Luring bacteria into a trap
2021-06-02
(Press-News.org) Developing vaccines against bacteria is in many cases much more difficult than vaccines against viruses. Like virtually all pathogens, bacteria are able to sidestep a vaccine's effectiveness by modifying their genes. For many pathogens, such genetic adaptations under selective pressure from vaccination will cause their virulence or fitness to decrease. This lets the pathogens escape the effects of vaccination, but at the price of becoming less transmissible or causing less damage. Some pathogens, however, including many bacteria, are extremely good at changing in ways that allow them to escape the effects of vaccination while remaining highly infectious.
For scientists looking to develop vaccines, this kind of immune evasion has been a fundamental problem for decades. If they set out to develop vaccines against bacterial pathogens, often they will notice that these quickly become ineffective.
Weaponising immune evasion
Now, however, researchers at ETH Zurich and the University of Basel have exploited precisely this mechanism to come up with an effective vaccine against bacteria. They succeeded in developing a Salmonella vaccine that, instead of trying to outright kill intestinal bacteria, rather guides their evolution in the gut to make them a weaker pathogen.
"This allowed us to show that immune evasion is not only a major challenge in vaccine development, but that it can in fact be put to good use in both human and veterinary medicine," explains ETH Professor Emma Slack. "We can use it to drive the evolution of pathogenic microorganisms in a certain direction - in our case, a dead end." Slack led the study, which involved many researchers from different groups at ETH Zurich and other institutions, together with ETH Professor Wolf-Dietrich Hardt and Médéric Diard, Professor at the University of Basel's Biozentrum.
Combination vaccine leads to the goal
In their study, the researchers inoculated mice with a series of slightly different vaccines against Salmonella typhimurium, and observed how the Salmonella in the animals' guts modified their genes to escape the vaccines' effects. This let the scientists identify the full spectrum of possible immune evasion mutations in Salmonella typhimurium. Subsequently, the researchers produced a combination vaccine from four Salmonella strains that covered the bacteria's full spectrum of genetic evasion options.
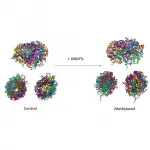
A surprising immune evasion was driven by this combined vaccine, causing an important Salmonella sugar coating on the surface to atrophy. While the affected bacteria were still able to multiply in the animals' guts, they were largely unable to infect body tissues and cause disease. This is because the sugar coating is part of the bacteria's protective coating that shields them from the host's defences as well as from viruses that often infect and kill the bacteria. In tests on mice, the scientists were able to show that their new vaccine was more effective at preventing Salmonella infections than existing vaccines approved for use in pigs and chickens.
The scientists now plan to use the same principle to develop vaccines against other microorganisms - for example, against antimicrobial-resistant bacterial strains. In addition, it ought to be possible to use the approach in biotechnology and bring about specific modifications in microorganisms by exerting selective pressure through vaccines.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-02
The white-tailed sea eagle is known for reacting sensitively to human disturbances. Forestry and agricultural activities are therefore restricted in the immediate vicinity of the nests. However, these seasonal protection periods are too short in the German federal States of Brandenburg (until August 31) and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania (until July 31), as a new scientific analysis by a team of scientists from the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) suggests. Using detailed movement data of 24 juvenile white-tailed sea eagles with GPS transmitters, they were able to track when they fledge and when they leave the parental territory: on average, a good 10 and ...
2021-06-02
Materials have a variety of properties that can be used to solve computational problems, according to studies in substrate-based computing. BZ computers, slime mould computers, plant computers, and collision-based liquid marbles computers are just a few examples of prototypes produced for future and emergent computing devices. Modelling the computational processes that exist in such systems, however, is a difficult task in general, and determining which part of the embodied system is doing the computation is still somewhat ill-defined.
Claiming that fungi are the most intelligent living organisms in the world sounds like an exaggeration. However, a recent study by Mohammad Mahdi Dehshibi, a UOC researcher who is contributing to a growing body of knowledge on the use of fungal materials, ...
2021-06-02
Eating at least two serves of fruit daily has been linked with 36 percent lower odds of developing type 2 diabetes, a new Edith Cowan University (ECU) study has found.
