(Press-News.org) Physiologically, milk contains biocomponents that are highly protective against infections. In light of this, the AGR-149-Infectious Diseases group at the University of Cordoba's Department of Animal Health is doing research that focuses on cow's milk as a possible source of Covid-19 control. The results have been published, partially, in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.
This is possible due to "crossed immunity", and there is already evidence of the protection it provides, explained one of the principal investigators, Mari Carmen Borge. "It has been shown that the immune cells that the vaccinated animal generates against bovine coronavirus are capable of controlling other coronaviruses as well, such as SARS-CoV-2, which causes Covid-19".
Antonio Arenas, principal investigator on the project, spoke of the similarity that exists between Bovine Coronavirus (BCoV) and SARS-CoV-2 to explain the effectiveness of this technique. "There are a number of highly conserved structures of the virus that are similar in both viruses. In fact, both belong to the genus Betacoronavirus. Thus, cow's milk could have a total or partial blocking action against SARS-CoV-2".
In this way, these bovine antibodies could neutralize the virus in people who are already infected, or help prevent the disease in those who have not been vaccinated, or who have been, but have not developed immunity.
Thus, the aim is to come up with a supplement that would boost the immune system through a dairy preparation with a high level of antibodies, helping the system control infection through different immune pathways.
The animals from which the milk is extracted have been previously vaccinated with commercial BCoV vaccines, thus generating high levels of antibodies. However, the time when milk is most effective is just after a birth: "then the level of immunoglobulin in the milk increases - what is called colostrum - but it has a certain duration," Arenas added.
Now the scientific challenge is to be able to extend the colostrum period, and also to study how to always ensure the same level of antibodies in the final product. Plans call for it to be marketed in single-dose format as of September. "For this, we have to readjust the reproduction cycles of bovine farms in order to always maintain a set of animals with high antibodies", the researcher explained.
This dairy preparation, which anyone can consume, has already been tested on more than 300 people. Amongst them, no serious Covid-19 process has been detected. As soon as it goes on the market an observational test will be carried out. In any case, it will not be harmful to health, and it could become a natural resource providing people with a certain level of immunity.
There are other technological challenges: herd management, hygiene processes, conservation, packaging, marketing, medical, etc., that make this a holistic and complex project.
INFORMATION:
Arenas A, Borge C, Carbonero A, Garcia-Bocanegra I, Cano-Terriza D, Caballero J, Arenas-Montes A. (2021) Bovine Coronavirus Immune Milk Against COVID-19. Front Immunol. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637152
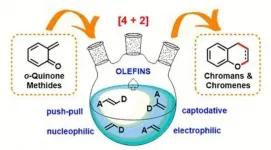
O-quinone methides have been studied at the Samara Polytech for more than ten years. Vitaly Osyanin, Doctor of Chemistry, Professor of the Department of Organic Chemistry, is in charge of scientific work in this area. The results of the latest research were published in the authoritative Russian journal "Russian Chemical Reviews" (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1070/RCR4971).
Thus Professor Osyanin and the Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department Dmitry Osipov and the Candidate of Chemical Sciences, the graduate of the Department Anton Lukashenko prepared a review article in which the main known examples of the transformation of o-quinone methides into chromene and ...
Skoltech scientists have studied the hydroxyl defects in LiFePO4, a widely used cathode material in commercial lithium-ion batteries, contributing to the overall understanding of the chemistry of this material. This work will help improve the LiFePO4 manufacturing process to avoid formation of adverse intrinsic structural defects which deteriorate its performance. The paper was published in the journal Inorganic Chemistry.
Lithium iron phosphate, LiFePO4, is a safe, stable and affordable cathode material for Li-ion batteries that has been very well optimized for practical applications despite its low conductivity and medium energy density. Yet scientists continue to study the various properties of this material, and in particular the impact ...
There has been concern at how the pandemic has not only hit physical health and the economy but has also impacted our mental health with the possibility of increased rates of suicide.
