(Press-News.org) When we inhale isolated coronavirus particles, more than 65% reach the deepest region of our lungs where damage to cells can lead to low blood oxygen levels, new research has discovered, and more of these aerosols reach the right lung than the left.
Lead author of the study Dr Saidul Islam, from the University of Technology Sydney, said while previous research has revealed how virus aerosols travel through the upper airways including the nose, mouth and throat - this study was the first to examine how they flow through the lower lungs.
"Our lungs resemble tree branches that divide up to 23 times into smaller and smaller branches. Due to the complexity of this geometry it is difficult to develop a computer simulation, however we were able to model what happens in the first 17 generations, or branches, of the airways," said Dr Islam.
"Depending on our breathing rate, between 32% and 35% of viral particles are deposited in these first 17 branches. This means around 65% of virus particles escape to the deepest regions of our lungs, which includes the alveoli or air sacs," he said.
The alveolar system is critical to our ability to absorb oxygen, so significant amounts of virus in this region, along with inflammation caused by our body's immune response, can cause severe damage, reducing the amount of oxygen in the blood and increasing the risk of death.
The study also revealed that more virus particles are deposited in the right lung, especially the right upper lobe and the right lower lobe, than in the left lung. This is due to the highly asymmetrical anatomical structure of the lungs and the way air flows through the different lobes.
The research is backed up by a recent study of chest CT scans of COVID-19 patients showing greater infection and disease in the regions predicted by the model.
The researchers modelled three different flow rates - 7.5, 15 and 30 litres per minute. The model showed greater virus deposition at lower flow rates.
As well as improving our understanding of coronavirus transmission, the findings have implications for the development of targeted drug delivery devices that can deliver medicine to the areas of the respiratory system most affected by the virus.
"Normally when we inhale drugs from a drug delivery device most of it is deposited in the upper airways, and only a minimum amount of drugs can reach the targeted position of the lower airways. However, with diseases like COVID-19 we need to target the areas most affected," said Dr Islam.
"We are working to develop devices that can target specific regions, and we also hope to build age and patient specific whole lung models to increase understanding of how SARS CoV-2 aerosols affect individual patients," said co-author and group leader of the UTS Computer Simulations and Modelling group, Dr Suvash Saha.
The World Health Organisation recently updated its advice about the importance of aerosol transmission, warning that because aerosols can remain suspended in the air, crowded indoor settings and areas with poor ventilation pose a significant risk for transmission of Covid-19.
"When we use an aerosol deodorant, the smallest particles of that liquid fall on us under extreme pressure in the form of gas. Similarly, when an infected person speaks, sings, sneezes or coughs, the virus is spread through the air and can infect those nearby," said Dr Saha.
The study has further applications, with researchers using portable devices to examine air quality - including PM2.5 and PM10 concentration and gasses such as carbon dioxide, formaldehyde and sulphur dioxide - in spaces such as train carriages. The researchers can then use this data to model the impact on our lungs.
The study, SARS CoV-2 aerosol: How far it can travel to the lower airways, was recently published in the journal Physics of Fluids.
INFORMATION:
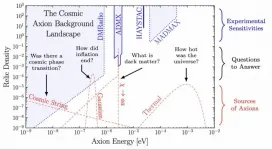
Finding the hypothetical particle axion could mean finding out for the first time what happened in the Universe a second after the Big Bang, suggests a new study published in Physical Review D on June 7.
How far back into the Universe's past can we look today? In the electromagnetic spectrum, observations of the Cosmic Microwave Background -- commonly referred to as the CMB -- allow us to see back almost 14 billion years to when the Universe cooled sufficiently for protons and electrons to combine and form neutral hydrogen. The CMB has taught us an inordinate amount about the evolution of the cosmos, but photons in the CMB were released 400,000 years after the Big Bang making it extremely challenging to learn about the history of ...
TAMPA, Fla. (June 4, 2021) — Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease in which a misdirected immune system gradually destroys healthy pancreatic islet β cells, resulting in a lack of insulin. The exact cause of T1D remains unknown. However, β cell-reactive autoantibodies can be detected in circulating blood months to years before diagnosis, raising the possibility of intervening to stop or delay T1D before children develop the disease.
Monitoring the number, type, and concentration of autoantibodies appearing in the blood can help predict the long-term risk of progression from autoimmunity to symptomatic T1D.
