(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON -- For more than 25 years, Burmese pythons have been living and breeding in the Florida Everglades where they prey on native wildlife and disrupt the region's delicate ecosystems. A new study shows that infrared cameras could make it easier to spot these invasive snakes in the Florida foliage, providing a new tool in the effort to remove them.
In the Optical Society (OSA) journal Applied Optics, researchers led by Dr. Kyle Renshaw from the University of Central Florida College of Optics and Photonics report that a near infrared camera helped people detect Burmese pythons at distances up to 1.3 times farther away than was possible using a traditional visible-wavelength camera. Because infrared sensors are small and low cost, they could easily be incorporated into handheld or vehicle-mounted systems designed for seeking out pythons.
"The removal of Burmese Pythons is vital to preventing further damage to the Floridian ecosystem and preventing their spread to other regions," said Hewitt, a PhD student and lead author on the study. "Our study -- one of the first to examine the efficacy of near infrared sensing in locating these pythons -- can help inform methods used to remove them from the environment."
Making snakes stand out
Burmese pythons can be up to 20 feet long and weigh as much as 200 pounds. They arrived in the U.S. as exotic pets in the 1980s and the snakes proliferated in the Everglades after a breeding facility was destroyed during Hurricane Andrew in 1992. Their natural camouflage makes them blend in with grass and foliage, making them hard to see with the human eye or a traditional visible-light camera. In a previous study, the authors measured the reflectivity spectra of Burmese pythons in the visible and infrared wavelengths, finding that pythons are more visible against the background at infrared wavelengths longer than 750 nm.
"Based on these earlier findings, we hypothesized that using near infrared wavelengths for imaging could make the pythons easier to see because they would appear dark against bright foliage," said Hewitt. "Although we haven't acquired reflectivity measurements from other species of snakes, the pythons should be easy to distinguish since they are larger than any other native species of snake."
To test their hypothesis, the researchers took images of Burmese pythons in grass using visible and infrared cameras with similar fields of view and resolution. They then asked volunteers to examine these images and indicate whether they saw a python. Based on the responses of the volunteers, the researchers calculated the advantage of using near infrared images compared to visible.
"The method we used to evaluate each of the sensors was originally established for military sensing applications," Hewitt explained. "It accounts for the attributes of human vision and perception in addition to the characteristics of the system components to determine how effective a system is at allowing the observer to accomplish a task."
Spotting pythons day or night
Although other studies have explored using thermal infrared sensors to find Burmese pythons, the snakes had to have been basking in the sun during the day for them to be detected at night. The thermal contrast against their environment also diminished over time.
"In this work, we don't rely on thermal contrast," said Hewitt. "We found that near infrared imaging can be used both during the day as well as at night with illumination to improve detection, even if the pythons have not been basking."
The researchers have contracted with the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) to work on a project that expands on these results. "We are evaluating whether or not this technology will be effective in the field, and, if so, how to make it field-ready in the challenging Florida everglades ecosystem," said McKayla Spencer, the FWC interagency python management coordinator. "We are just in the beginning stages of our project with the researchers."
INFORMATION:
Paper: J. Hewitt, O. Furxhi, K. Renshaw, R. Driggers, "Detection of Burmese pythons in the near infrared vs. visible band," Applied Optics, 60, 17, 5066-5073 (2021).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.419320
About Applied Optics
Applied Optics publishes in-depth peer-reviewed content about applications-centered research in optics. These articles cover research in optical technology, photonics, lasers, information processing, sensing and environmental optics. Applied Optics is published three times per month by The Optical Society and overseen by Editor-in-Chief Gisele Bennett, MEPSS LLC and Georgia Institute of Technology, USA. For more information, visit OSA Publishing.
About The Optical Society
Founded in 1916, The Optical Society (OSA) is the leading professional organization for scientists, engineers, students and business leaders who fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate achievements in the science of light. Through world-renowned publications, meetings and membership initiatives, OSA provides quality research, inspired interactions and dedicated resources for its extensive global network of optics and photonics experts. For more information, visit osa.org.
Media Contact
mediarelations@osa.org
AMES, Iowa - Scientists have invested great time and effort into making connections between a plant's genotype, or its genetic makeup, and its phenotype, or the plant's observable traits. Understanding a plant's genome helps plant biologists predict how that plant will perform in the real world, which can be useful for breeding crop varieties that will produce high yields or resist stress.
But environmental conditions play a role as well. Plants with the same genotype will perform differently when grown in different environments. A new study led by an Iowa State University scientist uses advanced data analytics to help scientists understand ...
