Salps fertilize the Southern Ocean more effectively than krill
The iron released by the tunicates' fecal pellets is more bioavailable than that from krill pellets
2021-06-02
(Press-News.org) Experts at the Alfred Wegener Institute have, for the first time, experimentally measured the release of iron from the fecal pellets of krill and salps under natural conditions and tested its bioavailability using a natural community of microalgae in the Southern Ocean. In comparison to the fecal pellets of krill, Antarctic phytoplankton can more easily take up the micronutrient iron from those produced by salps. Observations made over the past 20 years show that, as a result of climate change, Antarctic krill are increasingly being supplanted by salps in the Southern Ocean. In the future, salps could more effectively stimulate the fixation of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide in Antarctic microalgae than krill, as the team of researchers report in the journal Current Biology.
In many parts of the Southern Ocean, iron is the primary limiting resource for the growth of phytoplankton. Accordingly, the amount of available iron has a major impact on how much CO2 the microalgae can fix and, in turn, how much biomass is available at the base of the food web. Studies clearly show that, as climate change progresses, Antarctic krill, the key species in the Southern Ocean, will increasingly be supplanted by salps.
"We investigated what a dominance shift from krill to salps would mean for primary production," explains Dr Scarlett Trimborn from the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI). As head of the AWI research group EcoTrace, during an expedition with the Research Vessel Polarstern she and her colleagues conducted experiments with natural phytoplankton populations in the Southern Ocean near Elephant Island. As a source of iron, the researchers offered the microalgae communities fecal pellets from krill and salps, since a dominance shift between the two species would mean higher feces production by salps in the future.
"We were surprised to find that, compared to krill, the fecal pellet material from salps released more iron per microgram of carbon. In addition, we determined that the iron released by the salps' fecal pellets was more bioavailable for phytoplankton than the iron from krill pellets," reports Sebastian Böckmann from the EcoTrace group and first author of the study. The phytoplankton communities were able to take up as much as five times more iron from the salps' fecal pellets than from the krill feces. This improved uptake could be due to ligands, which enhance the iron's bioavailability for the algae. This aspect could result in significantly increased CO2 fixation among the phytoplankton.
The Southern Ocean is extremely important for the future of our climate, as its vast expanses of water can potentially absorb or release large quantities of CO2 from or into the atmosphere. In some regions, e.g. surrounding the Antarctic Peninsula, climate change is affecting the sea-ice cover. When the ocean is ice-free, more sunlight penetrates the upper water layers, providing an energy source for photosynthesis. That being said, the availability of the resource iron is what chiefly determines CO2 uptake in microalgae. "Although we know from which sources iron is transported into the Southern Ocean, it's still completely unclear how much of the iron the microalgae can take up, especially with regard to its release through recycling on the part of grazers like salps and krill. Our study makes an important contribution to modelling biogeochemical cycles in the Southern Ocean of tomorrow," Trimborn summarises.
INFORMATION:
Original Publication:
Sebastian Böckmann, Florian Koch, Bettina Meyer, Franziska Pausch, Morten Iversen, Ryan Driscoll, Luis Miguel Laglera, Christel Hassler, and Scarlett Trimborn: Salp fecal pellets release more bioavailable iron to Southern Ocean phytoplankton than krill fecal pellets. Current Biology (2021), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2021.02.033
EMBARGOED until: Wednesday, 2 June 2021, 17:00 CEST, 11:00 US Eastern Time
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-02
Peer reviewed
Experimental study / Meta-analysis
Animals / Human data
Protein disguise could be new target for cancer immunotherapy
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified a protein that helps tumours evade the immune system and, in certain types of cancers, is linked to a poorer chance of survival. The protein could become a target for future cancer treatments.
A crucial part of the immune system's response to cancer is a group of white blood cells, called CD8+ T-cells, which kill tumour cells. Before they launch their anti-tumour response, these cells must be told who to attack by another immune cell, ...
2021-06-02
They studied the extent to which cirrus clouds caused by aircraft occurred during the global hard lockdown between March and May 2020, and compared the values with those during the same period in previous years. The study was led by Johannes Quaas, Professor of Theoretical Meteorology at Leipzig University, and has now been published in the renowned journal "Environmental Research Letters".
Cirrus clouds, known for their high, wispy strands, contribute to warming the climate. When cirrus clouds occur naturally, large ice crystals form at an altitude of about 36 kilometres, in turn reflecting sunlight back into space - albeit ...
