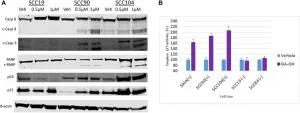
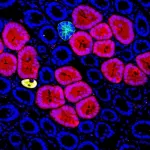
Aging: Cdkn1a transcript variant 2 is a marker of aging and cellular senescence
Upon treating mice systemically with doxorubicin, which induces widespread cellular senescence in vivo, variant 2 increased to a larger extent than variant 1
2021-06-02
(Press-News.org) Aging published "Cdkn1a transcript variant 2 is a marker of aging and cellular senescence" which reported that cellular senescence is a cell fate response characterized by a permanent cell cycle arrest driven primarily the by cell cycle inhibitor and tumor suppressor proteins p16Ink4a and p21Cip1/Waf1. In mice, the p21Cip1/Waf1 encoding locus, Cdkn1a, is known to generate two transcripts that produce identical proteins, but one of these transcript variants is poorly characterized.
The authors show that the Cdkn1a transcript variant 2, but not the better-studied variant 1, is selectively elevated during natural aging across multiple mouse tissues.
Importantly, mouse cells induced to senescence in culture by genotoxic stress upregulated both transcripts, but with different temporal dynamics: variant 1 responded nearly immediately to genotoxic stress, whereas variant 2 increased much more slowly as cells acquired senescent characteristics.
Upon treating mice systemically with doxorubicin, which induces widespread cellular senescence in vivo, variant 2 increased to a larger extent than variant 1. Variant 2 levels were also more sensitive to the senolytic drug ABT-263 in naturally aged mice.
Upon treating mice systemically with doxorubicin, which induces widespread cellular senescence in vivo, variant 2 increased to a larger extent than variant 1.
Thus, variant 2 is a novel and more sensitive marker than variant 1 or total p21Cip1/Waf1 protein for assessing the senescent cell burden and clearance in mice.
Dr. Judith Campisi from The Buck Institute for Research on Aging as well as The University of California said, "The stringent cell growth arrest associated with cellular senescence is determined, among other mechanisms, by activities of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor proteins p16Ink4a and p21Cip1/Waf1, encoded by the Cdkn2a and Cdkn1a loci, respectively."
The increased expression of these proteins is a major hallmark of senescence in most cells, and therefore have become markers of senescence both in culture and in vivo.
Consistent with the fact that senescent cells increase with age in many mouse and human tissues, Cdkn2a mRNA levels also increase with age in these tissues.
To date, possible changes in the expression of Cdkn1a transcript-specific variants during age or cellular senescence have not been explored.
The authors also analyze expression levels in a cell culture model of mouse cells subjected to genotoxic stress-induced senescence to evaluate their relative utility as senescence markers both in culture and in vivo.
The Campisi Research Team concluded in their Aging Research Output that it remains unexplored the possibility that the different transcript variants are preferentially associated with one or other cell fate.
Human cells also express several Cdkn1a transcript variants.
Among the ten human transcript variants currently annotated, at least one shares translational regulatory mechanisms with the murine p21var2.
Interestingly, even though murine variant 2 and human variant 4 do not appear to share sequence homology, the translational regulation in both transcripts is driven by the integrated stress response and results in cell cycle arrest.
The potential relevance of this mechanism for cellular senescence in humans remains unknown, and the functions and interrelations of the different Cdkn1a transcript variants have not been studied in depth.
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203110
Full Text - https://www.aging-us.com/article/203110/text
Correspondence to: Judith Campisi email: jcampisi@buckinstitute.org
Keywords: p21, p53, mouse dermal fibroblast, ionizing radiation, doxorubicin
About Aging-US
Launched in 2009, Aging-US publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research as well as topics beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, cancer, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
To learn more about Aging-US, please visit http://www.Aging-US.com or connect with @AgingJrnl
Aging-US is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit http://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
18009220957x105
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-02
Oncotarget published "A high-content AlphaScreen™ identifies E6-specific small molecule inhibitors as potential therapeutics for HPV+ head and neck squamous cell carcinomas" which reported that the incidence of human papillomavirus-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma has increased dramatically over the past decades due to an increase in infection of the oral mucosa by HPV.
The etiology of HPV -HNSCC is linked to expression of the HPV oncoprotein, E6, which influences tumor formation, growth and survival.
E6 effects this oncogenic phenotype in part through inhibitory ...
2021-06-02
Oncotarget published "Molecular characterization of lung squamous cell carcinoma tumors reveals therapeutically relevant alterations" which reported that unlike lung adenocarcinoma patients, there is no FDA-approved targeted-therapy likely to benefit lung squamous cell carcinoma patients.
The authors performed survival analyses of lung squamous cell carcinoma patients harboring therapeutically relevant alterations identified by whole exome sequencing and mass spectrometry-based validation across 430 lung squamous tumors.
They report a mean of 11.6 mutations/Mb with a characteristic smoking signature along with mutations in TP53, CDKN2A, NFE2L2, FAT1, KMT2C, LRP1B, FGFR1, PTEN and PREX2 among lung squamous cell carcinoma patients of Indian descent.
