High-intensity strength and impact training attenuates skeletal aging
The tibial bone properties of middle-aged and older male sprint athletes were followed over 10 years
2021-06-03
(Press-News.org) Regular strength and impact-type training may decrease or even prevent age-related bone deterioration in men, new research at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland, shows. The tibial bone properties of middle-aged and older male sprint athletes were followed over 10 years. The study presents novel findings on maintaining the adaptability of the aging skeleton and on the importance of regular intensive training for maintaining bone health.
"Part of the age-related bone loss is probably explained by reduced levels of physical activity. Especially intensive, bone-loading exercise typically decreases with age," says Tuuli Suominen, a doctoral researcher at the Gerontology Research Center, Faculty of Sport and Health Sciences at the University of Jyväskylä.
High-intensity strength, sprint and jumping training have beneficial effects on bone even in old age. However, the ability of such training to prevent or decrease age-related bone deterioration remains unclear, as no longitudinal studies have been conducted on the topic thus far.
Associations of regular strength and sprint training with bone aging were examined in a larger research program by the Gerontology Research Center and Faculty of Sport and Health Sciences at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland. A total of 69 men aged 40 to 85 years participated in the follow-up part of the study. At the beginning of the follow-up, all the men were training and competing actively.
Tibial bone properties of the participants were examined by computed tomography at baseline and after 10 years. The associations of the training status with the longitudinal changes in bone were examined in two groups: in athletes who had continued regular strength and sprint training and in athletes who had reduced their training load.
The study showed that regular strength and sprint training was associated with maintained or even improved tibial bone properties while in those athletes who had reduced their training load the bone properties declined over the 10-year follow-up period. The positive effects of the training were most evident in trabecular bone density and in cross-sectional geometry of the tibial shaft, which supports the benefits of both impact-type training and strength training.
"Although the intensive training of the athletes as such is not possible for all aging people, strength and power training is highly recommended at all ages, regardless of the functional status," Suominen says. "In the present study, the benefits of high-impact training were most evident among middle-aged while strength training may be effective in preserving bone in older populations. Muscle strength and power are highly important also in preventing falls and related fractures."
INFORMATION:
The study was part of a larger Athlete Aging Study research program examining the effects of long-term training on musculoskeletal aging and physical performance. The study was funded by the Academy of Finland, Ministry of Education and Culture, Peurunka Rehabilitation Center, Ellen and Artturi Nyyssönen Foundation, Juho Vainio Foundation, Finnish Cultural Foundation, Päivikki and Sakari Sohlberg Foundation and Alfred Kordelin Foundation.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-03
Affecting more than one in a hundred children, autism spectrum disorder is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders. It has a particular impact on social interaction, including difficulties in understanding other people's perspectives, beliefs, desires and emotions, known as 'theory of mind'. Bilingual families with an autistic child often tend - and are sometimes encouraged - to forego the use of one of the home languages, so as not to further complicate the development of their child's communicative skills. A researcher from the University of Geneva (UNIGE, Switzerland), in collaboration with the Universities ...
2021-06-03
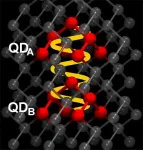
So-called quantum dots are a new class of materials with many applications. Quantum dots are realized by tiny semiconductor crystals with dimensions in the nanometre range. The optical and electrical properties can be controlled through the size of these crystals. As QLEDs, they are already on the market in the latest generations of TV flat screens, where they ensure particularly brilliant and high-resolution colour reproduction. However, quantum dots are not only used as "dyes", they are also used in solar cells or as semiconductor devices, right up to computational building blocks, the qubits, of a quantum computer.
Now, a team led by Dr. Annika Bande at HZB has extended the understanding of the interaction between several quantum dots with an ...
2021-06-03
A biomarker in the blood of patients with bowel cancer may provide valuable insight into the risk of cancer relapse after surgery and the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Research published in PLOS found circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) measured before and after surgery provided a reliable marker for predicting whether the cancer would recur following chemotherapy treatment.
The ctDNA also provided a real-time measure of the effectiveness of chemotherapy, highlighting the potential for this test to provide an early indication of the success of chemotherapy in eradicating microscopic cancer.
At a glance
By measuring levels of ctDNA present in the blood of bowel cancer patients after surgery, researchers were able to predict the likelihood ...
