INFORMATION:
This research received funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, project support by the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project, Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader, 'Shu Guang' project supported by Shanghai Municipal Education Commission and Shanghai Education Development Foundation.
See the article:
Siyu Sun, Liangwei Ma, Jie Wang, Xiang Ma,* and He Tian.
Red-light excited efficient metal-free near-infrared room-temperature phosphorescent films.
Natl Sci Rev nwab085.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwab085
Efficient metal-free near-infrared phosphorescence films
2021-06-07
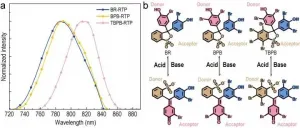
(Press-News.org) The fluorescence dyes were dominant species of the near-infrared (NIR) dyes, but the energy gap of the NIR dyes between S1 state and S0 state is generally small to induce the ultrafast internal conversion dynamics to quench the NIR emission of the fluorescence dyes. Therefore, the quantum yield of the fluorescence NIR dyes is usually low. On the other hand, the organic dyes with room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) in the NIR region could prevent the ultrafast internal conversion dynamics quenching because of the T1 state and S0 state the organic molecules are spin forbidden.
Recently, scientists in China reported a new assumption to construct efficient NIR materials based on the energy gap law on the National Science Review. In addition, a series of metal-free RTP films with NIR emission was constructed based on the assumption, and the first phosphorescence-based half-subtractor operation was also developed based on the stimuli-responsive properties of the dyes.
It could be an available strategy to construct efficient metal-free NIR materials by controlling the external environments of the organic molecules with red-light fluorescence to inhibit the non-radiation decay of the light-emitting molecules. The short lifetimes of the triplet state of the NIR RTP molecules could benefit their NIR emission because the other non-radiation decay processes of the long-lifetime triplet state of the NIR RTP molecules could offset the spin forbidden benefit factor of the IC to quench the NIR emission. This assumption could lower the threshold of the construction of the metal-free NIR materials. Therefore, phenolsulfonphthalein dyes with red-light emission (BR, BPB, TBPB) were chosen as NIR emitters in this research to demonstrate this assumption and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) were chosen as rigid matrixes to inhibit the non-radiation relaxation process. In conclusion, all phenolsulfonphthalein dyes emitted moderate NIR RTP in the PVA matrix, where TBPB@PVA films shown the best performance (ΦRTP = 3.0%, λp = 819 nm). This research preliminary proved that the spin forbidden IC process of the T state and the ground state of the organic molecules could be favorable to construct effective NIR dyes, and this assumption might provide a new train of thought for the development of the organic materials with NIR emission.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
84% of the Spanish population is in favor of the government investing in science
2021-06-07
The Spanish Foundation for Science and Technology (FECYT) has presented this week at the headquarters of the National Science and Technology Museum in Madrid the main results of the 10th Social Perception of Science Survey carried out in 2020.
The presentation was attended by Pedro Duque, Minister of Science and Innovation, Josep Lobera, Professor of Sociology at the Autonomous University of Madrid (UAM) and scientific co-director of the Survey and the subsequent study, and Rosa Capeáns, Director of the Scientific Culture and Innovation Department of FECYT. Pampa García, Editor-in-Chief of the SINC Agency, moderated a debate in which the results were presented in six blocks: Interest in ...
Regulation of protein homeostasis by cardiac glycosides
2021-06-07
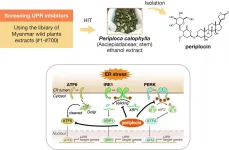
In the present study, Dr. Hidetoshi Hayashi (Professor, Nagoya City University) and collaborators screened small-molecule compounds that suppress UPR, using Myanmar wild plant extracts library. The screening system to track X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) splicing activity revealed that the ethanol extract of the Periploca calophylla stem inhibited the inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1)-XBP1 pathway. They isolated and identified periplocin as a potent inhibitor of the IRE1-XBP1 axis. Periplocin also suppressed other UPR axes, protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), and activating transcription ...
Nucleosome breathing from atomistic time snapshots
2021-06-07
Researchers from the Hubrecht Institute in Utrecht (The Netherlands) and the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine in Münster (Germany) used computer simulations to reveal in atomic detail how a short piece of DNA opens while it is tightly wrapped around the proteins that package our genome. These simulations provide unprecedented insights into the mechanisms that regulate gene expression. The results were published in PLOS Computational Biology on the 3rd of June, 2021.