In overall, the data suggests 13.5% ...
2021-06-02
When the COVID-19 pandemic arrived in North America in March 2020, health care facilities stopped providing all but "essential" care, to reduce infection risks and preserve protective gear known as PPE.
That included changes at many centers that provide ECT (electroconvulsive therapy) for severe depression and other conditions, a new survey shows.
Because ECT involves anesthesia, so that patients are unconscious when carefully controlled pulses of electricity are delivered to key areas of the brain, it is considered an 'aerosol generating' procedure. That means it poses special risks when a respiratory ...
2021-06-02
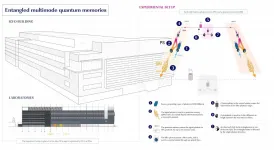
* ICFO researchers report in Nature on having achieved, for the first time, entanglement of two multimode quantum memories located in different labs separated by 10 meters, and heralded by a photon at the telecommunication wavelength.
* The scientists implemented a technique that allowed them to reach a record in the entanglement rate in a system that could be integrated into the fibre communication network, paving the way to operation over long distances.
* The results are considered a landmark for quantum communications and a major step forward in the development of quantum repeaters for the future quantum internet.
During the 90s, engineers made major advances in the telecom arena spreading out the network to distances beyond the ...
2021-06-02
TROY, N.Y. -- Oxygen levels in the world's temperate freshwater lakes are declining rapidly -- faster than in the oceans -- a trend driven largely by climate change that threatens freshwater biodiversity and drinking water quality.
Research published today in Nature found that oxygen levels in surveyed lakes across the temperate zone have declined 5.5% at the surface and 18.6% in deep waters since 1980. Meanwhile, in a large subset of mostly nutrient-polluted lakes, surface oxygen levels increased as water temperatures crossed a threshold favoring cyanobacteria, which can create toxins when they flourish in the form of harmful algal blooms.
"All complex life depends on oxygen. It's the support system for aquatic food webs. And when you start losing oxygen, you have the potential ...
2021-06-02
Chinese researchers realized an elementary link of a quantum repeater based on absorptive quantum memories (QMs) and demonstrated the multiplexed quantum repeater for the first time. On June 2nd?the work is published in Nature.
The fundamental task of a quantum network is to distribute quantum entanglement between two remote locations. However, the transmission loss of optical fiber has limited the distance of entanglement distribution to approximately 100 km on the ground. Quantum repeaters can overcome this difficulty by dividing long-distance transmission into several short-distance elementary links. The entanglement of two end nodes of each link is created firstly. Then the entanglement distance is gradually expanded through entanglement swapping between each link.
Previously, an ...
2021-06-02
HOUSTON - (June 2, 2021) - It's official: Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) is the iron man of 2D materials, so resistant to cracking that it defies a century-old theoretical description engineers still use to measure toughness.
"What we observed in this material is remarkable," said Rice University's Jun Lou, co-corresponding author of a Nature paper published this week. "Nobody expected to see this in 2D materials. That's why it's so exciting."
Lou explains the significance of the discovery by comparing the fracture toughness of h-BN with that of its better-known cousin ...
2021-06-02
The study, published in the journal Nature, shows how a drug available on the NHS can boost fitness of healthy stem cells in the gut, making them more resistant to sabotage from mutant stem cells that cause cancer.
Researchers in the Netherlands, funded by the UK charity Worldwide Cancer Research, have discovered a way to boost the fitness of healthy cells in the gut to prevent the development of bowel cancer. The findings have led to the initiation of a clinical trial to find out if a commonly used psychiatric drug could be used to prevent bowel cancer in people. The trial will recruit patients with a genetic mutation that means they are virtually 100% certain to develop bowel cancer in their lifetime, unless ...
2021-06-02
Metastases can develop in the body even years after apparently successful cancer treatment. They originate from cancer cells that migrated from the original tumor to other organs, and which can lie there inactive for a considerable time. Researchers have now discovered how these "sleeping cells" are kept dormant and how they wake up and form fatal metastases. They have reported their findings in the journal Nature.
A tumor can leave behind an ominous legacy in the body: cancer cells can migrate from the tumor to other tissues in the body, where they survive after treatment in a kind of hibernation called dormancy. Currently, cancer medicine relies on monitoring cancer patients ...
2021-06-02
Studies on cancer are limited by the threshold at which cellular transformations become clinically detectable. However, the very initial phase on the way to malignancy is histologically invisible, as the process originates from one single cell. In this early phase, a so-called "seeding cell" acquires an initial pro-cancerous mutation, also known as the "first oncogenic hit", while being completely surrounded by normal tissue. To overcome the detection barrier, a team of researchers around IMBA group leader Bon-Kyoung Koo and University of Cambridge group leader Professor Benjamin D. Simons developed a laboratory system to dissect the pre-cancerous steps that remained under the radar ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Aging: Cdkn1a transcript variant 2 is a marker of aging and cellular senescence
Upon treating mice systemically with doxorubicin, which induces widespread cellular senescence in vivo, variant 2 increased to a larger extent than variant 1