Stone Age raves to the beat of elk tooth rattles?
2021-06-03
(Press-News.org) "Ornaments composed of elk teeth suspended from or sown on to clothing emit a loud rattling noise when moving," says auditory archaeologist and Academy of Finland Research Fellow Riitta Rainio from the University of Helsinki. "Wearing such rattlers while dancing makes it easier to immerse yourself in the soundscape, eventually letting the sound and rhythm take control of your movements. It is as if the dancer is led in the dance by someone."
Rainio is well versed in the topic, as she danced, for research purposes, for six consecutive hours, wearing elk tooth ornaments produced according to the Stone Age model. Rainio and artist Juha Valkeapää held a performance to find out what kind of wear marks are formed in the teeth when they bang against each other and move in all directions. The sound of a tooth rattler can be clear and bright or loud and pounding, depending on the number and quality of the teeth, as well as the intensity of movement.
Microanalysis demonstrates that tooth wear marks are the result of dancing
The teeth worn out by dancing were analysed for any microscopic marks before and after the dancing. These marks were then compared to the findings made in the Yuzhniy Oleniy Ostrov graves by Evgeny Girya, an archaeologist specialised in micro-marks at the Russian Academy of Sciences. Girya documented and analysed the wear marks in the elk teeth found in four graves chosen for the experiment. Comparing the chips, hollows, cuts and smoothened surfaces of the teeth, he observed a clear resemblance between teeth worn out by dancing and the Stone Age teeth. However, the marks in the Stone Age teeth were deeper and more extensive. According to Girya, the results show that the marks are the result of similar activity.
"As the Stone Age teeth were worn for years or even decades, it's no surprise that their marks are so distinctive," Girya says.
Associate Professor of Archaeology Kristiina Mannermaa from the University of Helsinki is excited by the research findings.
"Elk tooth rattlers are fascinating, since they transport modern people to a soundscape that is thousands of years old and to its emotional rhythms that guide the body. You can close your eyes, listen to the sound of the rattlers and drift on the soundwaves to a lakeside campfire in the world of Stone Age hunter-gatherers."
A total of 177 graves of women, men and children have been found in the Yuzhniy Oleniy Ostrov burial site, of which more than half contain several elk tooth ornaments, some of them composed of as many as over 300 individual teeth.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-03
As G7 governments renew commitments to protecting marine spaces and biodiversity, global conservation initiatives such as 30x30 are feared to pay too little attention to the livelihood impacts on communities
Close-up inspection of an upcoming marine conservation area in Cambodia shows mixed livelihood consequences ranging from improving relationships to the state to increased anxiety and social division
In the long term and on a regional scale in Southeast Asia, communities exposed to marine conservation are poorer and experience higher child mortality
Researchers warn that the rapid global expansion of nominal marine protected area (MPA) coverage can undermine community livelihoods if it proceeds with a sole focus on marine resource conservation, a disregard of local ...
2021-06-03
Physiologically, milk contains biocomponents that are highly protective against infections. In light of this, the AGR-149-Infectious Diseases group at the University of Cordoba's Department of Animal Health is doing research that focuses on cow's milk as a possible source of Covid-19 control. The results have been published, partially, in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.
This is possible due to "crossed immunity", and there is already evidence of the protection it provides, explained one of the principal investigators, Mari Carmen Borge. "It has been shown that the immune cells that the vaccinated animal generates against bovine coronavirus ...
2021-06-03
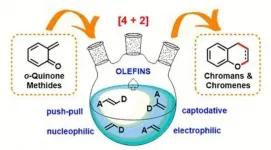
O-quinone methides have been studied at the Samara Polytech for more than ten years. Vitaly Osyanin, Doctor of Chemistry, Professor of the Department of Organic Chemistry, is in charge of scientific work in this area. The results of the latest research were published in the authoritative Russian journal "Russian Chemical Reviews" (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1070/RCR4971).
