Social media influencing grows more precarious in digital age
2021-06-02
(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. - Influencing millions of people on social media and being paid handsomely is not as easy as it looks, according to new Cornell University research.
Algorithm vagaries are just one of several challenges social media content creators face, according to study author Brooke Erin Duffy, associate professor of communication at Cornell.
"I think [our research] is a cautionary tale for aspiring creators as well as the broader public," Duffy said. "The people hoping to work as full-time YouTubers, Instagrammers, and TikTokers are led to believe it's easy and democratic. I disagree: if you look at who makes it as an influencer, for instance, they are not all that dissimilar to traditional celebrity exemplars, with a few exceptions. Social media celebrity remains lopsided."
Duffy and her collaborators interviewed 30 aspiring and professional content creators on a range of social media platforms - including Instagram YouTube, TikTok, Pinterest and Twitter - to learn about their experiences within and across platforms, including their pursuit of visibility and their understanding of the forces at play in their quest for metrics success.
In general, study participants all spoke the same language: They wished to have their content "seen," to "build an audience" and "get attention," to craft "posts that get more traction" and, in terms of metrics, "do well."
Relying on public sentiment and its taste for the flavor of the week is by no means a 21st century phenomenon. Content creators have for decades relied on opinion research - be it Nielsen ratings or newspaper subscription figures from the Audit Bureau of Circulation - to help guide creative decision making.
But nowadays, Duffy said, the science of determining what an audience likes and wants comes with a new twist: The tenuous nature of the platforms themselves.
"These [influencers and creators], they don't know if Instagram is going to be there when they wake up," she said. "And they don't know if TikTok is going to be banned the next day in the U.S. It's a much more accelerated, intensified form of precarity in the era of Google and Facebook."
Duffy and her collaborators view the "nested" precarities akin to a Russian matryoshka doll, with the outermost doll being capitalism itself, followed by the markets, the platform ecology and algorithms as the innermost doll. The promise of being seen, and talked about, is what drives many to the world of social media influencing. But it's not all that it appears, Duffy said.
"Despite the romanticism of social media creative careers, they are structured by various levels of precarity," she said. "Some of these precarities well predate the rise of social media, but one of the most novel forms is the precarity of these algorithmic systems."
INFORMATION:
The study, "The Nested Precarities of Creative Labor on Social Media," published June 2 in Social Media & Society.
For more information, check out this Cornell Chronicle story.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-02
One-quarter of people who take the drug methotrexate for common immune system disorders -- from rheumatoid arthritis to multiple sclerosis -- mount a weaker immune response to a COVID-19 vaccine, a new study shows.
Published (online May 25) recently in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, the study addressed disorders that result when the immune system, meant to fight disease and drive healing, is triggered abnormally. This in turn causes inflammation, the pain and swelling that come as immune cells rush into damaged or infected tissue, but often in the wrong amount or context. Called immune-mediated inflammatory disorders, they are typically treated ...
2021-06-02
The pollution of the world's oceans with plastic waste is one of the major environmental problems of our time. However, very little is known about how much plastic is distributed globally in the ocean. Models based on ocean currents have so far suggested that the plastic mainly collects in large ocean gyres. Now, researchers at the University of Bern have calculated the distribution of plastic waste on a global scale while taking into account the fact that plastic can get beached. In their study, which has just been published in the "Environmental Research Letters" scientific journal, ...
2021-06-02
Zebrafish exposed to the leading cannabinoids found in cannabis in the earliest stages of development suffer a significant drop in neural activity later in life, according to a University of Alberta study that has implications for prenatal development in humans.
Richard Kanyo, the lead author on the study and post-doctoral fellow in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, said despite the popular narrative that the health benefits of cannabis are many, it turns out there is a surprisingly large knowledge gap.
"Once the legalization happened, people got really excited about it and there's a lot of bias in the media about positive ...
2021-06-02
The number of specialty behavioral health establishments, their workforce and their wages have increased steadily between 2011 and 2019, according to a new study by Indiana University and University of Michigan researchers.
