Mice fathers pass down stress responses to offspring via sperm
Heritable stress responses linked to changes in sperm's genetic information
2021-06-07
(Press-News.org) Male mice more susceptible to stress can pass down their behaviors to offspring via changes in their sperm's genetic code, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Stressful experiences alter gene expression, which parents can pass down to their offspring. But it was unclear if sperm itself transmits this information, or if behavioral cues between the parents play a larger role.
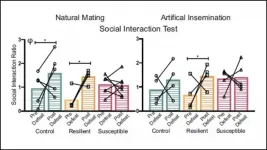
Cunningham et al. tracked the stress response of male mice after ten days of chronic stress and sorted them into resilient and susceptible groups, based on the severity of their response. The offspring of resilient and control mice showed decreased stress behaviors compared to the offspring of the susceptible mice. The same pattern appeared in offspring conceived via artificial insemination, indicating sperm plays a direct role in the transmission of stress responses. The researchers also sequenced the RNA in the father's sperm -- the transcriptome -- before and after the chronic stress. Stress changed 1460 genes in susceptible mice but only 62 genes in resilient mice. These results reveal sperm transmits short-term environmental information to offspring through changes in the transcriptome.
INFORMATION:
Paper title: Sperm Transcriptional State Associated With Paternal Transmission of Stress Phenotypes
About JNeurosci
JNeurosci, the Society for Neuroscience's first journal, was launched in 1981 as a means to communicate the findings of the highest quality neuroscience research to the growing field. Today, the journal remains committed to publishing cutting-edge neuroscience that will have an immediate and lasting scientific impact, while responding to authors' changing publishing needs, representing breadth of the field and diversity in authorship.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world's largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 37,000 members in more than 90 countries and over 130 chapters worldwide.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-07
Researchers at the University of Sydney's Charles Perkins Centre conducted the largest ever study of nutrient interactions by examining the health of mice on 33 different diets containing various combinations of protein to carbs, and different sources of carbohydrate.
They found that a low-protein (10% of dietary energy), high-carbohydrate (70%) diet produced either the healthiest or unhealthiest metabolic outcomes of all 33 diets, depending on the kind of carbs.
When carbs were made up mainly of resistant starch, a form of starch that is resistant to digestion and is fermented by bacteria in the gut, the low protein diet was the healthiest of all diets. When the ...
2021-06-07
A study examining gender bias and family-owned businesses found daughters were rarely encouraged nor received support to pursue entrepreneurship education while sons mostly did.
Professors James Combs, Peter Jaskiewicz, and Sabine Raul from the Telfer School of Management uncovered new insights about how gender bias - the preference of a gender over the other - affects the succession strategy in multi-generational family firms. Their findings are published in the Journal of Small Business Management.
When nurturing the next generation, entrepreneurial families often prepare their daughters and sons differently for their careers. The researchers noticed a common pattern in the stories shared by the next generation: Sons are often nurtured to ...
2021-06-07
It's hard to see more than a handful of stars from Princeton University, because the lights from New York City, Princeton and Philadelphia prevent our sky from ever getting pitch black, but stargazers who get into more rural areas can see hundreds of naked-eye stars -- and a few smudgy objects, too.
The biggest smudge is the Milky Way itself, the billions of stars that make up our spiral galaxy, which we see edge-on. The smaller smudges don't mean that you need glasses, but that you're seeing tightly packed groups of stars. One of the best-known of these "clouds" or "clusters" -- groups of stars that travel together -- is the Pleiades, also known as the Seven Sisters. Clusters are stellar nurseries where thousands of stars are born from clouds of gas and dust and then ...
2021-06-07
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Researchers have discovered a new electronic property at the frontier between the thermal and quantum sciences in a specially engineered metal alloy - and in the process identified a promising material for future devices that could turn heat on and off with the application of a magnetic "switch."
In this material, electrons, which have a mass in vacuum and in most other materials, move like massless photons or light - an unexpected behavior, but a phenomenon theoretically predicted to exist here. The alloy was engineered with the elements bismuth and antimony at precise ranges based ...
2021-06-07
Carbon dioxide emissions in Los Angeles fell 33% in April of 2020 compared with previous years, as roads emptied and economic activity slowed due to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study in Geophysical Research Letters. In the Washington, D.C./Baltimore region, emissions of carbon dioxide, or CO2, dropped by 34% during the same period.
The study was led by scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Notre Dame.
While the emissions reductions are significant, the method that scientists used to measure them may have the greater long-term impact.
In both locations, scientists had previously ...
2021-06-07
Research between the University of Liverpool, UK and National Tsing Hua University (NTHU), Taiwan has revealed a new charge storage mechanism that has the potential to allow rechargeability within calcium-air batteries.
In a paper published in the journal Chemical Science, Professor Laurence Hardwick from the University of Liverpool's Stephenson Institute for Renewable Energy (SIRE) and colleagues discover a distinctive form of charge storage at the electrode interface described as trapped interfacial redox. This new finding introduces a new mechanism of charge storage that could be harnessed in practical devices.
Lead author of the paper, Yi Ting (Leo) Lu, is a joint PhD student in ...
2021-06-07
A new study at the University of Chicago has determined that restoring a single microbial species -- Bacteroides sp. CL1-UC (Bc) -- to the gut microbiome at a key developmental timepoint can prevent antibiotic-induced colitis in a mouse model of the condition. The results, published on June 7 in END ...
2021-06-07
TROY, N.Y. -- More strategic and coordinated travel restrictions likely could have reduced the spread of COVID-19 in the early stages of the pandemic. That's according to new research published in Communications Physics. This finding stems from new modeling conducted by a multidisciplinary team of scientists and engineers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
The researchers evaluated the distance between countries in terms of air travel, a more complex measurement than simply mapping physical distance. For instance, while China and Thailand may be geographically more proximate to one another, if there are significantly ...
2021-06-07
In young women, Staphylococcus saprophyticus is a main cause of urinary tract infections (UTI), reaching 20% prevalence. Understanding the epidemiology of this microorganism can help identify its origin, distribution, causes, and risk factors. Now, ITQB NOVA researchers led by Maria Miragaia showed evidence that Staphylococcus saprophyticus can originate in food, namely in the meat-production chain.
Europe is the world's second-biggest producer of pork, the most favored meat type in these countries. One of the contaminants of that meat is S. saprophyticus, which is found also in the environment, ...
2021-06-07
BOSTON - Current guidelines recommend stopping cervical cancer screening at age 65, but women over age 65 make up over one in five new cervical cancer diagnoses, and are twice as likely to die after a cervical cancer diagnosis compared to younger women. New research from Boston Medical Center found that fewer than one in three women aged 64 to 66 met the criteria to discontinue cervical cancer screening while looking at patients with both private insurance and from a safety-net hospital setting. Published in Gynecologic Oncology, researchers found that even among women with 10 years of continuous insurance coverage, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mice fathers pass down stress responses to offspring via sperm
Heritable stress responses linked to changes in sperm's genetic information