A study conducted by a group of Brazilian researchers contributes to a deeper understanding of the molecular basis for schizophrenia, and potentially to the development of more specific and effective treatments for the disease. The medications currently available on the market act generically on the brain and can have severe adverse side effects.
Treatment of post-mortem samples from the hippocampus of schizophrenic patients with an NMDA receptor antagonist pointed to biological processes associated with the disease that are specific to neurons and oligodendrocytes. NMDA receptors are neurotransmitter receptors located in the postsynaptic ...
In those with fatty liver disease, a person's fat goes to their liver instead of their fat tissue, either because of an absence of fat depots, which is seen in the rare genetic disease lipodystrophy, or because the depots are too full, which is seen in people with obesity.
One third of these people will go on to develop nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH - an advanced form of fatty liver disease brought on by progressive inflammation and scarring in the organ.
In 2002, Michigan Medicine endocrinologist Elif Oral, M.D., who had just moved from the National Institutes of Health at the time, published her discovery that patients with severe lipodystrophy lack leptin, a hormone that helps curb appetite and control weight gain. When given ...
BOSTON - Automated emails and letters that provide personalized feedback related to cafeteria purchases at work may help employees make healthier food choices. That's the conclusion of a new study that was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and is published in END ...
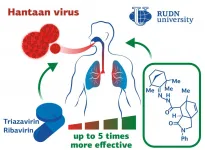
RUDN University chemists and their colleagues from Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk Institute of Organic Chemistry and The State Research Center of Virology and Biotechnology VECTOR have obtained a new class of compounds that inhibit the replication of the deadly Hantaan virus that affects blood vessels and internal organs of humans. The resulting substances were 5 times more effective than existing antiviral drugs. The results have been published Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters.
The Hantaan virus causes acute haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). The disease ...
Microgravity in space perturbs human physiology and is detrimental for astronaut health, a fact first realized during early Apollo missions when astronauts experienced inner ear disturbances, heart arrhythmia, low blood pressure, dehydration, and loss of calcium from their bones after their missions.
One of the most striking observations from Apollo missions was that just over half of astronauts became sick with colds or other infections within a week of returning to Earth. Some astronauts have even experienced re-activation of dormant viruses, such as the chickenpox virus. These findings stimulated studies on the effects of weak gravity, or ...
A new study from researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and colleagues suggests a slowdown in the use of convalescent plasma to treat hospitalized COVID-19 patients led to a higher COVID-19 mortality during a critical period during this past winter's surge.
U.S. hospitals began treating COVID-19 patients with convalescent plasma therapy--which uses antibody-rich blood from recovered COVID-19 patients--in the summer of 2020 when doctors were looking to identify treatments for the emerging disease. By the spring of 2021, doctors in the United States had treated over 500,000 COVID-19 patients with convalescent plasma. The use ...
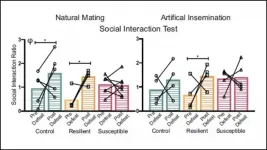
Male mice more susceptible to stress can pass down their behaviors to offspring via changes in their sperm's genetic code, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Stressful experiences alter gene expression, which parents can pass down to their offspring. But it was unclear if sperm itself transmits this information, or if behavioral cues between the parents play a larger role.
Cunningham et al. tracked the stress response of male mice after ten days of chronic stress and sorted them into resilient and susceptible groups, based on the severity of their response. The offspring of resilient and control mice showed decreased stress behaviors ...
Researchers at the University of Sydney's Charles Perkins Centre conducted the largest ever study of nutrient interactions by examining the health of mice on 33 different diets containing various combinations of protein to carbs, and different sources of carbohydrate.
They found that a low-protein (10% of dietary energy), high-carbohydrate (70%) diet produced either the healthiest or unhealthiest metabolic outcomes of all 33 diets, depending on the kind of carbs.
When carbs were made up mainly of resistant starch, a form of starch that is resistant to digestion and is fermented by bacteria in the gut, the low protein diet was the healthiest of all diets. When the ...
A study examining gender bias and family-owned businesses found daughters were rarely encouraged nor received support to pursue entrepreneurship education while sons mostly did.
Professors James Combs, Peter Jaskiewicz, and Sabine Raul from the Telfer School of Management uncovered new insights about how gender bias - the preference of a gender over the other - affects the succession strategy in multi-generational family firms. Their findings are published in the Journal of Small Business Management.
When nurturing the next generation, entrepreneurial families often prepare their daughters and sons differently for their careers. The researchers noticed a common pattern in the stories shared by the next generation: Sons are often nurtured to ...