Bioinspired acid-catalyzed C2 prenylation of indole derivatives
2021-06-07
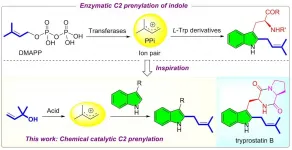
(Press-News.org) Terpenoids are omnipresent in almost all living organisms. Prenylated indoles are prominent representatives that usually display potent medicinal properties (e.g. tryprostatin B). Therefore, significant efforts have been devoted to indole prenylation over the past decades. The known protocols often require a multi-step procedure and rely on the use of stoichiometric promoters. From the viewpoint of step- and atom-economy, developing a direct catalytic C2 prenylation of indoles is highly desirable yet challenging, because the nucleophilicity of C2 site is weaker than that of other two positions (N, C3).
In biosynthesis, enzymatic indole prenylation proceeds through a Friedel-Crafts SN1-type alkylation with a prenyl cation-pyrophosphate ion (PPi) derived from dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP). Inspired by this mechanism, recently, a team led by Prof. Qing-An CHEN from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed a regioselective C2 prenylation of indoles enabled by Lewis acid catalysis. By employing cheap 2-methyl-3-buten-2-ol (tert-prenol) as precursor and Lewis acid AlCl3 as catalyst, various tryptophol and tryptamine derivatives can undergo C2 prenylation with high selectivity. Notably, this practical strategy can be applied to the late-stage diversification of tryptophan-based peptides. These results were published in Chinese Journal of Catalysis.
Prof. CHEN stated: "Our work represents an old reaction for new use. For anyone engaged in chemistry, it is difficult to imagine that tryptophol and tryptophan-based peptides can undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction with high selectivity, because of the presence of diverse free NH and OH. More importantly, this strategy can greatly shorten the synthesis of indole alkaloid tryprostatin B."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21801239, 22071239).
About the Journal
Chinese Journal of Catalysis is co-sponsored by Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Chemical Society, and it is currently published by Elsevier group. This monthly journal publishes in English timely contributions of original and rigorously reviewed manuscripts covering all areas of catalysis. The journal publishes Reviews, Accounts, Communications, Articles, Highlights, Perspectives, and Viewpoints of highly scientific values that help understanding and defining of new concepts in both fundamental issues and practical applications of catalysis. Chinese Journal of Catalysis ranks among the top six journals in Applied Chemistry with a current SCI impact factor of 6.146. The Editors-in-Chief are Profs. Can Li and Tao Zhang.
At Elsevier http://www.journals.elsevier.com/chinese-journal-of-catalysis
Manuscript submission https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/cjcatal
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-07
Consuming large amounts of daily caffeine may increase the risk of glaucoma more than three-fold for those with a genetic predisposition to higher eye pressure according to an international, multi-center study. The research led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is the first to demonstrate a dietary - genetic interaction in glaucoma. The study results published in the June print issue of Ophthalmology may suggest patients with a strong family history of glaucoma should cut down on caffeine intake.
The study is important because glaucoma is the leading cause of blindness in the United States. It looks at the impact of caffeine intake on glaucoma, ...
2021-06-07
Research Highlights:
Rates of Kawasaki disease - a condition that creates inflammation in blood vessels in the heart and is more common in children of Asian/Pacific Island descent - have substantially decreased in South Korea during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The decrease could be due to mask-wearing, hand-washing, school closures and physical distancing, suggesting Kawasaki disease may be prompted by infectious agents.
The cause of Kawasaki disease is unknown, though it may be an immune response to acute infectious illness.
DALLAS, June 7, 2021 -- The rate of Kawasaki disease in South Korea has substantially decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic, possibly due to pandemic prevention efforts, such as mask-wearing, ...
2021-06-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- MIT engineers have discovered a new way of generating electricity using tiny carbon particles that can create a current simply by interacting with liquid surrounding them.
The liquid, an organic solvent, draws electrons out of the particles, generating a current that could be used to drive chemical reactions or to power micro- or nanoscale robots, the researchers say.
"This mechanism is new, and this way of generating energy is completely new," says Michael Strano, the Carbon P. Dubbs Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT. "This technology is intriguing because all you have to do is flow a solvent through a bed of these particles. ...
2021-06-07
Many modern fitness trackers and smartwatches feature integrated LEDs. The green light emitted, whether continuous or pulsed, penetrates the skin and can be used to measure the wearer's heart rate during physical activity or while at rest.
These watches have become extremely popular. A team of ETH researchers now wants to capitalise on that popularity by using the LEDs to control genes and change the behaviour of cells through the skin. The team is led by Martin Fussenegger from the Department of Biosystems Science and Engineering in Basel. He explains the challenge to this undertaking: "No naturally occurring molecular ...
2021-06-07
Levels of a protein called neurofilament light chain (NfL) in the blood can identify those who might have neurodegenerative diseases such as Down's syndrome dementia, motor neuron disease (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia, when clinical symptoms are not definitive.
Published in Nature Communications and part-funded by the NIHR Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre, the research determined a set of age-related cut-off levels of NfL which could inform its potential use in primary care settings through a simple blood test.
Joint Senior Author on the study, Dr Abdul Hye from the NIHR Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre at King's College London and South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust said: 'For the first time we have shown ...
2021-06-07
The first double-blind experiment analysing the role of human decision-making in climate reconstructions has found that it can lead to substantially different results.
The experiment, designed and run by researchers from the University of Cambridge, had multiple research groups from around the world use the same raw tree-ring data to reconstruct temperature changes over the past 2,000 years.
While each of the reconstructions clearly showed that recent warming due to anthropogenic climate change is unprecedented in the past two thousand years, there were notable differences in variance, amplitude and sensitivity, ...
2021-06-07
NEW YORK, June 7, 2021--Recent studies suggest that new brain cells are being formed every day in response to injury, physical exercise, and mental stimulation. Glial cells, and in particular the ones called oligodendrocyte progenitors, are highly responsive to external signals and injuries. They can detect changes in the nervous system and form new myelin, which wraps around nerves and provides metabolic support and accurate transmission of electrical signals. As we age, however, less myelin is formed in response to external signals, and this progressive decline has been linked to the age-related cognitive and motor deficits detected in older people in the general population. Impaired ...
2021-06-07
Just a few bacterial taxa found in ecosystems across the planet are responsible for more than half of carbon cycling in soils. These new findings, made by researchers at Northern Arizona University and published in END ...
2021-06-07
In a white ocean, well above sea level, the algae thrive. Normally invisible to the naked eye, they are often spotted by hikers trekking through the mountains in late spring as strikingly coloured stretches of snow, in shades of ochre, orange and red. Known as "glacier blood", this colouring is the result of the punctual multiplication (or bloom) of the microalgae that inhabit the snow.
But apart from this impressive phenomenon, the life and organisation of mountain microalgae communities remains a secret. It is this still unknown ecosystem, now threatened by global warming, that needs to be explored. The ALPALGA* consortium aims to meet this challenge by organising and pooling research efforts on snow microalgae, and it has already received support from the Agence nationale ...
2021-06-07
Mental health visits for new mothers were 30% higher during the COVID-19 pandemic than before the pandemic, particularly in the first 3 months after giving birth, found new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal). https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.210151
"Increased visit rates began in March 2020, although the state of emergency was declared only midway through the month, suggesting that distress related to the pandemic translated into an increased need for care very quickly," writes Dr. Simone Vigod, chief of psychiatry, senior scientist and interim vice president of academics at Women's College Hospital (WCH), and senior adjunct scientist at ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Bioinspired acid-catalyzed C2 prenylation of indole derivatives