Researchers identify how to prevent cancer metastases
2021-06-02
(Press-News.org) Metastases can develop in the body even years after apparently successful cancer treatment. They originate from cancer cells that migrated from the original tumor to other organs, and which can lie there inactive for a considerable time. Researchers have now discovered how these "sleeping cells" are kept dormant and how they wake up and form fatal metastases. They have reported their findings in the journal Nature.
A tumor can leave behind an ominous legacy in the body: cancer cells can migrate from the tumor to other tissues in the body, where they survive after treatment in a kind of hibernation called dormancy. Currently, cancer medicine relies on monitoring cancer patients after their initial treatment in order to detect the awakening of these cells to form metastases. One of the biggest questions in cancer research is what exactly causes this transition.
"This dormancy period offers an important therapeutic window in which the number of cancer cells and their heterogeneity are still manageable," says Professor Mohamed Bentires-Alj, group leader at the Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel. "Understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying tumor dormancy is therefore crucial to preventing the recurrence of cancer." His team has made an important step in this direction.
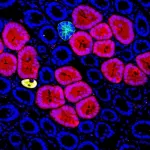
First author Dr. Anna Correia and her co-authors used mouse models and human tissue samples, and were able to determine how cancer cells, which had originally migrated from a mammary tumor to the liver, remained dormant or awoke to form metastases.
Two cell types play a key role in this transition. One of these cell types is the natural killer cell, i.e. a type of immune cell that traditionally kills abnormal or infected cells, but can also slow down their proliferation. As the researchers found, this is exactly what they appear to do to control dormant cancer cells. The natural killer cells secrete a messenger substance called interferon gamma, which keeps the cancer cells in hibernation.
The other cell type, the hepatic stellate cell, influences the natural killer cells. When hepatic stellate cells are activated, they inhibit the immune cells, which in turn allows the cancer cells to awaken from hibernation. "There can be various reasons why hepatic stellate cells are activated; for example, chronic inflammation in the body or persistent infection," Correia explains. The researchers will now investigate the exact causes in further studies.
The published results indicate several possible methods of preventing metastasis: immunotherapy based on interleukin-15, which increases the number of natural killer cells in the tissue; interferon gamma therapy, which maintains the dormant state of the cancer cells; and inhibitors of the mechanism through which the hepatic stellate cells paralyze the natural killer cells. Appropriate therapies already exist for all these approaches, but they still need to be clinically tested.
"Our findings raise the hope of immunotherapies that focus on natural killer cells as a preventive strategy for patients with dormant cancer cells at risk of developing metastases," says Bentires-Alj. "The next stage on the long road to an established treatment will be to show that stimulating natural killer cells prevents metastasis in human patients. We are currently looking for ways to finance this next step and are already in discussion with our clinical collaborators at the University Hospital Basel."
"These cells are a natural barrier against metastasis in the liver," Correia explains. If they could be used to prevent the development of metastases in other parts of the body, too, it might be possible to permanently prevent the recurrence of cancer. "My team is already studying such mechanisms in other metastatic sites and the results are promising," concludes Bentires-Alj.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-02
Studies on cancer are limited by the threshold at which cellular transformations become clinically detectable. However, the very initial phase on the way to malignancy is histologically invisible, as the process originates from one single cell. In this early phase, a so-called "seeding cell" acquires an initial pro-cancerous mutation, also known as the "first oncogenic hit", while being completely surrounded by normal tissue. To overcome the detection barrier, a team of researchers around IMBA group leader Bon-Kyoung Koo and University of Cambridge group leader Professor Benjamin D. Simons developed a laboratory system to dissect the pre-cancerous steps that remained under the radar ...
2021-06-02
A team of researchers led by the University of Cambridge and University of Utrecht examined trends in daily crime counts before and after COVID-19 restrictions were implemented in major metropolitan areas such as Barcelona, Chicago, Sao Paulo, Tel Aviv, Brisbane and London.
While both stringency of lockdowns and the resulting crime reductions varied considerably from city to city, the researchers found that most types of crime - with the key exception of homicide - fell significantly in the study sites.
Across all 27 cities, daily assaults fell ...
