Postpartum mental health visits 30% higher during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-06-07
(Press-News.org) Mental health visits for new mothers were 30% higher during the COVID-19 pandemic than before the pandemic, particularly in the first 3 months after giving birth, found new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal). https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.210151
"Increased visit rates began in March 2020, although the state of emergency was declared only midway through the month, suggesting that distress related to the pandemic translated into an increased need for care very quickly," writes Dr. Simone Vigod, chief of psychiatry, senior scientist and interim vice president of academics at Women's College Hospital (WCH), and senior adjunct scientist at ICES in Toronto, Ontario, with coauthors.
Postpartum mental illness affects as many as 1 in 5 mothers and can have long-term effects on children and families if it becomes chronic.
Researchers looked at mental health visits by 137,609 people in Ontario during the postpartum period (from date of birth to 365 days after) from March through November 2020 and collected data on age, number of children, neighbour
hood income based on postal codes, neighbourhood ethnic diversity and region of residence based on the province's 34 public health units. They also divided the province into northern and southern public health units.
During the study period, mental health visits to both family physicians and psychiatrists were higher than before the pandemic, especially among parents with anxiety, depression, and alcohol and substance use disorders. People living in northern public health units had relatively low increases after July 2020, perhaps because of fewer COVID-19 restrictions in those areas during the latter period.
The way care was delivered during the pandemic period differed from the period before: 84.8% of postpartum mental health visits were conducted virtually in April 2020 compared with only 3.1% of visits in the prepandemic period.
The authors suggest that increased use of virtual care may have removed barriers to postpartum mental health support, such as the need to travel, find childcare for older children, or manage erratic schedules, enabling more people to seek care.
Patients in the lowest income neighbourhoods had the smallest increase in mental health visits compared with people in other neighbourhoods, which the authors noted with surprise.
"This raises some concern about the potential for unmet need because low-income patients may have greater barriers to accessing care, including difficulty affording the required technology or finding private space to attend virtual appointments (e.g., crowded homes), or less opportunity to attend "live" appointments because of employment in front-line jobs," write the authors.
They recommend targeted approaches to providing mental health supports.
"Health systems should focus proactively on patients from high-risk groups, monitor waiting lists for care, and explore creative solutions to expand system capacity, with special attention to postpartum patients who may be experiencing barriers to care," they advise.
INFORMATION:
"Postpartum mental illness during the COVID-19 pandemic: a population-based repeated cross-sectional study" is published June 7, 2021.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-07
New research indicates that patients hospitalized with active cancer were more likely to die from COVID-19 than those with a history of cancer or those without any cancer diagnosis. The findings published by END ...
2021-06-07
A traditional Vietnamese meat snack could hold the key to developing a safe and natural food preservative, addressing the twin global problems of food waste and food-borne illnesses.
Key Points
Bacteria-killing compound discovered in Nem Chua, a fermented pork snack
Toxic to bacteria but safe for humans, it's a natural alternative to artificial food preservatives
New study reveals ideal growth conditions to potentially make the bacteria-killer at industrial scales
The fermented pork snack, Nem Chua, is eaten raw but does not cause food poisoning when prepared correctly.
This is because friendly bacteria that thrive in the fermented meat make a special compound that destroys more dangerous bacteria.
Now ...
2021-06-07
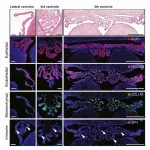
Once viewed merely as a producer of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) bathing the brain and spinal cord, the choroid plexus is now known to be a key player in brain development and immunity. These fronds of brain tissue, located in the CSF-filled brain cavities known as ventricles, secrete instructive cues into the CSF to regulate brain development. They also function as an important barrier between the brain and the rest of the body.
Maria Lehtinen, PhD, of Boston Children's Hospital has done much of the pioneering work in understanding this once-obscure tissue. In new work published in Cell, Lehtinen, Neil Dani, PhD, and other colleagues at Boston Children's and the Broad Institute created ...