Every cell in the body contains two meters of DNA. In order to fit all the DNA ...
Healthy environment, healthy kidneys!
2021-06-07
Health has always been affected by climate and weather, but is increasingly clear that the change in climate is a significant threat to human health. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 24% of global deaths are linked to environmental factors [1]. Climate change and pollution can lead to undernutrition, mental disorders, and noncommunicable diseases including chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury [2].
The burden of addressing the death and disability associated with climate change falls to nephrologists and other healthcare professionals. At the same time, the healthcare sector makes a major ...
Mechanisms of kidney protection by gliflozins
2021-06-07
SGLT2 inhibitors (gliflozins) were developed as oral antidiabetics. They enhance urinary glucose excretion by inhibiting SGLT-2 (sodium-dependent glucose co-transporter-2) in the renal tubuli. The discovery of kidney benefits beyond the lowering of blood sugar has been made by Professor Christoph Wanner from Germany: The EMPA-REG OUTCOME study [2] initially showed that the rate of cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetic pa-tients is significantly reduced if the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin is administered. Kidney function in diabetics who already had diabetic nephropathy was also found to benefit sig-nificantly from the treatment ...
Popularity runs in families
2021-06-07
HOUSTON - (June 7, 2021) - If identical versions of 20 people lived out their lives in dozens of different worlds, would the same people be popular in each world?
If you substitute "fruit flies" for "people" in that question, you have a fair description of a Rice University study showing that the evolution of social structures and the positions of individuals within those structures are based partly on genetics.
Cloned fruit flies played a starring role in the study that researchers jokingly likened to "The Truman Show," with video cameras observing how the flies behaved in a controlled environment.
In the study published online this week in Nature Communications, Rice bioscientists Eric Wice and Julia Saltz ...
COVID-19: Long-term consequences for the kidneys can be expected
2021-06-07
The kidneys are a target organ of COVID-19 and are affected very early in the course. However, this is precisely where there is strong prognostic potential: As early as last spring, COVID-19-associated nephritis was identified as an early warning signal for severe courses of the infectious disease and studies to that effect were published [1]. In that regard, the research group led by Professor Oliver Gross, Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology at Göttingen University Medical Center (UMG), screened 223 patients in a study and included 145 of them as a predictive cohort. Study endpoints were ICU admission or mortality. As a result, early urinary changes ...
COVID-19 as systemic disease: What does that mean for kidneys?
2021-06-07
It was clear at a relatively early stage of the pandemic that SARS-CoV-2 causes a wide range of symptoms; in addition to typical respiratory symptoms, patients also had neurological symptoms (starting with anosmia), gastrointestinal symptoms, elevated liver values, and renal, urinary or hematological changes, for example. The fact that such findings occurred not only in severely ill patients with general organ dysfunction suggested that the virus may potentially cause disorders in various organs directly, i.e. that it causes a multi-system disease.
In spring 2020, at the very beginning of the pandemic, the authorities in Hamburg ordered autopsies be performed on all patients who had died with COVID-19. This resulted in one of the ...
Targeted COVID-19 therapy: What can we learn from autoimmune kidney diseases?
2021-06-07
Various viruses and bacteria have long been known to cause autoimmune diseases where there is such a predisposition. This phenomenon also seems to play a major role in SARS-CoV-2, especially in severe courses. The body's own immune cells are activated, with the formation of autoantibodies that attack the body's own healthy cell structures (proteins, autoantigens); deposits of immune complexes can then trigger severe inflammatory processes and cell destruction in the body.
Some nephrological diseases are likewise of autoimmunological etiology, one example being systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a chronic, mostly relapsing-remitting inflammatory disease with life-threatening ...
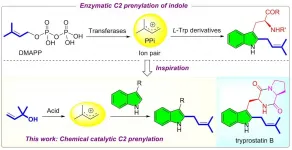
Bioinspired acid-catalyzed C2 prenylation of indole derivatives
2021-06-07
Terpenoids are omnipresent in almost all living organisms. Prenylated indoles are prominent representatives that usually display potent medicinal properties (e.g. tryprostatin B). Therefore, significant efforts have been devoted to indole prenylation over the past decades. The known protocols often require a multi-step procedure and rely on the use of stoichiometric promoters. From the viewpoint of step- and atom-economy, developing a direct catalytic C2 prenylation of indoles is highly desirable yet challenging, because the nucleophilicity of C2 site is weaker than that of other two positions ...