Quantum-optically integrated light cage on a chip
2021-06-03
(Press-News.org) In the rapidly growing field of hybrid quantum photonics, the realization of miniaturized, integrated quantum-optical systems with intense light-matter interaction is of great importance for both fundamental and applied research. In particular, the development of methods for reliably generating, controlling, storing and retrieving quantum states with high fidelity through coherent interaction of light and matter opened up a wide field of applications for quantum information and quantum networks. These include, for example, optical switching, quantum memories, and quantum repeaters.
One promising approach for efficient light-matter interaction is the integration of light-guiding platforms in a near-room-temperature alkali vapor. Several research groups have aimed to interface hollow-core photonic-crystal fibers or planar waveguides with atoms in vapor cells. However, when coupled to atoms, nearly all photonic structures reveal distinct limitations imposed by their design or they induce an unwanted level of complexity, especially when aiming for integrated applications.
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists from Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Leibniz Institute of Photonic Technology and Friedrich Schiller University, Jena, the University of Stuttgart, and Imperial College London has integrated a novel on-chip hollow-core light cage into an alkali atom vapor cell. This altogether overcomes the disadvantages of previously explored photonic structures, potentially providing a basis for quantum-storage and quantum-nonlinear applications.
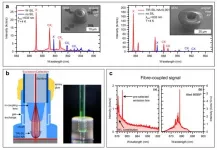
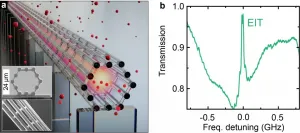
The researchers adopted the compact, easy-to-handle light-guiding structure of the laterally-accessible light cage as a container for coherent light-matter interaction, thus realizing stable non-degrading performance and extreme versatility. As a result, the observation of electromagnetically-induced transparency, a prominent quantum-optical effect, inside the novel on-chip hollow-core light cage demonstrates its potential for applications in quantum optics.
Implemented by 3D nanoprinting, the compact light cage on a chip exhibits several advantages compared to other hollow-core waveguide structures. Whereas hollow-core fibers or planar waveguides suffer from inefficient vapor-filling times -- exceeding months for few centimeter long devices -- the design of the light cage allows for high-speed gas diffusion through side-wise direct access to the hollow core within minutes.
Moreover, the high degree of integration and long-term stability allows for interfacing the device with other established technology platforms like silicon photonics and fiber optics, as well as customizing reproducible devices for a large variety of applications.
„We demonstrate the peculiar coherent quantum-optical interaction between the light field in a light cage and room-temperature cesium vapor. This is the first time we have succeeded in observing electromagnetically induced transparency inside such a structure", Tim Kroh from the Department of Physics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin explains.
„Apart from the beautiful physics that went into the discovery and design of the light cage, and the quantum optics experiment conducted with it, the technique we used for fabricating the light cage is fascinating -- directly writing it into a polymer block with a laser beam. This very versatile method has a great future for integrated optical devices", adds Prof. Dr. Stefan Maier, who is holding the Chair in Hybrid Nanosystems at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München.
Further improvements of the structure are straightforward, the researchers say. The generation of broad electromagnetically-induced transparency windows for light delay of spectrally broad light pulses, as emitted from single-photon sources, lays a foundation to synchronize photon arrival in quantum networks or to realize compact quantum storage on-a-chip. „Therefore, our results represent a major step forward by an unprecedented hybrid integration of designer laser-written structures and atom cells. The freedom to produce three-dimensional structures nearly without restrictions on the silicon-technology platform will allow us to combine light-matter interaction in the light cage with other Si-chip-compatible devices, i.e. lithium niobate waveguides for modulation and frequency conversion of light, as well as direct mode coupling from and to optical fibers. Extensive control of the single-photon properties in a quantum network could ultimately be applied all on one chip", the scientists forecast.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-03
Lithium is a vital element in the batteries that power electric vehicles, but soaring lithium demand is expected to exhaust land-based reserves by 2080. KAUST researchers have now developed an economically viable system that can extract high-purity lithium from seawater.
The oceans contain about 5,000 times more lithium than the land but at extremely low concentrations of about 0.2 parts per million (ppm). Larger ions, including sodium, magnesium and potassium, are all present in seawater at much higher concentrations; however, previous research efforts to tease ...
2021-06-03
Quantum computing and quantum communication are believed to be the future of information technology. In order to achieve the challenging and long-standing goal to make secure, wide-spread quantum communication networks a reality, high-brightness single-photon sources are indispensable. Single-photon emission from semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) has been shown to be a pure and efficient non-classical light source with a high degree of indistinguishability. However, the total internal reflection (TIR) as a result of the high semiconductor-to-air refractive index contrast severely limits the single-photon extraction efficiency. Another crucial step in the development ...
