperation ...
DNA circuits
2021-06-02
The myriad processes occurring in biological cells may seem unbelievably complex at first glance. And yet, in principle, they are merely a logical succession of events, and could even be used to form digital circuits. Researchers have now developed a molecular switching circuit made of DNA, which can be used to mechanically alter gels, depending on the pH. DNA-based switching circuits could have applications in soft robotics, say the researchers in their article in Angewandte Chemie.
DNA is a long molecule that can be folded and twisted in various ways. It has a backbone and bases that stick out from the backbone and pair up with counterparts in other DNA strands. When a series of these matching pairs comes ...
The best strawberries to grow in hot locations
2021-06-02
It's strawberry season in many parts of the U.S, and supermarkets are teeming with these fresh heart-shaped treats. Although the bright red, juicy fruit can grow almost anywhere with lots of sunlight, production in some hot, dry regions is a challenge. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Agricultural Food and Chemistry have identified five cultivars that are best suited for this climate, which could help farmers and consumers get the most fragrant, sweetest berries.
Most strawberries commercially grown in the U.S. come from California and Florida. With the expansion of local farmer's markets and people's excitement ...
Aging: Cdkn1a transcript variant 2 is a marker of aging and cellular senescence
2021-06-02
Aging published "Cdkn1a transcript variant 2 is a marker of aging and cellular senescence" which reported that cellular senescence is a cell fate response characterized by a permanent cell cycle arrest driven primarily the by cell cycle inhibitor and tumor suppressor proteins p16Ink4a and p21Cip1/Waf1. In mice, the p21Cip1/Waf1 encoding locus, Cdkn1a, is known to generate two transcripts that produce identical proteins, but one of these transcript variants is poorly characterized. The authors show that the Cdkn1a transcript variant 2, but not the better-studied variant 1, is selectively elevated during natural aging across multiple mouse tissues. Importantly, mouse cells induced ...
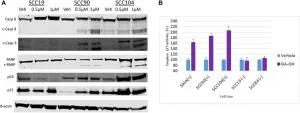
Oncotarget: E6-specific inhibitors as therapeutics for HPV+ head and neck carcinomas
2021-06-02
Oncotarget published "A high-content AlphaScreen™ identifies E6-specific small molecule inhibitors as potential therapeutics for HPV+ head and neck squamous cell carcinomas" which reported that the incidence of human papillomavirus-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma has increased dramatically over the past decades due to an increase in infection of the oral mucosa by HPV.
The etiology of HPV -HNSCC is linked to expression of the HPV oncoprotein, E6, which influences tumor formation, growth and survival.
E6 effects this oncogenic phenotype in part through inhibitory ...
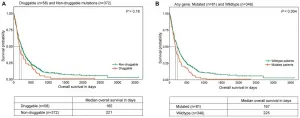
Oncotarget: Lung squamous cell carcinoma tumors reveal therapeutic alterations
2021-06-02
Oncotarget published "Molecular characterization of lung squamous cell carcinoma tumors reveals therapeutically relevant alterations" which reported that unlike lung adenocarcinoma patients, there is no FDA-approved targeted-therapy likely to benefit lung squamous cell carcinoma patients.
The authors performed survival analyses of lung squamous cell carcinoma patients harboring therapeutically relevant alterations identified by whole exome sequencing and mass spectrometry-based validation across 430 lung squamous tumors.
They report a mean of 11.6 mutations/Mb with a characteristic smoking signature along with mutations in TP53, CDKN2A, NFE2L2, FAT1, KMT2C, LRP1B, FGFR1, PTEN and PREX2 among lung squamous cell carcinoma patients of Indian descent.
In overall, the data suggests 13.5% ...
Pandemic shows essential role of ECT as treatment for severe depression
2021-06-02
When the COVID-19 pandemic arrived in North America in March 2020, health care facilities stopped providing all but "essential" care, to reduce infection risks and preserve protective gear known as PPE.
That included changes at many centers that provide ECT (electroconvulsive therapy) for severe depression and other conditions, a new survey shows.
Because ECT involves anesthesia, so that patients are unconscious when carefully controlled pulses of electricity are delivered to key areas of the brain, it is considered an 'aerosol generating' procedure. That means it poses special risks when a respiratory ...
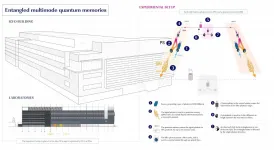
Entangled quantum memories for a quantum repeater: A step closer to the Quantum Internet
2021-06-02
* ICFO researchers report in Nature on having achieved, for the first time, entanglement of two multimode quantum memories located in different labs separated by 10 meters, and heralded by a photon at the telecommunication wavelength.
* The scientists implemented a technique that allowed them to reach a record in the entanglement rate in a system that could be integrated into the fibre communication network, paving the way to operation over long distances.
* The results are considered a landmark for quantum communications and a major step forward in the development of quantum repeaters for the future quantum internet.
During the 90s, engineers made major advances in the telecom arena spreading out the network to distances beyond the ...
World's lakes losing oxygen rapidly as planet warms
2021-06-02
TROY, N.Y. -- Oxygen levels in the world's temperate freshwater lakes are declining rapidly -- faster than in the oceans -- a trend driven largely by climate change that threatens freshwater biodiversity and drinking water quality.
Research published today in Nature found that oxygen levels in surveyed lakes across the temperate zone have declined 5.5% at the surface and 18.6% in deep waters since 1980. Meanwhile, in a large subset of mostly nutrient-polluted lakes, surface oxygen levels increased as water temperatures crossed a threshold favoring cyanobacteria, which can create toxins when they flourish in the form of harmful algal blooms.
"All complex life depends on oxygen. It's the support system for aquatic food webs. And when you start losing oxygen, you have the potential ...
USTC constructs a multiplexed quantum repeater based on absorptive quantum memories
2021-06-02
Chinese researchers realized an elementary link of a quantum repeater based on absorptive quantum memories (QMs) and demonstrated the multiplexed quantum repeater for the first time. On June 2nd?the work is published in Nature.
The fundamental task of a quantum network is to distribute quantum entanglement between two remote locations. However, the transmission loss of optical fiber has limited the distance of entanglement distribution to approximately 100 km on the ground. Quantum repeaters can overcome this difficulty by dividing long-distance transmission into several short-distance elementary links. The entanglement of two end nodes of each link is created firstly. Then the entanglement distance is gradually expanded through entanglement swapping between each link.
Previously, an ...