The largest increases were found in the number of outpatient establishments and the size of their workforce, as well as an increase in the average wage at residential health establishments.
Researchers say while these increases are important in closing the gaps in needed treatment, more work needs to be done to increase behavioral health workforce deficits, especially in areas with an elevated drug overdose mortality rate.
At ...
2021-06-02
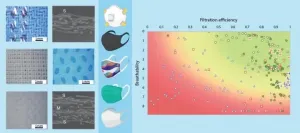
By Karina Toledo | Agência FAPESP - The novel coronavirus is transmitted mainly via inhalation of saliva droplets or respiratory secretions suspended in air, so that face covering and social distancing are the most effective ways to prevent COVID-19 until enough vaccines are available for all. In Brazil, fabric masks are among the most widely used because they are cheap, reusable and available in several colors or designs. However, this type of face covering's capacity to filter aerosol particles of a size equivalent to the novel coronavirus can vary between 15% and 70%, according to a study conducted in Brazil by the University of São Paulo (USP).
The study was supported by FAPESP, and the principal investigator was Paulo Artaxo, a professor in the university's ...
2021-06-02
(10 a.m. EDT, June 2, 2021--Denver) - New research published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology (JTO) suggests the method used to calculate how obesity is measured may affect whether it is considered a risk factor for lung cancer. The JTO is an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
Although the association between measures of obesity and both cancer incidence and outcome are clear in some solid tumor types such as breast, esophageal, and colon cancer, the relationship between obesity and lung cancer is more nuanced.
Now, a group of researchers led by Sai Yendamuri, M,D, from Rosewell Comprehensive ...
2021-06-02
Fluorinated compounds are an important group of compounds that are widely used in pharmaceuticals, agricultural chemicals, functional resins, and organic electronic materials. In particular, perfluorinated compounds with multiple carbon-fluorine bonds are attracting attention because of their high thermal and chemical stability and various excellent properties such as water and oil repellency and chemical resistance.
"C-F bonds are extremely strong; hence, their transformation under mild conditions is difficult, and the selective activation of a specific C-F bond from among multiple C-F bonds in perfluorinated compounds has not been achieved," explains Prof. Makoto Yasuda, corresponding author of the study.
The research team led by Prof. Makoto Yasuda has discovered ...
2021-06-02
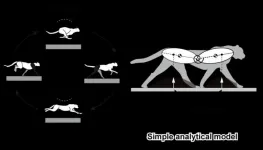
What makes cheetah the fastest land mammal? Why aren't other animals, such as horses, as fast? While we haven't yet figured out why, we have some idea about how--cheetahs, as it turns out, make use of a "galloping" gait at their fastest speeds, involving two different types of "flight": one with the forelimbs and hind limbs beneath their body following a forelimb liftoff, called "gathered flight," while another with the forelimbs and hind limbs stretched out after a hind limb liftoff, called "extended flight" (see Figure 1). Of these, the extended flight is what enables cheetahs to accelerate to high ...
2021-06-02
Developing vaccines against bacteria is in many cases much more difficult than vaccines against viruses. Like virtually all pathogens, bacteria are able to sidestep a vaccine's effectiveness by modifying their genes. For many pathogens, such genetic adaptations under selective pressure from vaccination will cause their virulence or fitness to decrease. This lets the pathogens escape the effects of vaccination, but at the price of becoming less transmissible or causing less damage. Some pathogens, however, including many bacteria, are extremely good at changing in ways that allow them to escape the effects of vaccination while remaining highly ...
2021-06-02
The white-tailed sea eagle is known for reacting sensitively to human disturbances. Forestry and agricultural activities are therefore restricted in the immediate vicinity of the nests. However, these seasonal protection periods are too short in the German federal States of Brandenburg (until August 31) and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania (until July 31), as a new scientific analysis by a team of scientists from the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) suggests. Using detailed movement data of 24 juvenile white-tailed sea eagles with GPS transmitters, they were able to track when they fledge and when they leave the parental territory: on average, a good 10 and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Social media influencing grows more precarious in digital age