2021-06-02
Clinical trials published in high-profile medical journals rarely report on income or other key sociodemographic characteristics of study participants, according to a new study that suggests these gaps may create blind spots when it comes to health care, especially for disadvantaged populations.
The study, publishing June 2 in JAMA Network Open, analyzed 10 per cent of 2,351 randomized clinical trials published in New England Journal of Medicine, JAMA, The BMJ, The Lancet and Annals of Internal Medicine between Jan. 1, 2014 and July 31, 2020.
The most commonly reported sociodemographic variables were sex and gender (in 98.7 per cent of trials) and race/ethnicity (in 48.5 per cent). All other sociodemographic ...
2021-06-02
Experts at the Alfred Wegener Institute have, for the first time, experimentally measured the release of iron from the fecal pellets of krill and salps under natural conditions and tested its bioavailability using a natural community of microalgae in the Southern Ocean. In comparison to the fecal pellets of krill, Antarctic phytoplankton can more easily take up the micronutrient iron from those produced by salps. Observations made over the past 20 years show that, as a result of climate change, Antarctic krill are increasingly being supplanted by salps in the Southern Ocean. In the future, salps could more effectively stimulate the fixation of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide in Antarctic microalgae than krill, as the team of researchers report ...
2021-06-02
Peer reviewed
Experimental study / Meta-analysis
Animals / Human data
Protein disguise could be new target for cancer immunotherapy
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified a protein that helps tumours evade the immune system and, in certain types of cancers, is linked to a poorer chance of survival. The protein could become a target for future cancer treatments.
A crucial part of the immune system's response to cancer is a group of white blood cells, called CD8+ T-cells, which kill tumour cells. Before they launch their anti-tumour response, these cells must be told who to attack by another immune cell, ...
2021-06-02
They studied the extent to which cirrus clouds caused by aircraft occurred during the global hard lockdown between March and May 2020, and compared the values with those during the same period in previous years. The study was led by Johannes Quaas, Professor of Theoretical Meteorology at Leipzig University, and has now been published in the renowned journal "Environmental Research Letters".
Cirrus clouds, known for their high, wispy strands, contribute to warming the climate. When cirrus clouds occur naturally, large ice crystals form at an altitude of about 36 kilometres, in turn reflecting sunlight back into space - albeit ...
2021-06-02
What drives the feasibility of climate scenarios commonly reviewed by organizations like the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)? And can they actually be achieved in practice? A new systematic framework can help understand what to improve in the next generation of scenarios and explore how to make ambitious emission reductions possible by strengthening enabling conditions.
While the IPCC is in the midst of the drafting cycle of the Sixth Assessment Report, whose publication will start in the second half of 2021, there is an ongoing debate ...
2021-06-02
ITHACA, N.Y. - Influencing millions of people on social media and being paid handsomely is not as easy as it looks, according to new Cornell University research.
Algorithm vagaries are just one of several challenges social media content creators face, according to study author Brooke Erin Duffy, associate professor of communication at Cornell.
"I think [our research] is a cautionary tale for aspiring creators as well as the broader public," Duffy said. "The people hoping to work as full-time YouTubers, Instagrammers, and TikTokers are led to believe it's easy and democratic. ...
2021-06-02
One-quarter of people who take the drug methotrexate for common immune system disorders -- from rheumatoid arthritis to multiple sclerosis -- mount a weaker immune response to a COVID-19 vaccine, a new study shows.
Published (online May 25) recently in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, the study addressed disorders that result when the immune system, meant to fight disease and drive healing, is triggered abnormally. This in turn causes inflammation, the pain and swelling that come as immune cells rush into damaged or infected tissue, but often in the wrong amount or context. Called immune-mediated inflammatory disorders, they are typically treated ...
2021-06-02
The pollution of the world's oceans with plastic waste is one of the major environmental problems of our time. However, very little is known about how much plastic is distributed globally in the ocean. Models based on ocean currents have so far suggested that the plastic mainly collects in large ocean gyres. Now, researchers at the University of Bern have calculated the distribution of plastic waste on a global scale while taking into account the fact that plastic can get beached. In their study, which has just been published in the "Environmental Research Letters" scientific journal, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers identify how to prevent cancer metastases