(Press-News.org) Lead is a toxic metal, and its widespread use has led to significant environmental pollution and public health problems in many parts of the world. This has led the WHO to include it on a list of ten chemicals that cause serious health problems. However, lead poisoning continues to affect many population groups. A study published today in open access in the journal Environment International found high levels of lead in indigenous people in Peruvian Amazonia living near areas where oil extraction takes place. The research was led by Cristina O'Callaghan-Gordo, a professor and researcher in Health Sciences Studies at the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) and the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation and the National Institute of Health of Peru.
"The main hypothesis is that the metal reaches them through their diet in areas with the most serious environmental pollution, as the population hunts and fishes for food, and previous studies have shown the that lead is present in animals in this region. On the other hand, in places with lower levels of environmental pollution, the most likely route is occupational exposure, such as coming into direct contact with oil due to participating in clean-up tasks after oil spills," explained Cristina O'Callaghan-Gordo.
The closer and more intense the extraction, the higher the levels of lead
The study included 1,047 people, of whom 309 (31%) were children under 12 years old. The population studied lives in four river basins in Peruvian Amazonia, a remote non-industrialized region.
The work took place between May and June 2016, and involved face-to-face interviews to collect data on the participants' risk factors and lifestyle, as well as blood tests. The research also took the distance between where the population lived and the oil extraction facility into account. The highest blood lead levels were found among participants from the Corrientes river basin, which accounts for most of the oil extraction activity in the region.
The study also found higher levels of lead in the blood of people living less than an hour's walk from an oil facility. The values observed in this study are twice as high as the values reported for children in Europe between 1999 and 2007, at a time when leaded petrol was still used in Europe (which in some countries continued until 2005).
The results showed high levels of lead, especially among males. "This is quite common, as men tend to be involved more often in activities that expose them to lead, such as cleaning up spills," said O'Callaghan-Gordo.
Health problems
This study is the result of an agreement reached between the indigenous peoples' federations in the river basins affected and the Peruvian Government, aimed at addressing their concerns about the potential effects on health. "This study came about at the request of the indigenous communities, as they have been calling upon the Government to do something in this respect for decades," said the researcher.
Alterations in the nervous, haematological, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular and renal systems are associated with exposure to lead in both adults and children, according to the United Nations Environment Programme.
"Levels of lead like those we found in Peru have effects on health. In fact, any amount of this metal in the blood has consequences for health. The most well-known known effects are neurological and neurodevelopmental problems in children," warned Cristina O'Callaghan-Gordo.
INFORMATION:
The study received funds from the National Institute of Health of Peru and count with the collaboration of the indigenous federations FEDIQUEP, ACODECOSPAT, FECONACOR and OPIKAFPE, which are part of the Amazonian Indigenous Peoples United in Defence of their Territories (PUINAMUDT). The research has also been carried out in collaboration with Centro de Políticas Públicas y Derechos Humanos in Peru, the University of Cambridge, Universitat Central de Catalunya-Universitat de Vic, Institut de Ciència i Tecnologia Ambientals from the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona and the e-Tech International from the USA.
This research contributes to achieving sustainable development goal (SDG) number 3, "To ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages".
Reference article:
Cristina O'Callaghan-Gordo, Jaime Rosales, Pilar Lizárraga, Frederica Barclay, Tami Okamoto, Diana M. Papoulias, Ana Espinosa, Martí Orta-Martinez, Manolis Kogevinas, John Astete, "Blood lead levels in indigenous peoples living close to oil extraction areas in the Peruvian Amazon" (2021) Environmental Research, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106639
UOC R&I
The UOC's research and innovation (R&I) is helping overcome pressing challenges faced by global societies in the 21st century, by studying interactions between technology and human & social sciences with a specific focus on the network society, e-learning and e-health. Over 500 researchers and 51 research groups work among the University's seven faculties and two research centres: the Internet Interdisciplinary Institute (IN3) and the eHealth Center (eHC).
The United Nations' 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and open knowledge serve as strategic pillars for the UOC's teaching, research and innovation. More information: research.uoc.edu. #UOC25years
As Australia officially enters winter, UniSA ecologists are urging coastal communities to embrace all that the season brings, including the sometimes-unwelcome deposits of brown seaweed that can accumulate on the southern shores.
While tidal seaweed (or sea wrack) may seem unsightly - especially at beach-side tourist destinations - new research from the University of South Australia shows that it plays a vital role for many migratory seabirds and should be protected.
In the first study of its kind, UniSA researchers show that beach-cast seaweed provides shelter, ...
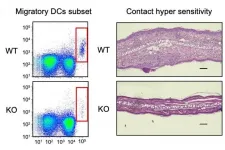
Osaka, Japan - In a new study, researchers from Osaka University discovered a novel molecular mechanism by which immune cells migrate to fight off infections. These findings may help in understanding the development of certain immune deficiency disorders and establish novel therapies against them.