Thus Professor Osyanin and the Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department Dmitry Osipov and the Candidate of Chemical Sciences, the graduate of the Department Anton Lukashenko prepared a review article in which the main known examples of the transformation of o-quinone methides into chromene and ...
2021-06-03
Skoltech scientists have studied the hydroxyl defects in LiFePO4, a widely used cathode material in commercial lithium-ion batteries, contributing to the overall understanding of the chemistry of this material. This work will help improve the LiFePO4 manufacturing process to avoid formation of adverse intrinsic structural defects which deteriorate its performance. The paper was published in the journal Inorganic Chemistry.
Lithium iron phosphate, LiFePO4, is a safe, stable and affordable cathode material for Li-ion batteries that has been very well optimized for practical applications despite its low conductivity and medium energy density. Yet scientists continue to study the various properties of this material, and in particular the impact ...
2021-06-03
There has been concern at how the pandemic has not only hit physical health and the economy but has also impacted our mental health with the possibility of increased rates of suicide.
Now a new study - a collaboration between Swansea University, Cardiff University, and the NHS in Wales - has investigated exactly which Covid-related stressors are most likely to trigger suicidal thoughts and behaviours.
The researchers also discovered the important role that hope for the future can play - along with individuals' levels resilience - when it comes to coping with these stressors.
More than 12,000 people responded to the Wales Wellbeing survey which asked volunteers to share their experiences during the ...
2021-06-03
To limit the impacts of climate change it is essential to predict them as accurately as possible. Regional Climate Models are high-resolution models of the Earth's climate that are able to improve simulations of extreme weather events that may be affected by climate change and thus contribute to limiting impacts through timely action.
At their highest resolutions, Regional Climate Models are capable of simulating atmospheric convection, a key process in many extreme weather events which is often the cause of very intense and localized precipitations. Although "convection permitting" models are widely used in weather forecasting, they require large supercomputing ...
2021-06-03
Building on their previous findings, scientists from the Immuno-Pharmacology and Interactomics group at the Department of Infection and Immunity of the Luxembourg Institute of Health (LIH), in collaboration with the Center for Drug Discovery at RTI International (RTI), a nonprofit research institute, have demonstrated that conolidine, a natural painkiller derived from the pinwheel flower and traditionally used in Chinese medicine, interacts with the newly identified opioid receptor ACKR3/CXCR7 that regulates opioid peptides naturally produced in the brain. The researchers ...
2021-06-03
A nasal therapy, built upon on the application of a new engineered IgM antibody therapy for COVID-19, was more effective than commonly used IgG antibodies at neutralizing the COVID-19 virus in animal models, according to research recently published by The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth), The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston (UTMB Health), the University of Houston, and IGM Biosciences, Inc.
The study was published today in Nature.
Researchers engineered IgM antibodies and found that in all cases, these antibodies were significantly more potent than standard ...
2021-06-03
CHAPEL HILL, NC - Airway mucus consists of various proteins such as long mucins MUC5AC and MUC5B, both of which contribute greatly to the proper gel-like consistency of this most essential bodily fluid. UNC School of Medicine researchers led by mucin expert Mehmet Kesimer, PhD, had previously discovered that the total mucin concentrations in the lungs are associated with COPD disease progression and could be used as diagnostic markers of chronic bronchitis, a hallmark condition for patients with COPD. Kesimer and colleagues now report that one of these mucins, MUC5AC, is more closely and reliably associated with the development ...
2021-06-03
The University of Guam College of Liberal Arts and Social Sciences has released Volume 11 of its peer-reviewed online journal "Pacific Asia Inquiry: Multidisciplinary Perspectives." The volume is available for download on the UOG website at http://www.uog.edu/pai.
This latest volume includes manuscripts representing examples of historical, socio-cultural, and philosophical research. Topics range from the impact of climate change and food security in the Marshall Islands to the Jesuit presence in the Mariana Islands, among others. Inserted between the articles are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Stone Age raves to the beat of elk tooth rattles?