* The scientists implemented a technique that allowed them to reach a record in the entanglement rate in a system that could be integrated into the fibre communication network, paving the way to operation over long distances.
* The results are considered a landmark for quantum communications and a major step forward in the development of quantum repeaters for the future quantum internet.
During the 90s, engineers made major advances in the telecom arena spreading out the network to distances beyond the cities and metropolitan areas. To achieve this scalability factor, they used repeaters, which enhanced attenuated signals and allowed these to travel farther distances with the same features such as intensity or fidelity. Now, with the addition of satellites, it is completely normal to be in the middle of a mountain in Europe and talk with your loved ones living in the other part of the world.
In the road towards building the future Quantum internet, quantum memories play the same role. Together with sources of qubits, they are the building blocks of this novel internet, acting as quantum repeaters of data operations and using superposition and entanglement as the key ingredients of the system. But to operate such system at a quantum level, the entanglement between quantum memories had to be created over long distances and maintained as efficiently as possible.
All together in one
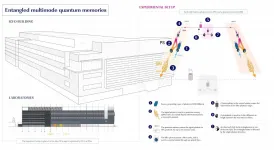
In a recently published study in Nature, ICFO scientists Dario Lago, Samuele Grandi, Alessandro Seri and Jelena Rakonjac, led by ICREA Prof at ICFO, Hugues de Riedmatten, have achieved scalable, telecom-heralded matter-matter entanglement between two remote, multimode and solid-state quantum memories. In simpler words, they were able to store, for a maximum of 25 microseconds, one single photon in two quantum memories placed 10m apart.
The researchers knew that the photon was in one of the two memories, but they did not know in which one, which emphasized this counter-intuitive notion that we have of nature, which allows the photon to be in a quantum superposition state in the two quantum memories at the same time but, amazingly, 10 meters apart. The team also knew that the entanglement was created with the detection of a photon at telecom wavelength, and it was stored in the quantum memories in a multiplexed fashion, "a feature akin to allowing several messages to be sent at the same time in a classical channel". These two key features have been achieved together for the first time and define the stepping stone in extending this scheme to much longer distances.
As Dario Lago, a PhD student at ICFO and first author of the study, enthusiastically pinpoints "So far, several of the milestones achieved in this experiment were done by other groups, like entangling quantum memories or achieving storage of the photons in quantum memories with a very high efficiency and high rates. But, the uniqueness about this experiment is that our techniques achieved very high rates and can be extended to longer distances."
Setting up the experiment
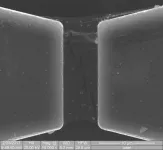
Achieving this landmark took its effort and time. During the course of several months, the team setup the experiment, where they used a rare-earth doped crystal as a quantum memory for the basis of their test.
Then, they took two sources generating correlated pairs of single photons. In each pair, one photon, named idler, is at a 1436nm (telecom wavelength), and the other, named signal, is at a wavelength of 606nm. The single signal photons, were sent to a quantum memory, made up of millions of atoms all randomly placed inside a crystal, and stored there via a protocol called atomic frequency comb. Alongside, the idler photons, also called heralding or messenger photons, were sent through an optical fiber to a device called beam-splitter, where the information about their origin and path was completely erased. Samuele Grandi, postdoctoral researcher and co-first author of the study, comments, "We erased any sort of feature that would tell us where the idler photons were coming from, let it be source 1 or 2, and we did this because we did not want to know any information about the signal photon and in which Quantum Memory it was being stored in". By erasing these features, the signal photon could have been stored in any of the quantum memories, which means that entanglement was created between them.
Every time that the scientists saw on the monitor a click of an idler photon arriving at the detector, they were able to confirm and verify that there was, in fact, entanglement. This entanglement consisted in a signal photon in a superposition state between the two quantum memories, where it was stored as an excitation shared by tens of millions of atoms for up to 25 microseconds.
As Sam and Dario mention, "The curious thing about the experiment is that it is not possible to know if the photon was stored in the quantum memory in the lab 1 or in Lab 2, which was more than 10 meters away. Although this was the principal feature of our experiment, and one that we kind of expected, the results in the lab were still counter-intuitive, and even more peculiar and mind-blowing to us is that we were capable of controlling it!"