The study, published today in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, revealed that people who ate at least two serves of fruit per day had higher measures of insulin sensitivity than those who ate less than half a serve.
Type 2 diabetes is a growing public health concern with an estimated 451 million people worldwide living with the condition. A further 374 million people are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The study's lead author, Dr Nicola ...
2021-06-02
Researchers at Linköping University in Sweden have developed an app to help women achieve a healthy weight gain and lifestyle during a pregnancy. The results from an evaluation of the app have now been published in two scientific articles. Using the app contributed to a better diet. Pregnant women with overweight or obesity who received the app also gained less weight during pregnancy.
"Pregnancy is a phase in life when many people try to do what is best for themselves and their baby. We think it's important to be able to offer a tool that has ...
2021-06-02
Good acoustics in the workspace improve work efficiency and productivity, which is one of the reasons why acoustic materials matter. The acoustic insulation market is already expected to hit 15 billion USD by 2022 as construction firms and industry pay more attention to sound environments. Researchers at Aalto University, in collaboration with Finnish acoustics company Lumir, have now studied how these common elements around us could become more eco-friendly, with the help of cellulose fibres.
'Models for acoustic absorption are based on tests done with synthetic fibres, and ...
2021-06-02
An international research team determined that ancestors of modern domestic horses and the Przewalski horse moved from the territory of Eurasia (Russian Urals, Siberia, Chukotka, and eastern China) to North America (Yukon, Alaska, continental USA) from one continent on another at least twice. It happened during the Late Pleistocene (2.5 million years ago - 11.7 thousand years ago). The analysis results are published in the journal. The findings and description of horse genomes are published in the journal Molecular Ecology.
"We found out that the Beringian Land Bridge, or the area known as Beringia, influenced genetic ...
2021-06-02
All the cells of an organism share the same DNA sequence, but their functions, shapes or even lifespans vary greatly. This happens because each cell "reads" different chapters of the genome, thus producing alternative sets of proteins and embarking on different paths. Epigenetic regulation--DNA methylation is one of the most common mechanisms--is responsible for the activation or inactivation of a given gene in a specific cell, defining a secondary cell-specific genetic code.
Researchers led by Dr. Modesto Orozco, head of the Molecular Modelling and Bioinformatics lab at IRB Barcelona, have described how methylation has a protein-independent regulatory role by increasing the stiffness of DNA, which affects the 3D structure ...
2021-06-02
Autistic people's ability to accurately identify facial expressions is affected by the speed at which the expression is produced and its intensity, according to new research at the University of Birmingham.
In particular, autistic people tend to be less able to accurately identify anger from facial expressions produced at a normal 'real world' speed. The researchers also found that for people with a related disorder, alexithymia, all expressions appeared more intensely emotional.
The question of how people with autism recognise and relate to emotional expression has been debated by scientists for more than three decades and it's only in the past 10 years ...
2021-06-02
The gut and the brain communicate with each other in order to adapt satiety and blood sugar levels during food consumption. The vagus nerve is an important communicator between these two organs. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Metabolism Research in Cologne, the Cluster of Excellence for Ageing Research CECAD at the University of Cologne and the University Hospital Cologne now took a closer look at the functions of the different nerve cells in the control centre of the vagus nerve, and discovered something very surprising: although the nerve cells are located in the same control center, they innervate different regions of the gut and also differentially control satiety and blood sugar levels. This discovery could play an important role in the development of future ...
2021-06-02
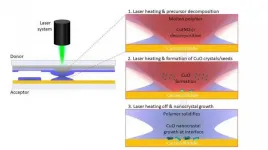
In the journal Nature Communications, an interdisciplinary team from the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces presents for the first time a laser-driven technology that enables them to create nanoparticles such as copper, cobalt and nickel oxides. At the usual printing speed, photoelectrodes are produced in this way, for example, for a wide range of applications such as the generation of green hydrogen.
Previous methods produce such nanomaterials only with high energy input in classical reaction vessels and in many hours. With the laser-driven technology developed at the institute, the scientists can deposit small amounts of material on a surface and simultaneously perform chemical synthesis in a very short time using high temperatures from the laser. 'When I discovered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Luring bacteria into a trap