(Press-News.org) ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A study by researchers at Mayo Clinic Cancer Center has found that cancer patients diagnosed with COVID-19 who received care at home via remote patient monitoring were significantly less likely to require hospitalization for their illness, compared to cancer patients with COVID-19 who did not participate in the program. Results of the study were presented Friday, June 4, at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting and published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
"For our study, we evaluated 224 Mayo Clinic patients with cancer who were found to have COVID-19 through standardized screening prior to receiving cancer treatment, or due to symptoms or close exposure," says Tufia Haddad, M.D., a Mayo Clinic medical oncologist and the study's senior author. Researchers followed the patients March 18-July 31, 2020.
Dr. Haddad says that at the outset of the COVID-19 pandemic, Mayo Clinic rapidly developed and implemented a remote patient monitoring program to support Mayo Clinic patients who were diagnosed with COVID-19 and at risk for severe illness.
The program featured the use of in-home technology to monitor oxygen levels, vital signs and symptoms of COVID-19 infection, and a centralized virtual care team of nurses and physicians to manage patients. Dr. Haddad says the program had served more than 8,000 patients in rural and urban locations across 41 states by November 2020.
Researchers found that among patients who did not require urgent hospitalization at the time of their COVID-19 diagnosis, those whose care was managed by the remote patient monitoring program were significantly less likely to require hospitalization for their illness, compared with those who were not managed by the program.
"After balancing the two groups of patients who were or were not managed by the remote monitoring program for factors known to impact COVID-19 outcomes, such as old age, male gender and obesity, there was a 78% reduction in the risk of hospitalization (a 2.8% risk for patients on the remote monitoring program, compared to 13% for patients not on the program) attributed to the remote monitoring program," says Dr. Haddad.
In addition, Dr. Haddad says that when cancer patients who had been managed through the remote monitoring program were hospitalized, they experienced fewer hospitalizations of more than a week, ICU admissions and deaths.
"It is possible that our results were due to early detection of adverse symptoms and vital sign trends that enabled earlier care interventions to alter the trajectory of disease." Dr. Haddad is encouraged by the results, but she cautions that further research will be necessary to confirm them.
INFORMATION:
About Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit organization committed to innovation in clinical practice, education and research, and providing compassion, expertise and answers to everyone who needs healing. Visit the Mayo Clinic News Network for additional Mayo Clinic news. For information on COVID-19, including Mayo Clinic's Coronavirus Map tracking tool, which has 14-day forecasting on COVID-19 trends, visit the Mayo Clinic COVID-19 Resource Center.
Media contact:
Joe Dangor, Mayo Clinic Public Affairs, 507-284-5005, newsbureau@mayo.edu
While previous research early in the pandemic suggested that the vitamin D cuts the risk of contracting COVID-19, a new study from McGill University finds there is no genetic evidence that the vitamin works as a protective measure against the coronavirus.
"Vitamin D supplementation as a public health measure to improve outcomes is not supported by this study. Most importantly, our results suggest that investment in other therapeutic or preventative avenues should be prioritized for COVID-19 randomized clinical trials," say the authors.
To assess the relationship between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 ...
Effector and killer T cells are types of immune cells. Their job is to attack pathogens and cancers. These cells can also go after normal cells causing autoimmune diseases. But, if harnessed properly, they can destroy cancer cells that resist treatment.
Scientists at St. Jude wanted to understand how these T cells are controlled. They looked at enhancers, sequences of DNA that when bound to certain proteins determine how genes are turned on or off.
The scientists found that enhancers of a gene named Foxp3 work as a pair to keep effector and killer T cells in check. The enhancers working together is essential.
"These ...
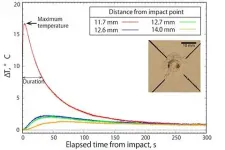
A research group from Kobe University has demonstrated that the heat generated by the impact of a small astronomical body could enable aqueous alteration (*1) and organic solid formation to occur on the surface of an asteroid. They achieved this by first conducting high-velocity impact cratering experiments using an asteroid-like target material and measuring the post-impact heat distribution around the resulting crater. From these results, they then established a rule-of-thumb for maximum temperature and the duration of the heating, and developed a heat ...
The melodic and diverse songs of birds frequently inspire pop songs and poems, and have been for centuries, all the way back to Shakespeare's "Romeo and Juliet" or "The Nightingale" by H.C. Andersen.
Despite our fascination with birdsong, we are only beginning to figure out how this complicated behavior is being produced and which extraordinary specializations enabled songbirds to develop the diverse sound scape we can listen to every morning.
Songbirds produce their beautiful songs using a special vocal organ unique to birds, the syrinx. It is surrounded by muscles that contract with superfast speed, two orders of magnitude faster than e.g. human leg muscles.
"We found that songbirds have incredible fine control of their song, including frequency ...
Philadelphia, June 4, 2021--ADHD medications may lower suicide risk in children with hyperactivity, oppositional defiance and other behavioral disorders, according to new research from the Lifespan Brain Institute (LiBI) of Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania. The findings, published today in JAMA Network Open, address a significant knowledge gap in childhood suicide risk and could inform suicide prevention strategies at a time when suicide among children is on the rise.
"This study is an important step in the much-needed effort of childhood suicide prevention, ...
What The Study Did: This survey study in California assesses what the public knows about extreme risk protection orders and if people are willing to use them to prevent firearm-related harm, both in general and when a family member is at risk, and if not, why not. The orders temporarily suspend firearm and ammunition access by individuals a judge has deemed to be at substantial risk of harming themselves or others.
Authors: Nicole Kravitz-Wirtz, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the University of California Davis School of Medicine in Sacramento, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.0975)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please ...
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- Extreme risk protection orders, also known as END ...
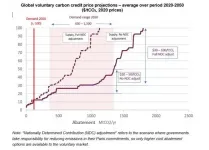
The cost of offsetting corporate carbon emissions needs to increase ten-fold to drive meaningful climate action, says a landmark report by Trove Research and UCL.
Current prices of carbon offsets are unsustainably low and need to increase significantly to encourage greater investment in new projects that remove carbon from the atmosphere.
If prices stay low companies could be accused of greenwashing their emissions, as real emissions reduction and carbon removals are more costly than today's prices.
Prices of carbon credits used by companies to offset their emissions are currently low, due to an excess of supply built up over several years, together with issues over whether payments for credits really result in additional reductions ...
Details:
Peripersonal space (PPS) is defined as the space near the body within which we can reach external objects and be reached by others. It has the special function of multisensory facilitation. A research team at Toyohashi University of Technology, in collaboration with researchers at Keio University and the University of Tokyo, investigated PPS representation in the front, rear, left, and right directions by audio-tactile multisensory integration using tactile detection with task-irrelevant approaching and receding sounds. They found that the tactile stimulus was detected faster near the body space than far from it when sound approached from any direction, but not when it receded. Thus, peripersonal representations exist with approaching sound, irrespective ...
Proteins are the key players in our cellular processes. Their generation follows principles called transcription and translation. First, DNA copies its genetic information to messenger RNA (mRNA), which then determines the sequence in a chain of amino acids, which finally fold into a protein. The reality, however, is more complex: More than 90 per cent of our genes do not result in only one mRNA and then one protein, but a process called alternative splicing produces several mRNA variants, only some of which are then translated into a specific protein isoform in a specific cell at a given time. Conventional techniques to detect alternative splicing are mostly single time-point measurements that are work-intense and cannot reliably ...