New research examines the science behind superfoods
Findings suggest that consuming mangos, honey and spices could bring important health benefits
2021-06-07
(Press-News.org) Rockville, Md. (June 7, 2021) - Superfoods like turmeric and honey have long been recognized for their ability to promote health and wellness. New studies being presented at END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How kids eat: Five new insights on daily habits and childhood obesity
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- What we eat during childhood can affect the health of individuals--and populations--for years to come. As rates of childhood obesity continue to rise, five studies being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE bring new insights into the diets of children and teens around the world.
Families report substantial child weight gain during COVID-19
Researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University surveyed over 400 parents about their children's weight and eating habits before the COVID-19 pandemic and at two points during ...
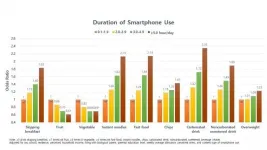
Smartphone use associated with unhealthy eating and overweight in teens
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Even moderate smartphone use may influence teens' diet and weight, according to a new study of more than 53,000 Korean adolescents. Teens who used a smartphone for more than 2 hours per day were significantly more likely to eat more junk food and fewer fruits and vegetables than those spending less time on their phone. Teens spending more than 3 hours per day on a smartphone were significantly more likely to be overweight or obese.
"While earlier studies have shown that TV watching is an important factor that increases the risk of obesity in children and adolescents, little is known about the effects of modern screen time such as smartphone use on diet and obesity," said Hannah Oh, ScD, assistant professor at ...
How a global pandemic changed the way we eat and shop
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Studies being presented at END ...
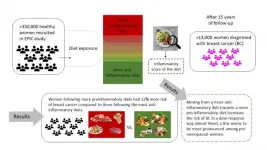
Diets that promote inflammation could increase breast cancer risk
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- A new study of more than 350,000 women found that women with diets incorporating more foods that increase inflammation in the body had a 12% increase in their risk of breast cancer compared to women who consume more anti-inflammatory diets. The new findings are being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE.
The study authors found that moving from a more anti-inflammatory diet toward one that increases inflammation upped breast cancer risk in an almost linear manner. Foods that increase inflammation include red and processed meat; high-fat foods such as butter, margarines and frying fats; and ...
When the economy goes down, so does the quality of our diets
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- What did Americans eat during the Great Recession? A new study suggests dietary quality plummeted along with the economy.
According to the study, adults overall ate more refined grains and solid fats and children increased their intake of added sugar during the recession. The impacts of the downturn were especially pronounced in food-insecure households, where individuals significantly reduced their intake of protein and dark green vegetables while increasing total sugars.
"Overall, we found that the Great Recession had a negative impact on dietary ...
Study compares heart benefits of low-fat and plant-centered diets
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- There has been a long-standing debate as to whether a low-fat or a plant-centered diet is better at lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease. A new study that followed more than 4,700 people over 30 years, found that a plant-centered diet was associated with a lower long-term risk for cardiovascular disease. However, both diets were linked with lower LDL, or bad cholesterol, levels.
"Since 1980, dietary guidelines in the United States and in Europe have recommended eating low amounts of saturated fat because of the high rates of heart disease in these regions," said research team leader David Jacobs, PhD, from the University of Minnesota. "This is not necessarily wrong, but our study shows that plant-centered ...
New research shows trend toward unhealthy eating during pandemic
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- As COVID-19 spread throughout the world, our daily routines and behaviors changed drastically. A new study of more than 2,000 people in the U.S. found that the pandemic has also affected how we eat. The authors found a decrease in the consumption of many food groups, particularly healthy foods such as vegetables and whole grains, compared to before the pandemic.
"When the pandemic began, we saw panic buying, problems in the food supply chain, increases in food prices and rising unemployment rates," said Caroline Um, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at ...
Global youth draft 'Blue New Deal' to protect oceans: 'Time to end generational injustice'
2021-06-07
Concerned youths worldwide today delivered a policy vision for policy-makers to address the declining state of the world's ocean.
A carbon neutral economy, preserving biodiversity, achieving sustainable seafood production, and reforming ocean governance are the four fundamental pillars supporting policy recommendations debuted in the Global Blue New Deal, an ocean policy framework built around crowd-sourced youth priorities.
"Healthy oceans are essential to human survival and well-being, and environmental health must be a global priority as we recover from the pandemic and build a sustainable blue economy," says Mark Haver, Chair of the Sustainable Ocean Alliance's Youth Policy Advisory Council.
He and 14 fellow Young Ocean Leaders ...
New connector for sustainable structures on Earth and in space
2021-06-07
During his time at EPFL under the Erasmus program, Romain van Wassenhove came up with an idea for a connector that could be used to make modular structures out of sustainable bamboo rather than wood, plastic or metal. "I wanted to focus my Master's on a topic that had meaning to me and that would lead to a concrete application," he says. "Working with bamboo was something I already had in mind while I was studying in Brussels." His connectors can be 3D-printed in biosourced plastic and are customizable to the type of material used for the structure.
Van Wassenhove got the idea for his connector during a class at EPFL on composite materials and developed the concept further through his Master's project, co-directed at EPFL by Senior Scientist Anastasios Vassilopoulos and by associate ...
Holes in the solar atmosphere: Artificial intelligence spots coronal holes to automate space weather
2021-06-07
Scientists from the University of Graz (Austria), Skoltech and their colleagues from the US and Germany have developed a new neural network that can reliably detect coronal holes from space-based observations. This application paves the way for more reliable space weather predictions and provides valuable information for the study of the solar activity cycle. The paper was published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Much like our life on Earth depends on the light of the Sun, our electronic "life" depends on the activity of our closest star and its interactions with Earth's magnetic field. For the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] New research examines the science behind superfoodsFindings suggest that consuming mangos, honey and spices could bring important health benefits