2021-06-07
The friendship paradox is the observation that the degrees of the neighbors of a node within any network will, on average, be greater than the degree of the node itself. In other words: your friends probably have more friends than you do.
While the standard framing of the friendship paradox is essentially about averages, significant variations occur too.
In the Journal of Complex Networks, Santa Fe Institute and University of Michigan researchers George Cantwell, Alec Kirkley, and Mark Newman address this by developing the mathematical theory ...
2021-06-07
Carried like stowaways in the guts of international travelers, new and potentially deadly strains of antimicrobial resistant superbugs may be coming to a community near you, suggests new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
"Even before the COVID-19 pandemic, we knew that international travel was contributing to the rapid global increase and spread of antimicrobial resistance," said Alaric D'Souza, an MD/PhD student at Washington University and a co-first author of the study to be published June 6 in Genome Medicine. "But what's new here is that we've found numerous completely novel genes associated with antimicrobial ...
2021-06-07
Climate experts warn that, without urgent action, climate change will continue to cause an increase in the intensity of extreme rainfall that can lead to severe flooding.
An international research team have concluded that increases in extreme rainfall and associated flooding are projected to continue as global temperatures continue to rise. Efforts to limit warming to +1.5C will help limit changes in extreme rainfall, though some societal adaptations will still be required.
Sharing their findings in a new ScienceBrief Review, published today (7 June), scientists ...
2021-06-06
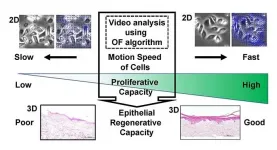
Niigata, Japan - A comprehensive investigation on cells and colony motion offers new insight into the proliferative and epithelial regenerative capacities of human primary oral keratinocyte cultures with implications for quality control of engineered cells used in regenerative medicine. Dr. Kenji Izumi and his colleagues, Dr. Emi Hoshikawa and Dr. Taisuke Sato, modified the optical flow (OF) protocol originally presented in their 2019 paper to add the capacity to determine the threshold of the cells/colony motion speed required to differentiate substandard oral keratinocyte populations before manufacturing a tissue-engineered oral mucosa tissue construct. ...
2021-06-06
The world is one step closer to ultimately secure conference calls, thanks to a collaboration between Quantum Communications Hub researchers and their German colleagues, enabling a quantum-secure conversation to take place between four parties simultaneously.
The demonstration, led by Hub researchers based at Heriot-Watt University and published in Science Advances, is a timely advance, given the global reliance on remote collaborative working, including conference calls, since the start of the C19 pandemic.
There have been reports of significant escalation of cyber-attacks on popular teleconferencing platforms in the last year. This advance in quantum secured communications could lead to conference calls with inherent unhackable security measures, underpinned by the principles of ...
2021-06-05
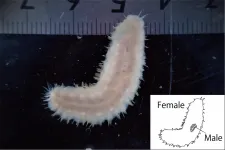
In the Kumano Sea, off the southeast coast of Japan, an evolutionary mystery lay in wait. Researchers collected samples from the muddy sea floor, including hermit crabs, mollusks and discarded shells. Here, in and on these shells, they found scale worms living mostly in pairs with a striking difference compared to the almost 900 already known species of scale worms: one was a quarter the size of its mate.
The discovery was published on March 29 as the cover of the Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research.
"The species is characterized by males being dwarf, with their minute bodies always riding on the dorsal side of females," said paper author Naoto Jimi, postdoctoral researcher at the National Institute of Polar Research, Research ...
2021-06-05
(Geneva, 5 June 2021) Mass screening of school age children has led to significantly higher numbers of coeliac disease cases being diagnosed, according to a new study presented today at the 6th World Congress of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition.
Researchers in Italy found double the number of cases of the autoimmune disease - where the body produces antibodies to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye - in school children compared to a similar study by the same group 25 years ago.
A new screening programme of 7,760 children aged from five ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Postpartum mental health visits 30% higher during COVID-19 pandemic