(Press-News.org) Wider clean chemistry applications of the extraordinary Vortex Fluidic Device - invented by Flinders University's Professor Colin Raston - are likely in the wake of new research that has been published outlining the seemingly endless possible uses.
The defining paper on understanding fluid flow in the Vortex Fluidic Device has just been comprehensively explained in an article published in Nanoscale Advances (DOI: 10.1039/D1NA00195G).
This took more than 100,000 experiments to work out - and Professor Raston hopes this publication will encourage more researchers to embrace the VFD and explore yet more innovative applications for this ingenious device.
"How fluid flows is one of the grand challenges of science," says Professor Raston. "What we have been doing with the VFD provides answers for liquids subjected to mechanical energy."
Since 2013, Professor Raston has been working with his team to explore the possibilities of the VFD, which is capable of controlling chemical reactivity, materials processing and probing the structure of self-organised systems, enabling rapid and now predictable modifications.
The VFD has shown its capability in the synthesis of esters, amides, ureas, imines, alpha-amino phosphates, beta-Keto esters, modified amino acids and the local anaesthetic, lidocaine.
Professor Raston says the high-tech, yet simple device can be used in medical and pharmaceutical research, food processing, materials processing and more, aligned with a range of industries - all with a focus on cleaner, greener and cheaper production - and he hopes that the new conclusive summaries about the VFD experiments will see it embraced by more research organisations around the world, and be taken up by industry.
"The topological fluid flows, which were established as 'spinning top' flow, double helical flow and specular flow, account for all the processing outcomes and applications of the VFD - this is an exciting discovery," says Professor Raston.
"We have established the topological features of high shear fluid flow in the vortex fluidic device at sub-micron dimensions, at a critical tilt angle of 45 degrees, being the optimal angle for myriad applications of the device."
The proposed flow patterns in the VFD provide insights that allow accurate prediction and control the formation of nanostructures in the VFD and chemical reactions. The flow patterns also provide an understanding of the advantages of VFD processing relative to using other methods, showing the VFD processing to be without precedent.
As the latest example of green chemistry innovation, PhD candidate Matt Jellicoe has led research into using the VFD to control the coating of particles without using other waste generating reagents.
The paper - High shear spheroidal topological fluid flow induced coating of polystyrene beads with C60 spicules, by Matt Jellicoe, Kasturi Vimalanathan, Jason Gascooke, Xuan Luo and Colin Raston, has been published by Royal Society of Chemistry's ChemComm (10.1039/d0cc07165j).
"I believe the outcome of this research to be significant because we demonstrate the coating of particles 2-6 microns in diameter with zero waste and up to 98% efficiency. This could be beneficial towards the pharmaceutical companies which coat drugs with significant lower yield, thus leading to run off of dangerous chemicals into freshwater streams and the air," says Mr Jellicoe.
He expects the next stage of testing will investigate the possibility of using the VFD as a drug-coating device.
"This may significantly reduce the effects on the environment," says Mr Jellicoe, "and this is what excites me the most. The potential impact, especially on the environment and the economy, could be unfathomable."
INFORMATION:
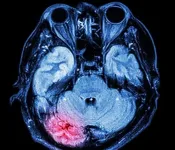
A world-first international study led by the University of South Australia has identified a new drug to stop athletes developing dementia after sustaining repeated head injuries in their career.
The link between concussion and neurogenerative diseases is well established, but new research findings could halt the progression of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) in sportspeople who sustain repeated blows to the head.
CTE is a progressive and fatal brain disease associated with the accumulation of a protein known as hyperphosphorylated tau which affects cognition and behaviour.
In a paper published in Scientific Reports, ...
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - June 7, 2021 - A preclinical study led by scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys has established that AAV8-TNAP-D10--a gene therapy that replaces a key enzyme found in bone--may be a safe and effective single-dose treatment for hypophosphatasia (HPP). The study, published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research and performed in a murine model of the disease, further supports advancing the therapy toward human clinical trials.
"This is the most promising gene therapy study to date demonstrating a successful increase in life span, and improvement ...
Monash University researchers have provided a fundamental advance regarding how T cells become activated when encountering pathogens such as viruses.