Now new findings suggest that measuring how patterns ...
A research team from the University of Copenhagen and University of Helsinki demonstrates it is possible to predict individual preferences based on how a person's brain responses match up to others. This could potentially be used to provide individually-tailored media content -- and perhaps even to enlighten us about ourselves.
We have become accustomed to online algorithms trying to guess our preferences for everything from movies and music to news and shopping. This is based not only on what we have searched for, looked at, or listened to, but also on how these activities compare to others. Collaborative filtering, as the technique is called, uses hidden ...
A team of astronomers from the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA-TIFR) in Pune, and the Raman Research Institute (RRI), in Bangalore, has used the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) to measure the atomic hydrogen gas content of galaxies 9 billion years ago, in the young universe. This is the earliest epoch in the universe for which there is a measurement of the atomic hydrogen content of galaxies. The new result is a crucial confirmation of the group's earlier result, where they had measured the atomic hydrogen content of galaxies 8 billion years ago, and pushes our understanding of galaxies to even earlier in the universe. ...
Decades of research has revealed the remarkable morphological adaptations of sea snakes to aquatic life, which include paddle-shaped tails, salt-excreting glands, and the ability to breathe through their skin.
In a new study published in Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, researchers at the University of Adelaide detail the enlarged touch receptors that evolved in male turtle-headed sea snakes (Emydocephalus annulatus), to help them locate and court females in aquatic environments.
Lead author, Jenna Crowe-Riddell, PhD graduate at the University of Adelaide's School of Biological Sciences, says on land, snakes use tongue-flicking ...
Older people need digital skills training to learn to use digital technology more independently, but they also seek digital training opportunities because of the social benefits they offer, according to a recent study from the University of Eastern Finland. Published in International Journal of Lifelong Education, the study examined perceived benefits of digital skills training among older adult learners, their teachers and peer tutors. Data for the study were collected in liberal adult education organisations, such as community colleges, as well as in peer tutoring sessions organised by third sector actors.
New skills and friendships
The coronavirus pandemic has, for its part, highlighted inequalities in the availability and ...
The Amami, Okinawa region of Japan may be designated a World Heritage Site in July of 2021 based on the recent recommendation from the IUCN. The Iriomote wild cat is a symbolic species of the region, having evolved independently on the island. The area is home to many other highly endemic and unique evolutionary species. A research group comprised mostly of former students of Professor Koji Tojo's Faculty of Science lab of Shinshu University focused on the study of dragonflies, continuing from their previous study of their comparative embryogenesis. About 5,000 species of insects belonging to 26 families of the order Dragonfly are known ...
A long-standing basic question in biology relates to how life satisfies the fundamental constraints put on it by physics and chemistry. Darwin's warm pond hypothesis for the origin of primordial cells is a familiar one. Advances have been made in mapping out the organic molecules that likely existed on the early Earth, and recently candidate prototypic pathways in early cells have been formulated. But how did these candidates' early biochemistry actually function as a system, on which subsequent cellular life is based?
A team of bioengineers at the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Biosustainability, DTU, has now defined ten overarching classes of constraints on early metabolic ...
A minimally-invasive procedure that targets the nerves near the kidney has been found to significantly reduce blood pressure in hypertension patients, according to the results of a global multicentre clinical trial led in the UK by researchers at Queen Mary University of London and Barts Health NHS Trust.
The study, published in The Lancet and presented at the American College of Cardiology meeting, suggests that the procedure could offer hope to patients with high blood pressure who do not respond to recommended treatments (resistant hypertension), and are at greatly increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke and heart attack.
The international clinical trial tested a one-hour procedure called 'renal denervation', which uses ultrasound energy to ...
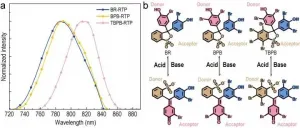
The fluorescence dyes were dominant species of the near-infrared (NIR) dyes, but the energy gap of the NIR dyes between S1 state and S0 state is generally small to induce the ultrafast internal conversion dynamics to quench the NIR emission of the fluorescence dyes. Therefore, the quantum yield of the fluorescence NIR dyes is usually low. On the other hand, the organic dyes with room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) in the NIR region could prevent the ultrafast internal conversion dynamics quenching because of the T1 state and S0 state the organic molecules are spin forbidden.
Recently, scientists in China reported a new assumption to construct ...