2021-06-03
For decades, researchers have debated whether the buildup of certain electrical activities in the brain indicates that human beings are unable to act out of free will.
Experiments spanning the 1960s and 1980s measured brain signals noninvasively and led many neuroscientists to believe that our brains make decisions before we do--that human actions were initiated by electrical waves that did not reflect free, conscious thought.
However, a new article in Trends in Cognitive Science argues that recent research undermines this case against free will.
"This new perspective on the data turns on its head the way well-known findings have been interpreted," said Adina Roskies, the Helman Family Distinguished Professor and professor of philosophy at ...
2021-06-03
Durham, NC -- Type 2 diabetes patients who are not overweight and who have had the disorder for less than a decade can benefit from stromal stem cells transplanted from their own bone marrow, according to a study published today in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine.
In a randomized clinical trial at Vinmec Research Institute of Stem Cell and Gene Technology in Hanoi, Vietnam, researchers investigated the safety and potential therapeutic value of administering bone marrow stromal stem cells to patients with Type 2 diabetes. In each case, the cells were autologous, ...
2021-06-03
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (June 3, 2021) -- Since arriving to the northern Atlantic Ocean less than 30 years ago, lionfish have quickly become one of the most widespread and voracious invasive species, negatively impacting marine ecosystems--particularly coral reefs--from the northeast coast of the United States to the Caribbean Islands. In a new study, an international research team including the California Academy of Sciences presents four new records of lionfish off the coast of Brazil, confirming the invasion of the predatory fish into the South Atlantic for the first time. Their findings, published today in Biological Invasions, discuss how the lionfish may have arrived in the ...
2021-06-03
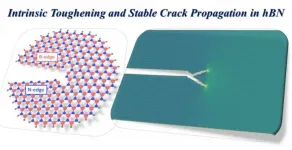
A team of scientists led by Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore) and Rice University in the US, has uncovered the key to the outstanding toughness of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). h-BN can withstand ten times the amount of force that graphene can, which is known as one of the toughest materials on Earth.
A two-dimensional (2D) material, h-BN has a thickness of just one atom. First used in cosmetics in the 1940s, it was soon abandoned due to its high price, making a resurgence in the late 1990s after technology made its production cheaper.
Today, it is used by nearly all leading producers of cosmetic products because of its ability to absorb excess facial sebum and disperse pigment evenly, ...
2021-06-03
Mangrove vegetation, which grows naturally in subtropical shorelines, provides a wide range of ecosystem functions such as reducing coastal erosion, promoting biodiversity, and removing nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon dioxide. These vital ecological functions are influenced by the water flow around the intricate mangrove roots, which create a complex energetic process that mixes up sediments and generates a depositional region behind the roots. How these mangrove roots interact with water flow is believed to be a key element in mitigating coastal erosion.
Accurately projecting hydrodynamic erosion and the essential amount of mangrove species has been a challenge for managers and restoration experts to forecast a successful component of project designs. That is because ...
2021-06-03
WASHINGTON (June 3, 2021) - Nearly three-quarters of breast cancer patients (73%) report using at least one type of complementary medicine after cancer diagnosis, while oncologists believe that less than half (43%) of patients are using these approaches during cancer care. These and other findings from a national survey of oncologists and breast cancer patients were released in conjunction with the 2021 ASCO Annual Meeting. The study found that doctors report discussing integrative health with only about half of patients, leading patients to seek information outside the clinic.
"Cancer is a complex ...
2021-06-03
Astronomers studying the fast-moving jet of material ejected by a still-forming, massive young star found a major difference between that jet and those ejected by less-massive young stars. The scientists made the discovery by using the U.S. National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) to make the most detailed image yet of the inner region of such a jet coming from a massive young star.
Both low- and high-mass young stars, or protostars, propel jets outward perpendicular to a disk of material closely orbiting the star. In stars with masses similar to the Sun, these jets are narrowed, or focused, relatively tightly near to the star in a process called collimation. Because most high-mass protostars are more distant, studying ...
2021-06-03
New research into Alzheimer's disease (AD) suggests that secondary infections and new inflammatory events amplify the brain's immune response and affect memory in mice and in humans - even when these secondary events occur outside the brain.
Scientists believe that key brain cells (astrocytes and microglia) are already in an active state due to inflammation caused by AD and this new research shows that secondary infections can then trigger an over-the-top response in those cells, which has knock-on effects on brain rhythms and on cognition.
In the study, just published in Alzheimer's & Dementia, the journal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Quantum-optically integrated light cage on a chip