(Press-News.org) When the COVID-19 pandemic arrived in North America in March 2020, health care facilities stopped providing all but "essential" care, to reduce infection risks and preserve protective gear known as PPE.
That included changes at many centers that provide ECT (electroconvulsive therapy) for severe depression and other conditions, a new survey shows.
Because ECT involves anesthesia, so that patients are unconscious when carefully controlled pulses of electricity are delivered to key areas of the brain, it is considered an 'aerosol generating' procedure. That means it poses special risks when a respiratory virus such as the novel coronavirus is in widespread circulation.
In a new END
Pandemic shows essential role of ECT as treatment for severe depression
Survey of 20 centers nationwide reveals impacts of reduced services
2021-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
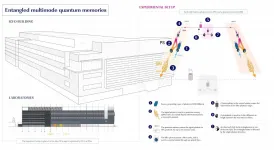
Entangled quantum memories for a quantum repeater: A step closer to the Quantum Internet
2021-06-02
* ICFO researchers report in Nature on having achieved, for the first time, entanglement of two multimode quantum memories located in different labs separated by 10 meters, and heralded by a photon at the telecommunication wavelength.
* The scientists implemented a technique that allowed them to reach a record in the entanglement rate in a system that could be integrated into the fibre communication network, paving the way to operation over long distances.
* The results are considered a landmark for quantum communications and a major step forward in the development of quantum repeaters for the future quantum internet.
During the 90s, engineers made major advances in the telecom arena spreading out the network to distances beyond the ...
World's lakes losing oxygen rapidly as planet warms
2021-06-02
TROY, N.Y. -- Oxygen levels in the world's temperate freshwater lakes are declining rapidly -- faster than in the oceans -- a trend driven largely by climate change that threatens freshwater biodiversity and drinking water quality.
Research published today in Nature found that oxygen levels in surveyed lakes across the temperate zone have declined 5.5% at the surface and 18.6% in deep waters since 1980. Meanwhile, in a large subset of mostly nutrient-polluted lakes, surface oxygen levels increased as water temperatures crossed a threshold favoring cyanobacteria, which can create toxins when they flourish in the form of harmful algal blooms.
"All complex life depends on oxygen. It's the support system for aquatic food webs. And when you start losing oxygen, you have the potential ...
USTC constructs a multiplexed quantum repeater based on absorptive quantum memories
2021-06-02
Chinese researchers realized an elementary link of a quantum repeater based on absorptive quantum memories (QMs) and demonstrated the multiplexed quantum repeater for the first time. On June 2nd?the work is published in Nature.
The fundamental task of a quantum network is to distribute quantum entanglement between two remote locations. However, the transmission loss of optical fiber has limited the distance of entanglement distribution to approximately 100 km on the ground. Quantum repeaters can overcome this difficulty by dividing long-distance transmission into several short-distance elementary links. The entanglement of two end nodes of each link is created firstly. Then the entanglement distance is gradually expanded through entanglement swapping between each link.
Previously, an ...
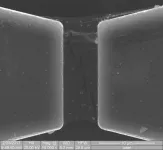
Hexagonal boron nitride's remarkable toughness unmasked
2021-06-02
HOUSTON - (June 2, 2021) - It's official: Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) is the iron man of 2D materials, so resistant to cracking that it defies a century-old theoretical description engineers still use to measure toughness.
"What we observed in this material is remarkable," said Rice University's Jun Lou, co-corresponding author of a Nature paper published this week. "Nobody expected to see this in 2D materials. That's why it's so exciting."
Lou explains the significance of the discovery by comparing the fracture toughness of h-BN with that of its better-known cousin ...
Clinical trial launched following discovery that psychiatric drug may prevent bowel cancer
2021-06-02
The study, published in the journal Nature, shows how a drug available on the NHS can boost fitness of healthy stem cells in the gut, making them more resistant to sabotage from mutant stem cells that cause cancer.
Researchers in the Netherlands, funded by the UK charity Worldwide Cancer Research, have discovered a way to boost the fitness of healthy cells in the gut to prevent the development of bowel cancer. The findings have led to the initiation of a clinical trial to find out if a commonly used psychiatric drug could be used to prevent bowel cancer in people. The trial will recruit patients with a genetic mutation that means they are virtually 100% certain to develop bowel cancer in their lifetime, unless ...
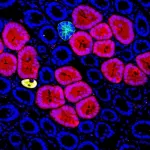
Researchers identify how to prevent cancer metastases
2021-06-02
Metastases can develop in the body even years after apparently successful cancer treatment. They originate from cancer cells that migrated from the original tumor to other organs, and which can lie there inactive for a considerable time. Researchers have now discovered how these "sleeping cells" are kept dormant and how they wake up and form fatal metastases. They have reported their findings in the journal Nature.
A tumor can leave behind an ominous legacy in the body: cancer cells can migrate from the tumor to other tissues in the body, where they survive after treatment in a kind of hibernation called dormancy. Currently, cancer medicine relies on monitoring cancer patients ...
Coloring tumors reveals their bad influence
2021-06-02
Studies on cancer are limited by the threshold at which cellular transformations become clinically detectable. However, the very initial phase on the way to malignancy is histologically invisible, as the process originates from one single cell. In this early phase, a so-called "seeding cell" acquires an initial pro-cancerous mutation, also known as the "first oncogenic hit", while being completely surrounded by normal tissue. To overcome the detection barrier, a team of researchers around IMBA group leader Bon-Kyoung Koo and University of Cambridge group leader Professor Benjamin D. Simons developed a laboratory system to dissect the pre-cancerous steps that remained under the radar ...
Urban crime fell by over a third around the world during COVID-19 shutdowns, study suggests
2021-06-02
A team of researchers led by the University of Cambridge and University of Utrecht examined trends in daily crime counts before and after COVID-19 restrictions were implemented in major metropolitan areas such as Barcelona, Chicago, Sao Paulo, Tel Aviv, Brisbane and London.
While both stringency of lockdowns and the resulting crime reductions varied considerably from city to city, the researchers found that most types of crime - with the key exception of homicide - fell significantly in the study sites.
Across all 27 cities, daily assaults fell ...
Income level, literacy, and access to health care rarely reported in clinical trials
2021-06-02
Clinical trials published in high-profile medical journals rarely report on income or other key sociodemographic characteristics of study participants, according to a new study that suggests these gaps may create blind spots when it comes to health care, especially for disadvantaged populations.
The study, publishing June 2 in JAMA Network Open, analyzed 10 per cent of 2,351 randomized clinical trials published in New England Journal of Medicine, JAMA, The BMJ, The Lancet and Annals of Internal Medicine between Jan. 1, 2014 and July 31, 2020.
The most commonly reported sociodemographic variables were sex and gender (in 98.7 per cent of trials) and race/ethnicity (in 48.5 per cent). All other sociodemographic ...
Salps fertilize the Southern Ocean more effectively than krill
2021-06-02
Experts at the Alfred Wegener Institute have, for the first time, experimentally measured the release of iron from the fecal pellets of krill and salps under natural conditions and tested its bioavailability using a natural community of microalgae in the Southern Ocean. In comparison to the fecal pellets of krill, Antarctic phytoplankton can more easily take up the micronutrient iron from those produced by salps. Observations made over the past 20 years show that, as a result of climate change, Antarctic krill are increasingly being supplanted by salps in the Southern Ocean. In the future, salps could more effectively stimulate the fixation of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide in Antarctic microalgae than krill, as the team of researchers report ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
[Press-News.org] Pandemic shows essential role of ECT as treatment for severe depressionSurvey of 20 centers nationwide reveals impacts of reduced services