The recent study published in Science, co-led by Professor Nicole La Gruta, Professor Jamie Rossjohn and Professor Stephanie Gras with first author Dr Pirooz Zareie from the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute, have found that T Cells need to recognise pathogens in a particular orientation in order to receive a strong activating signal.
T cells play a key role in the immune system by eliminating invading pathogens, such as viruses, and it is crucial to understand ...
When we inhale isolated coronavirus particles, more than 65% reach the deepest region of our lungs where damage to cells can lead to low blood oxygen levels, new research has discovered, and more of these aerosols reach the right lung than the left.
Lead author of the study Dr Saidul Islam, from the University of Technology Sydney, said while previous research has revealed how virus aerosols travel through the upper airways including the nose, mouth and throat - this study was the first to examine how they flow through the lower lungs.
"Our ...
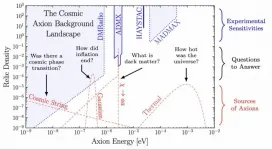
Finding the hypothetical particle axion could mean finding out for the first time what happened in the Universe a second after the Big Bang, suggests a new study published in Physical Review D on June 7.
How far back into the Universe's past can we look today? In the electromagnetic spectrum, observations of the Cosmic Microwave Background -- commonly referred to as the CMB -- allow us to see back almost 14 billion years to when the Universe cooled sufficiently for protons and electrons to combine and form neutral hydrogen. The CMB has taught us an inordinate amount about the evolution of the cosmos, but photons in the CMB were released 400,000 years after the Big Bang making it extremely challenging to learn about the history of ...
TAMPA, Fla. (June 4, 2021) — Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease in which a misdirected immune system gradually destroys healthy pancreatic islet β cells, resulting in a lack of insulin. The exact cause of T1D remains unknown. However, β cell-reactive autoantibodies can be detected in circulating blood months to years before diagnosis, raising the possibility of intervening to stop or delay T1D before children develop the disease.
Monitoring the number, type, and concentration of autoantibodies appearing in the blood can help predict the long-term risk of progression from autoimmunity to symptomatic T1D.
Now new findings suggest that measuring how patterns ...
A research team from the University of Copenhagen and University of Helsinki demonstrates it is possible to predict individual preferences based on how a person's brain responses match up to others. This could potentially be used to provide individually-tailored media content -- and perhaps even to enlighten us about ourselves.
We have become accustomed to online algorithms trying to guess our preferences for everything from movies and music to news and shopping. This is based not only on what we have searched for, looked at, or listened to, but also on how these activities compare to others. Collaborative filtering, as the technique is called, uses hidden ...
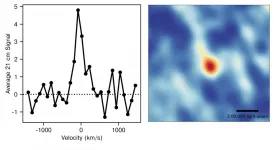
A team of astronomers from the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA-TIFR) in Pune, and the Raman Research Institute (RRI), in Bangalore, has used the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) to measure the atomic hydrogen gas content of galaxies 9 billion years ago, in the young universe. This is the earliest epoch in the universe for which there is a measurement of the atomic hydrogen content of galaxies. The new result is a crucial confirmation of the group's earlier result, where they had measured the atomic hydrogen content of galaxies 8 billion years ago, and pushes our understanding of galaxies to even earlier in the universe. ...
Decades of research has revealed the remarkable morphological adaptations of sea snakes to aquatic life, which include paddle-shaped tails, salt-excreting glands, and the ability to breathe through their skin.
In a new study published in Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, researchers at the University of Adelaide detail the enlarged touch receptors that evolved in male turtle-headed sea snakes (Emydocephalus annulatus), to help them locate and court females in aquatic environments.
Lead author, Jenna Crowe-Riddell, PhD graduate at the University of Adelaide's School of Biological Sciences, says on land, snakes use tongue-flicking ...
Older people need digital skills training to learn to use digital technology more independently, but they also seek digital training opportunities because of the social benefits they offer, according to a recent study from the University of Eastern Finland. Published in International Journal of Lifelong Education, the study examined perceived benefits of digital skills training among older adult learners, their teachers and peer tutors. Data for the study were collected in liberal adult education organisations, such as community colleges, as well as in peer tutoring sessions organised by third sector actors.
New skills and friendships
The coronavirus pandemic has, for its part, highlighted inequalities in the availability and ...