The importance of heralded photons
Most of the previous studies that have experimented with entanglement and quantum memories used herald photons to know whether or not the entanglement between quantum memories had been successful. A heralding photon is like a messenger dove and the scientists can know upon its arrival that the entanglement between the quantum memories has been established. When this happens, the entanglement attempts stop and the entanglement is stored in the memories before being analyzed.
In this experiment, the scientists used a heralding photon in the telecom frequency, confirming that the entanglement being produced could be established with a photon that is compatible with existing telecom networks, an important feat since it allows entanglement to be created over long distances and, even more so, enables these quantum technologies to be easily integrated into the existing classical network infrastructures.
Multiplexing is key
Multiplexing is the capability of a system to send several messages at the same time through only one channel of transmission. In classical telecommunications, this is a frequent tool used to transmit data over the internet. In quantum repeaters, such technique is slightly more complex. With standard quantum memories, one has to wait for the message heralding the entanglement to come back to the memories, before one can try again to create entanglement. But with the use of the atomic frequency comb protocol, which allows this multiplexing approach, the researchers were able to store the entangled photons at many different times in the quantum memory, without having to wait for a successful heralding event before generating the next entangled pair. This condition, called "temporal multiplexing" is a key feature that represents a major increase in the operational time of the system, leading to an increment in the final entanglement rate.
Future Steps
As Prof. ICREA at ICFO Hugues de Riedmatten enthusiastically remarks "This idea was conceived more than 10 years ago and I am thrilled to see that it has now succeeded in the lab. The next steps are to bring the experiment outside of the lab, to try and link different nodes together and distribute entanglement over much larger distances, beyond what we currently have now. In fact, we are in the midst of achieving the first quantum link of 35km, which will be done between Barcelona and ICFO, in Castelldefels".
It is clear that the future quantum network will bring many applications in the near future. This achieved landmark proves and confirms that we are in the correct pathway towards developing these disruptive technologies and beginning to deploy them into what will be a new way of communicating, the Quantum Internet.
INFORMATION:
Reference: Telecom-heralded entanglement between multimode solid-state quantum memories,
Dario Lago-Rivera, Samuele Grandi, Jelena V. Rakonjac, Alessandro Seri, and Hugues de Riedmatten, Nature, 2021, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-03481-8
Links of Interest
Link to the Video Abstract - Youtube video with English, Spanish, Catalan subtitles:
https://youtu.be/yEuWyta9O6Y
Link to Audio-visual Material - Images, Photos, Infographs
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1YUQFrxPZzIUFNmvvUoiMOPQ9NT4i_c31?usp=sharing
Link to the research group led by ICREA Prof. Hugues de Riedmatten
https://www.icfo.eu/lang/research/groups/groups-details?group_id=32
Funding Entities
This study has received partial funding from the Quantum Flagship research project Quantum Internet Alliance (QIA), by the Gordon and Betty Moore foundation, as well as the Fundació Cellex, Fundació Mir-Puig, Generalitat de Catalunya, and the Spanish government, among other entities.
About ICFO
ICFO is a CERCA research centre member of the Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, founded in 2002 by the Government of Catalonia and the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya · Barcelona Tech, both of which are members of ICFO's board of trustees along with the Cellex and Mir-Puig Foundations, philanthropic entities that have played a critical role in the advancement of the institute. Located in the Mediterranean Technology Park in the metropolitan area of Barcelona, the institute currently hosts 450 people, organized in 26 research teams that use 80 state-of-the-art research laboratories. Research lines encompass diverse areas in which photonics plays a decisive role, with an emphasis on basic and applied themes relevant to medicine and biology, advanced imaging techniques, information technologies, a range of environmental sensors, tunable and ultra-fast lasers, quantum science and technologies, photovoltaics and the properties and applications of nano and quantum materials such as graphene, among others. In addition to three consecutive accreditations of the Severo Ochoa national program for top research excellence, ICFOnians have been awarded 15 elite ICREA Professorships as well as 40 European Research Council grants. ICFO is very proactive in fostering entrepreneurial activities, spin-off creation, and creating collaborations and links between industry and ICFO researchers. To date, ICFO has helped create 10 start-up companies.