University study highlights alarming rise in usage and costs of antidepressants
2021-06-03
(Press-News.org) RESEARCHERS at the University of Huddersfield have warned there is an urgent need for the country's mental health interventions to create strategies optimising the use of antidepressants after conducting a study which has highlighted an alarming rise in relation to usage and costs.
The open-access study, published by the international DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, is entitled 'Surging trends in prescriptions and costs of antidepressants in England amid COVID-19' and has investigated the trends in prescriptions and costs of various antidepressants in England during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The researchers discovered that the total number of antidepressant prescriptions drugs dispensed during 2020 had increased by four million items since 2019 costing NHS England £139 million more than in the previous year.
This is attributed to the active pharmaceutical ingredient shortages witnessed during COVID19 coupled with a significantly higher cost of generic drugs during the pandemic, with just one product alone sertraline, an SSRI antidepressant drug, accounting for a majority of the additional costs.
While an increase in the number of prescriptions had been predicted because of the pandemic, said the University's Dr Syed Shahzad Hasan, one of the co-authors of the study, it was the sharp rise in antidepressant prescription costs which was a potential cause for concern and highlighted the urgent need for mental health interventions in the country and strategies to optimise the use of antidepressants.
The study also observes a meta-analysis of 100,000 patients using antidepressants which concluded that the risk of suicide doubled in children and adolescents.
"These findings are particularly important in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic," said Dr Hamid Merchant from the University. "Observational data suggest that young adults, up to 25 years of age, were impacted by the mental health issues during the pandemic, and hence, were more likely to use antidepressants."
Recommendations
The research recommends that further studies are needed to assess the age distribution of antidepressant prescriptions particularly focusing on adolescents and young adults who are at a higher risk of experiencing life-threatening adverse effects.
"It is, therefore, important to optimise the safe use of antidepressants, particularly in young adults," added Dr Merchant. "Not only to help with mental health but also in preventing the associated side-effects that may further increase the morbidity and mortality associated with depression in younger adults."
INFORMATION:
The paper is co-authored by Shahad A. Rabeea, Dr Hamid A. Merchant & Dr Syed Shahzad Hasan from the University's Department of Pharmacy in the School of Applied Sciences, Muhammad Umair Khan from the Department of Pharmacy Practice at Pakistan's Ziauddin University and Chia Siang Know from the International Medical University in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
The study originated as part of a University Clinical Pharmacy Practice Masters' degree student project and it was when Dr Hamid Merchant and Dr Syed Shahzad Hasan noticed the results and preliminary findings that they decided to investigate the matter further.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-03
When bringing technologies into the workplace, it pays to be realistic. Often, for instance, bringing new digital technology into an organization does not radically improve a firm's operations. Despite high-level planning, a more frequent result is the messy process of frontline employees figuring out how they can get tech tools to help them to some degree.
That task can easily fall on overburdened workers who have to grapple with getting things done, but don't always have much voice in an organization. So isn't there a way to think systematically about implementing digital technology in the workplace?
MIT Professor Kate Kellogg thinks there is, and calls it "experimentalist governance of digital technology": Let different parts of an organization experiment with the technology -- ...
2021-06-03
A new study by ecologist André de Roos* shows that differences between juveniles and adults of the same species are crucial for the stability of complex ecological communities. The research, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, represents a major advance in ecological modeling at a time when biodiversity is declining and species around the world are rapidly going extinct.
Up to now, ecological models have focused exclusively on the interactions between species, ignoring the variations within them. The dragonflies, frogs, trout, and phytoplankton in a freshwater pond, for example, would be represented as nodes in a network, connected by edges that ...
2021-06-03
LAWRENCE -- A strange thing sometimes happens when we listen to a spoken phrase again and again: It begins to sound like a song.
This phenomenon, called the "speech-to-song illusion," can offer a window into how the mind operates and give insight into conditions that affect people's ability to communicate, like aphasia and aging people's decreased ability to recall words.
Now, researchers from the University of Kansas have published a study in PLOS ONE examining if the speech-to-song illusion happens in adults who are 55 or older as powerfully as it does with younger ...
2021-06-03
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) - An international team of researchers, led by END ...
2021-06-03
Alexandria, Va., USA -- Dental care professionals are thought to be at enhanced risk of occupational exposure to SARS-CoV-2, but robust data to support this is lacking. The study "COVID-19: Seroprevalence and Vaccine Responses in UK Dental Care Professionals," published in the Journal of Dental Research (JDR), provides a longitudinal analysis of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, including early analysis of the impact of vaccination on the immune response.
In June 2020, I,507 West Midlands dental care professionals were recruited to test for baseline seroprevalence, or the proportion of the population that have circulating antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, indicating prior ...
2021-06-03
Viruses can spread not only via droplets or aerosols like the new coronavirus, but in water, too. In fact, some potentially dangerous pathogens of gastrointestinal diseases are water-borne viruses.
To date, such viruses have been removed from water using nanofiltration or reverse osmosis, but at high cost and severe impact on the environment. For example, nanofilters for viruses are made of petroleum-based raw materials, while reverse osmosis requires a relatively large amount of energy.
Environmentally friendly membrane developed
Now an international team of researchers led by Raffaele ...
2021-06-03
People in both the United States and China who think others are being duped by online misinformation about COVID-19 are also more likely to support corporate and political efforts to address that misinformation, according to a new study. The study suggests negative emotions may also play a role in the U.S. - but not in China.
"A lot of misinformation has been shared online over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic, and we had a range of questions about how people are responding to this misinformation," says Yang Cheng, co-lead author of the study and an assistant professor of communication at North Carolina State University.
"How do different emotions influence ...
2021-06-03
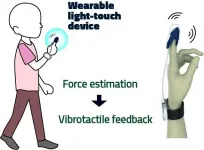
Japanese researchers have developed and tested a prototype device -- wearable on the fingertips -- that incorporates the concept of 'light touch' to enhance the sense of balance. If widely implemented, the device should significantly reduce incidence of falls amongst seniors.
The findings are published in the journal Scientific Reports on April 1.
As we age, our sense of balance can become impaired. The resulting increase in postural sway in turn increases the risk of falls and consequent injuries. Meanwhile, older people make up a large and increasing proportion of the population in highly developed countries. ...
2021-06-03
Research involving scientists from the University of A Coruña has succeeded in sequencing the oldest mitochondrial genome of the immediate ancestor of modern cows that has been analysed to date. The remains, some 9,000 years old, were found next to a woman. Why were they with her if cattle had not yet been domesticated? Do they belong to ancestors of today's Iberian cows?
Humans have maintained a very close relationship with aurochs (Bos primigenius) since their beginnings, first by hunting them and then by breeding and selecting them.
This extinct species of mammal is little known in the Peninsula because its skeletal remains are difficult to distinguish from bison. In fact, there have been references to the presence of "large bovids" in many sites because ...
2021-06-03
Interactions in the network can lower the critical temperature thresholds beyond which individual tipping elements begin destabilizing on the long-run, according to the study - the risk already increases significantly for warming of 1.5°C to 2°C, hence within the temperature range of the Paris Agreement.
"We provide a risk analysis, not a prediction, yet our findings still raise concern," says Ricarda Winkelmann, Lead of FutureLab on Earth Resilience in the Anthropocene at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK). "We find that the interaction of these four tipping elements can make them overall more vulnerable due to mutual destabilization on the long-run. The feedbacks between them tend to lower the critical temperature ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] University study highlights alarming rise in usage and costs of antidepressants