(Press-News.org) What drives the feasibility of climate scenarios commonly reviewed by organizations like the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)? And can they actually be achieved in practice? A new systematic framework can help understand what to improve in the next generation of scenarios and explore how to make ambitious emission reductions possible by strengthening enabling conditions.
While the IPCC is in the midst of the drafting cycle of the Sixth Assessment Report, whose publication will start in the second half of 2021, there is an ongoing debate on how to assess the feasibility of ambitious climate mitigation scenarios developed through integrated assessment models and to what extent they are actually achievable in the real world. In their new study published in Environmental Research Letters, researchers from IIASA and the RFF-CMCC European Institute on Economics and the Environment (EIEE) developed a systematic framework that allows identifying the type, timing, and location of feasibility concerns raised by climate mitigation scenarios.
"Feasibility - in other words, how plausible it is that a scenario materializes in the real world - is a complex concept that is currently getting significant academic attention. In our research, we built on past advancements in theoretical discussions and propose to operationalize feasibility in terms of the timing, disruptiveness, and scale of transformation across geophysical, technological, economic, institutional, and sociocultural feasibility dimensions," explains the paper's first author, Elina Brutschin, researcher in the IIASA Transformative Institutional and Social Solutions Research Group.
"Another major insight concerns the necessity to improve the assessment of socio-cultural feasibility concerns by including more indicators and incorporating insights on attitudes and behavioral changes from the social sciences," says Silvia Pianta, a postdoctoral researcher at EIEE and PhD fellow at Bocconi University.
"We found that the current generation of scenarios does not explore demand-side mitigation to its full potential and that more research is necessary in this area," adds coauthor Bas van Ruijven, IIASA Sustainable Service Systems Research Group leader.
To address these issues, the researchers developed a feasibility evaluation of indicators in each decade, with a flexible aggregation procedure that allows assessing feasibility concerns across dimensions and time. This flexible approach enabled them to look at the "big picture" to, for instance, assess which dimension raises major feasibility concerns, but also to analyze more detailed questions such as trade-offs over time, both within and across different dimensions. The resulting systematic framework is extremely useful, not only to understand what to improve in the next generation of scenarios, but also to analyze more systematically what type of enabling factors might bring us closer to more ambitious mitigation paths in the future.
The authors specifically applied the framework to the publicly available scenario set from the IPCC Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C and found that many scenarios currently assume a relatively fast overall decarbonization rate in regions that have a relatively low mitigation capacity. According to Brutschin, this suggests that many feasibility concerns are related to institutional constraints such as government effectiveness. While improving the quality of governance in many regions might be complicated, targeted capacity building and investments can significantly contribute to overcoming this challenge.
The authors highlight that the framework allows tracing important trade-offs over time, noting that while past studies focused on mitigation costs, the new research clearly shows that delayed climate action might generally be much more risky than an early disruptive transformation as delayed action requires an overall larger system to be transformed much faster and by relying on new technologies. In this regard, a better understanding of inter-temporal and inter-dimensional trade-offs incorporating insights from experts and policymakers is essential to take the overall understanding of the feasibility concepts to the next level.
"The new versatile framework that emerged from this collaborative project can be applied to any set of scenarios and can be constantly improved by incorporating new insights from the empirical literature on what is feasible in the real world. Although it was originally developed to evaluate global scenarios, it can be adjusted to have a more systematic evaluation of regional or national feasibility concerns in the future," notes IIASA Energy, Climate, and Environment Program Director, Keywan Riahi, who is also a coordinating lead author in Working Group III of the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report.
In addition to the new framework, the researchers also developed an interactive visual tool with key contributions by Giacomo Marangoni, a researcher at EIEE and Assistant Professor at Politecnico di Milano.
"A new data visualization method is extremely valuable when looking at multidimensional concepts such as feasibility. The tool we developed allows us to visualize our feasibility evaluations for different scenarios and to assess the sensitivity of our results to the definition of different feasibility concern thresholds," he says.
The data visualization tool can be accessed here: https://data.ece.iiasa.ac.at/climate-action-feasibility-dashboard/
Reference
Brutschin, E., Pianta, S., Tavoni, M., Riahi, K., Bosetti, V., Marangoni, G., & van Ruijven, B. (2021) A multidimensional feasibility evaluation of low-carbon scenarios. Environmental Research Letters DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/abf0ce
Contacts:
Researcher contact
Elina Brutschin
Research Scholar
Transformative Institutional and Social Solutions Research Group
Energy, Climate, and Environment Program
Tel: +43 2236 807 350
brutschin@iiasa.ac.at
Press Officer
Ansa Heyl
IIASA Press Office
Tel: +43 2236 807 574
Mob: +43 676 83 807 574
heyl@iiasa.ac.at
About IIASA:
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an international scientific institute that conducts research into the critical issues of global environmental, economic, technological, and social change that we face in the twenty-first century. Our findings provide valuable options to policymakers to shape the future of our changing world. IIASA is independent and funded by prestigious research funding agencies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Europe.
About: RFF-CMCC European Institute on Economics and the Environment (EIEE)
RFF-CMCC European Institute on Economics and the Environment leverages two leading international centers for economic and environmental research: RFF - Resources for the Future and CMCC - Euro-Mediterranean Center on Climate Change. EIEE's research aims to improve environmental, energy, and natural resource decisions through impartial economic research and policy engagement to facilitate the transition to a sustainable, inclusive society. The focus is on issues surrounding but not limited to climate change, including a wide range of environmental, energy, natural resource, and societal issues.