2021-06-03
If insomnia keeps you awake at night, Flinders University researchers recommend a trip to the doctor - not for a sleeping pill prescription but for a short course of intensive behavioural therapy.
Researchers have developed new clinical guidelines for Australian doctors to give family GPs insights into the most effective treatment for insomnia - Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for insomnia (or 'CBTi').
CBTi improves insomnia, mental health and quality of life, and can be more successful than sleeping pills, say Adelaide Institute for Sleep Health (AISH) sleep experts from Flinders University in a new paper in the Australian Journal of General Practice.
Most patients with insomnia managed in general practice are prescribed potentially addictive ...
2021-06-03
Paleo researcher Charlotte Prud'homme, who until recently worked at the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry and is now a researcher at the Université Lausanne, explains: "The 80-meter-thick sedimentary sequence we found at Charyn Canyon in southeast Kazakhstan provides us with a virtually continuous record of five million years of climate change. This is a very rare occurrence on land!" The alternating dust and soil layers provide the first reliable evidence, in one place, of long-term interactions between major climate systems on the Eurasian continent. "Over the past five million years, the land surfaces of Eurasia appear to ...
2021-06-03
The so-called 'bullshit jobs theory' - which argues that a large and rapidly increasing number of workers are undertaking jobs that they themselves recognise as being useless and of no social value - contains several major flaws, argue researchers from the universities of Cambridge and Birmingham.
Even so, writing in Work, Employment and Society, the academics applaud its proponent, American anthropologist David Graeber, who died in September 2020, for highlighting the link between a sense of purpose in one's job and psychological wellbeing.
Graeber initially put forward the concept of 'bullshit jobs' - jobs that even those who do them view as worthless - in his 2013 essay ...
2021-06-03
Researchers at the University of Turku, Finland, showed that the antibody treatment reactivates the immune defense in patients with advanced-stage cancer. The treatment alters the function of the body's phagocytes and facilitates extensive activation of the immune system.
The immune defense is the body's own defense system equipped to combat cancer. However, cancer learns to hide from immune attacks and harnesses this system to promote its own growth. Therefore, it would be beneficial to be able to return the immune defense back to restricting the advancement of cancer.
Macrophages, a type of white blood cell, are central in the fight against cancer. Cancer educates ...
2021-06-03
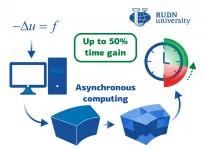
RUDN University mathematician and his colleagues from France and Hungary developed an algorithm for parallel computing, which allows solving applied problems, such as electrodynamics or hydrodynamics. The gain in time is up to 50%. The results are published in the Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics.
Parallel computing methods are often used to process practical problems in physics, engineering, biology, and other fields. It involves several processors joined in a net to simultaneously solve a single problem -- each has its own small part. The way to distribute the work between the processors and make them "communicate" with each other is a choice based on the specifics of a particular problem. ...
2021-06-03
"Ornaments composed of elk teeth suspended from or sown on to clothing emit a loud rattling noise when moving," says auditory archaeologist and Academy of Finland Research Fellow Riitta Rainio from the University of Helsinki. "Wearing such rattlers while dancing makes it easier to immerse yourself in the soundscape, eventually letting the sound and rhythm take control of your movements. It is as if the dancer is led in the dance by someone."
Rainio is well versed in the topic, as she danced, for research purposes, for six consecutive hours, wearing elk tooth ornaments produced according to the Stone Age model. Rainio and artist Juha Valkeapää held a performance to ...
2021-06-03
As G7 governments renew commitments to protecting marine spaces and biodiversity, global conservation initiatives such as 30x30 are feared to pay too little attention to the livelihood impacts on communities
Close-up inspection of an upcoming marine conservation area in Cambodia shows mixed livelihood consequences ranging from improving relationships to the state to increased anxiety and social division
In the long term and on a regional scale in Southeast Asia, communities exposed to marine conservation are poorer and experience higher child mortality
Researchers warn that the rapid global expansion of nominal marine protected area (MPA) coverage can undermine community livelihoods if it proceeds with a sole focus on marine resource conservation, a disregard of local ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] High-intensity strength and impact training attenuates skeletal aging
The tibial bone properties of middle-aged and older male sprint athletes were followed over 10 years