2021-06-02
What drives the feasibility of climate scenarios commonly reviewed by organizations like the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)? And can they actually be achieved in practice? A new systematic framework can help understand what to improve in the next generation of scenarios and explore how to make ambitious emission reductions possible by strengthening enabling conditions.
While the IPCC is in the midst of the drafting cycle of the Sixth Assessment Report, whose publication will start in the second half of 2021, there is an ongoing debate ...
2021-06-02
ITHACA, N.Y. - Influencing millions of people on social media and being paid handsomely is not as easy as it looks, according to new Cornell University research.
Algorithm vagaries are just one of several challenges social media content creators face, according to study author Brooke Erin Duffy, associate professor of communication at Cornell.
"I think [our research] is a cautionary tale for aspiring creators as well as the broader public," Duffy said. "The people hoping to work as full-time YouTubers, Instagrammers, and TikTokers are led to believe it's easy and democratic. ...
2021-06-02
One-quarter of people who take the drug methotrexate for common immune system disorders -- from rheumatoid arthritis to multiple sclerosis -- mount a weaker immune response to a COVID-19 vaccine, a new study shows.
Published (online May 25) recently in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, the study addressed disorders that result when the immune system, meant to fight disease and drive healing, is triggered abnormally. This in turn causes inflammation, the pain and swelling that come as immune cells rush into damaged or infected tissue, but often in the wrong amount or context. Called immune-mediated inflammatory disorders, they are typically treated ...
2021-06-02
The pollution of the world's oceans with plastic waste is one of the major environmental problems of our time. However, very little is known about how much plastic is distributed globally in the ocean. Models based on ocean currents have so far suggested that the plastic mainly collects in large ocean gyres. Now, researchers at the University of Bern have calculated the distribution of plastic waste on a global scale while taking into account the fact that plastic can get beached. In their study, which has just been published in the "Environmental Research Letters" scientific journal, ...
2021-06-02
Zebrafish exposed to the leading cannabinoids found in cannabis in the earliest stages of development suffer a significant drop in neural activity later in life, according to a University of Alberta study that has implications for prenatal development in humans.
Richard Kanyo, the lead author on the study and post-doctoral fellow in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, said despite the popular narrative that the health benefits of cannabis are many, it turns out there is a surprisingly large knowledge gap.
"Once the legalization happened, people got really excited about it and there's a lot of bias in the media about positive ...
2021-06-02
The number of specialty behavioral health establishments, their workforce and their wages have increased steadily between 2011 and 2019, according to a new study by Indiana University and University of Michigan researchers.
The largest increases were found in the number of outpatient establishments and the size of their workforce, as well as an increase in the average wage at residential health establishments.
Researchers say while these increases are important in closing the gaps in needed treatment, more work needs to be done to increase behavioral health workforce deficits, especially in areas with an elevated drug overdose mortality rate.
At ...
2021-06-02
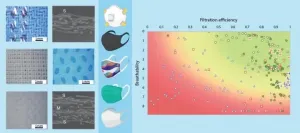
By Karina Toledo | Agência FAPESP - The novel coronavirus is transmitted mainly via inhalation of saliva droplets or respiratory secretions suspended in air, so that face covering and social distancing are the most effective ways to prevent COVID-19 until enough vaccines are available for all. In Brazil, fabric masks are among the most widely used because they are cheap, reusable and available in several colors or designs. However, this type of face covering's capacity to filter aerosol particles of a size equivalent to the novel coronavirus can vary between 15% and 70%, according to a study conducted in Brazil by the University of São Paulo (USP).
The study was supported by FAPESP, and the principal investigator was Paulo Artaxo, a professor in the university's ...
2021-06-02
(10 a.m. EDT, June 2, 2021--Denver) - New research published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology (JTO) suggests the method used to calculate how obesity is measured may affect whether it is considered a risk factor for lung cancer. The JTO is an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
Although the association between measures of obesity and both cancer incidence and outcome are clear in some solid tumor types such as breast, esophageal, and colon cancer, the relationship between obesity and lung cancer is more nuanced.
Now, a group of researchers led by Sai Yendamuri, M,D, from Rosewell Comprehensive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Salps fertilize the Southern Ocean more effectively than krill
The iron released by the tunicates' fecal pellets is more bioavailable than that from krill pellets