INFORMATION:
ITHACA, N.Y. - Influencing millions of people on social media and being paid handsomely is not as easy as it looks, according to new Cornell University research.
Algorithm vagaries are just one of several challenges social media content creators face, according to study author Brooke Erin Duffy, associate professor of communication at Cornell.
"I think [our research] is a cautionary tale for aspiring creators as well as the broader public," Duffy said. "The people hoping to work as full-time YouTubers, Instagrammers, and TikTokers are led to believe it's easy and democratic. ...
One-quarter of people who take the drug methotrexate for common immune system disorders -- from rheumatoid arthritis to multiple sclerosis -- mount a weaker immune response to a COVID-19 vaccine, a new study shows.
Published (online May 25) recently in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, the study addressed disorders that result when the immune system, meant to fight disease and drive healing, is triggered abnormally. This in turn causes inflammation, the pain and swelling that come as immune cells rush into damaged or infected tissue, but often in the wrong amount or context. Called immune-mediated inflammatory disorders, they are typically treated ...
The pollution of the world's oceans with plastic waste is one of the major environmental problems of our time. However, very little is known about how much plastic is distributed globally in the ocean. Models based on ocean currents have so far suggested that the plastic mainly collects in large ocean gyres. Now, researchers at the University of Bern have calculated the distribution of plastic waste on a global scale while taking into account the fact that plastic can get beached. In their study, which has just been published in the "Environmental Research Letters" scientific journal, ...
Zebrafish exposed to the leading cannabinoids found in cannabis in the earliest stages of development suffer a significant drop in neural activity later in life, according to a University of Alberta study that has implications for prenatal development in humans.
Richard Kanyo, the lead author on the study and post-doctoral fellow in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, said despite the popular narrative that the health benefits of cannabis are many, it turns out there is a surprisingly large knowledge gap.
"Once the legalization happened, people got really excited about it and there's a lot of bias in the media about positive ...
The number of specialty behavioral health establishments, their workforce and their wages have increased steadily between 2011 and 2019, according to a new study by Indiana University and University of Michigan researchers.
The largest increases were found in the number of outpatient establishments and the size of their workforce, as well as an increase in the average wage at residential health establishments.
Researchers say while these increases are important in closing the gaps in needed treatment, more work needs to be done to increase behavioral health workforce deficits, especially in areas with an elevated drug overdose mortality rate.
At ...
By Karina Toledo | Agência FAPESP - The novel coronavirus is transmitted mainly via inhalation of saliva droplets or respiratory secretions suspended in air, so that face covering and social distancing are the most effective ways to prevent COVID-19 until enough vaccines are available for all. In Brazil, fabric masks are among the most widely used because they are cheap, reusable and available in several colors or designs. However, this type of face covering's capacity to filter aerosol particles of a size equivalent to the novel coronavirus can vary between 15% and 70%, according to a study conducted in Brazil by the University of São Paulo (USP).
The study was supported by FAPESP, and the principal investigator was Paulo Artaxo, a professor in the university's ...
(10 a.m. EDT, June 2, 2021--Denver) - New research published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology (JTO) suggests the method used to calculate how obesity is measured may affect whether it is considered a risk factor for lung cancer. The JTO is an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
Although the association between measures of obesity and both cancer incidence and outcome are clear in some solid tumor types such as breast, esophageal, and colon cancer, the relationship between obesity and lung cancer is more nuanced.
Now, a group of researchers led by Sai Yendamuri, M,D, from Rosewell Comprehensive ...
Fluorinated compounds are an important group of compounds that are widely used in pharmaceuticals, agricultural chemicals, functional resins, and organic electronic materials. In particular, perfluorinated compounds with multiple carbon-fluorine bonds are attracting attention because of their high thermal and chemical stability and various excellent properties such as water and oil repellency and chemical resistance.
"C-F bonds are extremely strong; hence, their transformation under mild conditions is difficult, and the selective activation of a specific C-F bond from among multiple C-F bonds in perfluorinated compounds has not been achieved," explains Prof. Makoto Yasuda, corresponding author of the study.
The research team led by Prof. Makoto Yasuda has discovered ...
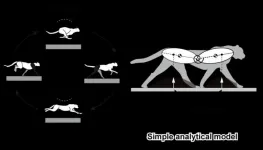
What makes cheetah the fastest land mammal? Why aren't other animals, such as horses, as fast? While we haven't yet figured out why, we have some idea about how--cheetahs, as it turns out, make use of a "galloping" gait at their fastest speeds, involving two different types of "flight": one with the forelimbs and hind limbs beneath their body following a forelimb liftoff, called "gathered flight," while another with the forelimbs and hind limbs stretched out after a hind limb liftoff, called "extended flight" (see Figure 1). Of these, the extended flight is what enables cheetahs to accelerate to high ...
Developing vaccines against bacteria is in many cases much more difficult than vaccines against viruses. Like virtually all pathogens, bacteria are able to sidestep a vaccine's effectiveness by modifying their genes. For many pathogens, such genetic adaptations under selective pressure from vaccination will cause their virulence or fitness to decrease. This lets the pathogens escape the effects of vaccination, but at the price of becoming less transmissible or causing less damage. Some pathogens, however, including many bacteria, are extremely good at changing in ways that allow them to escape the effects of vaccination while remaining highly ...