How a global pandemic changed the way we eat and shop
Studies reveal how COVID-19 influenced food choices, attitudes and prices
2021-06-07
(Press-News.org) Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Studies being presented at END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
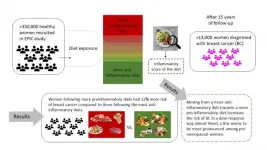
Diets that promote inflammation could increase breast cancer risk
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- A new study of more than 350,000 women found that women with diets incorporating more foods that increase inflammation in the body had a 12% increase in their risk of breast cancer compared to women who consume more anti-inflammatory diets. The new findings are being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE.
The study authors found that moving from a more anti-inflammatory diet toward one that increases inflammation upped breast cancer risk in an almost linear manner. Foods that increase inflammation include red and processed meat; high-fat foods such as butter, margarines and frying fats; and ...
When the economy goes down, so does the quality of our diets
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- What did Americans eat during the Great Recession? A new study suggests dietary quality plummeted along with the economy.
According to the study, adults overall ate more refined grains and solid fats and children increased their intake of added sugar during the recession. The impacts of the downturn were especially pronounced in food-insecure households, where individuals significantly reduced their intake of protein and dark green vegetables while increasing total sugars.
"Overall, we found that the Great Recession had a negative impact on dietary ...
Study compares heart benefits of low-fat and plant-centered diets
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- There has been a long-standing debate as to whether a low-fat or a plant-centered diet is better at lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease. A new study that followed more than 4,700 people over 30 years, found that a plant-centered diet was associated with a lower long-term risk for cardiovascular disease. However, both diets were linked with lower LDL, or bad cholesterol, levels.
"Since 1980, dietary guidelines in the United States and in Europe have recommended eating low amounts of saturated fat because of the high rates of heart disease in these regions," said research team leader David Jacobs, PhD, from the University of Minnesota. "This is not necessarily wrong, but our study shows that plant-centered ...
New research shows trend toward unhealthy eating during pandemic
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- As COVID-19 spread throughout the world, our daily routines and behaviors changed drastically. A new study of more than 2,000 people in the U.S. found that the pandemic has also affected how we eat. The authors found a decrease in the consumption of many food groups, particularly healthy foods such as vegetables and whole grains, compared to before the pandemic.
"When the pandemic began, we saw panic buying, problems in the food supply chain, increases in food prices and rising unemployment rates," said Caroline Um, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at ...
Global youth draft 'Blue New Deal' to protect oceans: 'Time to end generational injustice'
2021-06-07
Concerned youths worldwide today delivered a policy vision for policy-makers to address the declining state of the world's ocean.
A carbon neutral economy, preserving biodiversity, achieving sustainable seafood production, and reforming ocean governance are the four fundamental pillars supporting policy recommendations debuted in the Global Blue New Deal, an ocean policy framework built around crowd-sourced youth priorities.
"Healthy oceans are essential to human survival and well-being, and environmental health must be a global priority as we recover from the pandemic and build a sustainable blue economy," says Mark Haver, Chair of the Sustainable Ocean Alliance's Youth Policy Advisory Council.
He and 14 fellow Young Ocean Leaders ...
New connector for sustainable structures on Earth and in space
2021-06-07
During his time at EPFL under the Erasmus program, Romain van Wassenhove came up with an idea for a connector that could be used to make modular structures out of sustainable bamboo rather than wood, plastic or metal. "I wanted to focus my Master's on a topic that had meaning to me and that would lead to a concrete application," he says. "Working with bamboo was something I already had in mind while I was studying in Brussels." His connectors can be 3D-printed in biosourced plastic and are customizable to the type of material used for the structure.
Van Wassenhove got the idea for his connector during a class at EPFL on composite materials and developed the concept further through his Master's project, co-directed at EPFL by Senior Scientist Anastasios Vassilopoulos and by associate ...
Holes in the solar atmosphere: Artificial intelligence spots coronal holes to automate space weather
2021-06-07
Scientists from the University of Graz (Austria), Skoltech and their colleagues from the US and Germany have developed a new neural network that can reliably detect coronal holes from space-based observations. This application paves the way for more reliable space weather predictions and provides valuable information for the study of the solar activity cycle. The paper was published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Much like our life on Earth depends on the light of the Sun, our electronic "life" depends on the activity of our closest star and its interactions with Earth's magnetic field. For the ...
Climate warming to increase carbon loss in Canadian peatland by 103 per cent
2021-06-07
Carbon loss in Canadian peatland is projected to increase by 103 per cent under a high emission scenario, according to new research led by scientists from the University of Waterloo.
The results of the study, which was published today in Nature's Communications Earth & Environment journal, reinforces the urgent need for a comprehensive understanding of peatlands as evolving sources of atmospheric CO2 in a warming world.
Peatlands, which are a type of wetland, are some of the most valuable ecosystems globally. In addition to their role in preserving biodiversity and minimizing ...
Older Chinese Americans can improve family relationships & cognition through acculturation
2021-06-07
Older Chinese immigrants who adjust to their new cultural environment by learning the language, following the country's media and socializing with local residents can reduce acculturation gap with their adult children and protect their cognitive function, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in the journal Aging and Mental Health, is one of the first to explore the relationship between intergenerational families, acculturation and cognitive function among older Chinese Americans.
Researchers looked 2,900 Chinese Americans over age 60 who had at least one child and who participated in the PINE Study, an epidemiological study of older Chinese Americans. They analyzed three areas of acculturation - language, media use and ethnic social relations - and how they corresponded ...
Meet Australia's largest dinosaur -- Australotitan, the southern titan!
2021-06-07
What's as long a basketball court, taller than a b-double and has just stomped into the record books as Australia's largest dinosaur? It's time to meet Australotitan cooperensis - a new species of giant sauropod dinosaur from Eromanga, southwest Queensland.
Australotitan, "the southern titan", has been scientifically described and named by Queensland Museum and Eromanga Natural History Museum palaeontologists.
It is estimated to have reached a height of 5-6.5 metres at the hip and 25- 30 metres in length and sits within the top 10-15 largest dinosaurs world-wide, representing Australia's entry into the largest species to have ever walked the Earth.
The fossilised skeleton was originally nicknamed 'Cooper' after Cooper Creek, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
[Press-News.org] How a global pandemic changed the way we eat and shopStudies reveal how COVID-19 influenced food choices, attitudes and prices