Now a new study - a collaboration between Swansea University, Cardiff University, and the NHS in Wales - has investigated exactly which Covid-related stressors are most likely to trigger suicidal thoughts and behaviours.
The researchers also discovered the important role that hope for the future can play - along with individuals' levels resilience - when it comes to coping with these stressors.
More than 12,000 people responded to the Wales Wellbeing survey which asked volunteers to share their experiences during the ...
To limit the impacts of climate change it is essential to predict them as accurately as possible. Regional Climate Models are high-resolution models of the Earth's climate that are able to improve simulations of extreme weather events that may be affected by climate change and thus contribute to limiting impacts through timely action.
At their highest resolutions, Regional Climate Models are capable of simulating atmospheric convection, a key process in many extreme weather events which is often the cause of very intense and localized precipitations. Although "convection permitting" models are widely used in weather forecasting, they require large supercomputing ...
Building on their previous findings, scientists from the Immuno-Pharmacology and Interactomics group at the Department of Infection and Immunity of the Luxembourg Institute of Health (LIH), in collaboration with the Center for Drug Discovery at RTI International (RTI), a nonprofit research institute, have demonstrated that conolidine, a natural painkiller derived from the pinwheel flower and traditionally used in Chinese medicine, interacts with the newly identified opioid receptor ACKR3/CXCR7 that regulates opioid peptides naturally produced in the brain. The researchers ...
A nasal therapy, built upon on the application of a new engineered IgM antibody therapy for COVID-19, was more effective than commonly used IgG antibodies at neutralizing the COVID-19 virus in animal models, according to research recently published by The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth), The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston (UTMB Health), the University of Houston, and IGM Biosciences, Inc.
The study was published today in Nature.
Researchers engineered IgM antibodies and found that in all cases, these antibodies were significantly more potent than standard ...
CHAPEL HILL, NC - Airway mucus consists of various proteins such as long mucins MUC5AC and MUC5B, both of which contribute greatly to the proper gel-like consistency of this most essential bodily fluid. UNC School of Medicine researchers led by mucin expert Mehmet Kesimer, PhD, had previously discovered that the total mucin concentrations in the lungs are associated with COPD disease progression and could be used as diagnostic markers of chronic bronchitis, a hallmark condition for patients with COPD. Kesimer and colleagues now report that one of these mucins, MUC5AC, is more closely and reliably associated with the development ...
The University of Guam College of Liberal Arts and Social Sciences has released Volume 11 of its peer-reviewed online journal "Pacific Asia Inquiry: Multidisciplinary Perspectives." The volume is available for download on the UOG website at http://www.uog.edu/pai.
This latest volume includes manuscripts representing examples of historical, socio-cultural, and philosophical research. Topics range from the impact of climate change and food security in the Marshall Islands to the Jesuit presence in the Mariana Islands, among others. Inserted between the articles are ...
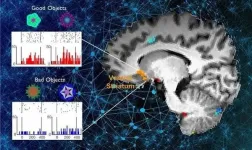
Researchers have been investigating how the brain controls habitual seeking behaviors such as addiction. A recent study by Professor Sue-Hyun Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering revealed that a long-term value memory maintained in the ventral striatum in the brain is a neural basis of our habitual seeking behavior. This research was conducted in collaboration with the research team lead by Professor Hyoung F. Kim from Seoul National University. Given that addictive behavior is deemed a habitual one, this research provides new insights for developing therapeutic interventions for addiction.
Habitual seeking behavior involves ...
MORGANTOWN, W.Va.--If someone joins a church, mosque or synagogue, they may be seeking better emotional or spiritual health. But according to research out of West Virginia University, faith communities have the potential to promote physical wellbeing, as well.
A new study led by Angel Smothers, Stephanie Young and Elizabeth Morrissey--researchers with the WVU School of Nursing--and James Thomas from the School of Medicine's Division of Exercise Physiology suggests that healthcare providers who work directly with a faith community can help congregants stick with an exercise program.
Their results appear in the Journal of Interprofessional Education and Practice.
"Even in Biblical texts, there were always caregivers who ...