Immune cells represent a diverse group of cells. Some circulate in the blood stream and migrate to infected tissues after receiving signals from damaged tissues. Others reside in tissues to take up the invading microbe, migrate to lymph nodes and activate an immune response. Therefore, to function effectively, the immune system's activities ...
June 7, 2021 - Nyon, Switzerland -- A new report by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) draws attention to the burden of osteoporosis and the gaps and inequalities in the provision of primary and secondary prevention of fractures due to osteoporosis across Europe. 'SCOPE 2021: a new scorecard for osteoporosis in Europe' provides detailed findings for the 27 countries of the European Union as well as Switzerland and the United Kingdom (referred to as 'EU27+2'), covering key indicators for four domains: burden of disease, policy framework, service provision and service uptake.
Professor John A. Kanis, IOF Honorary President and lead author of SCOPE, stated:
"Osteoporosis is a major concern in Europe as it results in 4.3 million fragility fractures and health ...
Scientists have established the most reliable estimates to date of past temperature variations in Antarctica.
They highlight significant differences in behaviour between West and East Antarctica.
This study makes it possible to test and consolidate future climate projections.
Antarctica has experienced significant temperature changes, especially since the last glacial period. An international collaboration including scientists from the CNRS1 has now challenged previously accepted estimates of these variations, using new measurements published on June 4, 2021 in Science. Their study highlights differences in behaviour between East and West Antarctica, connected in particular ...
New research identified a novel interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the galectin-3-binding protein (LGALS3BP) which could be a new therapeutic anti-viral target. The research also found the presence of detectable viral RNA in blood in COVID-19 patients is a strong predictor of mortality.
The paper, published today in Nature Communications, was led by a group of researchers from King's College London, Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust and King's British Heart Foundation Centre. The research was funded by the NIHR Guy's and St Thomas' Biomedical Research Centre and supported by grants from BHF.
In the study, authors analysed close to 500 blood samples from patients ...
Cows can pass on the hypoglycin A toxin through their milk, a study by the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Leibniz Institute of Plant Biochemistry (IPB) in Toxins shows. The substance can cause severe symptoms in humans and animals. Small amounts of the toxin were detected in the raw milk of cows that grazed in a pasture exposed to sycamore maple. The team calls for further investigations to realistically assess the potential dangers.
High concentrations of hypoglycin A can be found in unripe akee and lychee fruit and in the seeds and seedlings of various maple trees. These include, for example, the sycamore maple, which is common throughout Europe. The toxin can cause severe illness in humans. In 2017, a team of researchers in India ...
Travellers abroad may pick up bacteria and other vectors containing genes conferring antimicrobial resistance which remain in the gut when returning to their home country, according to a study published in Genome Medicine.
A team of researchers at Washington University, USA and Maastricht University, Netherlands investigated the presence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) genes in the human gut microbiome by analysing the faecal samples of 190 Dutch travellers before and after travel to destinations in Northern Africa, Eastern Africa, Southern Asia ...
RApid DIgital Crispr Approach (RADICA) is a molecular rapid testing methodology that allows absolute quantification of viral nucleic acids in 40-60 minutes.
RADICA is four times faster and significantly less expensive than conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods as it does not require costly equipment for precise temperature control and cycling.
Method has been tested on SARS-CoV-2 synthetic DNA and RNA, Epstein-Barr virus in human B cells and serum, and can be easily adapted to detect other kinds of viruses.
Singapore, 7 June 2021 - Researchers from Critical Analytics for Manufacturing Personalized-Medicine (CAMP), an Interdisciplinary Research Group (IRG) at the Singapore-MIT ...
Nanoclusters, which consist of several or even thousands of atoms, represent an important intermediate state between microscopic atoms and macroscopic matter. A profound comprehension of the composition, structure, and properties of nanoclusters is crucial for exploring or extending their functional applications. Among the numerous types of nanoclusters, metal chalcogenide supertetrahedral clusters (MCSCs) have attracted great attention since the 1980s for their uniform sizes, well-defined structures, and semiconductor properties. Notably, because ...
Russian paleontologists discovered the skull of a Pleistocene small cave bear with artificial damage in the Imanay Cave (Bashkiria, Russia). A bear aged 9-10 years was killed with a spear during hibernation about 35 thousand years ago. If the assumptions of scientists are confirmed, the find will become the world's first direct evidence of a Paleolithic man hunting for a small cave bear. The description of the skull was published in the Vestnik Archeologii, Anthropologii I Ethnographii.
"The hole in the skull could be either natural or artificial," said senior researcher of the laboratories at the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences and ...