'Asian American': A rallying cry that united Asians in the 1960s but is it still relevant?
How Asian Americans' public policy opinions are divided by generation and national origin, especially on immigration
2021-06-07
(Press-News.org) The recent attacks against Asian Americans have put Asians in the U.S. in the spotlight. Many of the victims are first-generation immigrants in ethnic communities, while those rallying for the victims are second-generation Asian Americans. A new Dartmouth study explores who Asian Americans are today and the range of identities this category encompasses.
The study, by END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
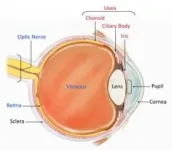
International coalition classifies 25 subtypes of uveitis, an inflammatory eye disease
2021-06-07
An international coalition of eye researchers used machine learning to develop classification criteria for 25 of the most common types of uveitis, a collection of over 30 diseases characterized by inflammation inside the eye. Together, these diseases are the fifth leading cause of blindness in the United States. The Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) Working Group, funded by the National Eye Institute (NEI), published its classification criteria in the American Journal of Ophthalmology. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
"In the past, clinical research in the field of uveitis has been hampered by the lack of widely-accepted ...
High blood lead levels found in indigenous peoples in Peruvian Amazonia
2021-06-07
Lead is a toxic metal, and its widespread use has led to significant environmental pollution and public health problems in many parts of the world. This has led the WHO to include it on a list of ten chemicals that cause serious health problems. However, lead poisoning continues to affect many population groups. A study published today in open access in the journal Environment International found high levels of lead in indigenous people in Peruvian Amazonia living near areas where oil extraction takes place. The research was led by Cristina O'Callaghan-Gordo, a professor and researcher in Health Sciences Studies at the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) and the Barcelona ...
Conserving coastal seaweed: a must have for migrating sea birds
2021-06-07
As Australia officially enters winter, UniSA ecologists are urging coastal communities to embrace all that the season brings, including the sometimes-unwelcome deposits of brown seaweed that can accumulate on the southern shores.
While tidal seaweed (or sea wrack) may seem unsightly - especially at beach-side tourist destinations - new research from the University of South Australia shows that it plays a vital role for many migratory seabirds and should be protected.
In the first study of its kind, UniSA researchers show that beach-cast seaweed provides shelter, ...
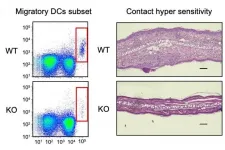
The molecular underpinnings of immune cell migration
2021-06-07
Osaka, Japan - In a new study, researchers from Osaka University discovered a novel molecular mechanism by which immune cells migrate to fight off infections. These findings may help in understanding the development of certain immune deficiency disorders and establish novel therapies against them.
Immune cells represent a diverse group of cells. Some circulate in the blood stream and migrate to infected tissues after receiving signals from damaged tissues. Others reside in tissues to take up the invading microbe, migrate to lymph nodes and activate an immune response. Therefore, to function effectively, the immune system's activities ...
Fragility fractures cost European health care systems €56.9 billion annually
2021-06-07
June 7, 2021 - Nyon, Switzerland -- A new report by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) draws attention to the burden of osteoporosis and the gaps and inequalities in the provision of primary and secondary prevention of fractures due to osteoporosis across Europe. 'SCOPE 2021: a new scorecard for osteoporosis in Europe' provides detailed findings for the 27 countries of the European Union as well as Switzerland and the United Kingdom (referred to as 'EU27+2'), covering key indicators for four domains: burden of disease, policy framework, service provision and service uptake.
Professor John A. Kanis, IOF Honorary President and lead author of SCOPE, stated:
"Osteoporosis is a major concern in Europe as it results in 4.3 million fragility fractures and health ...
Antarctica: How have temperatures varied since the last glacial period?
2021-06-07
Scientists have established the most reliable estimates to date of past temperature variations in Antarctica.
They highlight significant differences in behaviour between West and East Antarctica.
This study makes it possible to test and consolidate future climate projections.
Antarctica has experienced significant temperature changes, especially since the last glacial period. An international collaboration including scientists from the CNRS1 has now challenged previously accepted estimates of these variations, using new measurements published on June 4, 2021 in Science. Their study highlights differences in behaviour between East and West Antarctica, connected in particular ...
Protein identified as new therapeutic anti-viral target for COVID-19
2021-06-07
New research identified a novel interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the galectin-3-binding protein (LGALS3BP) which could be a new therapeutic anti-viral target. The research also found the presence of detectable viral RNA in blood in COVID-19 patients is a strong predictor of mortality.
The paper, published today in Nature Communications, was led by a group of researchers from King's College London, Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust and King's British Heart Foundation Centre. The research was funded by the NIHR Guy's and St Thomas' Biomedical Research Centre and supported by grants from BHF.
In the study, authors analysed close to 500 blood samples from patients ...
Researchers find toxin from maple tree in cow's milk
2021-06-07
Cows can pass on the hypoglycin A toxin through their milk, a study by the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Leibniz Institute of Plant Biochemistry (IPB) in Toxins shows. The substance can cause severe symptoms in humans and animals. Small amounts of the toxin were detected in the raw milk of cows that grazed in a pasture exposed to sycamore maple. The team calls for further investigations to realistically assess the potential dangers.
High concentrations of hypoglycin A can be found in unripe akee and lychee fruit and in the seeds and seedlings of various maple trees. These include, for example, the sycamore maple, which is common throughout Europe. The toxin can cause severe illness in humans. In 2017, a team of researchers in India ...
International travel may spread destination-specific antimicrobial resistance genes
2021-06-07
Travellers abroad may pick up bacteria and other vectors containing genes conferring antimicrobial resistance which remain in the gut when returning to their home country, according to a study published in Genome Medicine.
A team of researchers at Washington University, USA and Maastricht University, Netherlands investigated the presence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) genes in the human gut microbiome by analysing the faecal samples of 190 Dutch travellers before and after travel to destinations in Northern Africa, Eastern Africa, Southern Asia ...
SMART researchers develop method for rapid, accurate detection of viruses
2021-06-07
RApid DIgital Crispr Approach (RADICA) is a molecular rapid testing methodology that allows absolute quantification of viral nucleic acids in 40-60 minutes.
RADICA is four times faster and significantly less expensive than conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods as it does not require costly equipment for precise temperature control and cycling.
Method has been tested on SARS-CoV-2 synthetic DNA and RNA, Epstein-Barr virus in human B cells and serum, and can be easily adapted to detect other kinds of viruses.
Singapore, 7 June 2021 - Researchers from Critical Analytics for Manufacturing Personalized-Medicine (CAMP), an Interdisciplinary Research Group (IRG) at the Singapore-MIT ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
[Press-News.org] 'Asian American': A rallying cry that united Asians in the 1960s but is it still relevant?How Asian Americans' public policy opinions are divided by generation and national origin, especially on immigration