INFORMATION:
This research was funded by an Alan Turing Institute Research fellowship under an EPSRC research grant, EPSRC/BBSRC Innovation fellowships and an EMBO fellowship.
Dawn Burst Network
View the full early morning gene network to observe patterns in the complete network and to search for a particular gene.
Dawn Burst Network website
Reference
Martin Balcerowicz, Mahiar Mahjoub, Duy Nguyen, Hui Lan, Dorothee Stoeckle, Susana Conde, Katja E. Jaeger, Philip A. Wigge, Daphne Ezer (2021) An early-morning gene network controlled by phytochromes and cryptochromes regulates photomorphogenesis pathways in Arabidopsis. Molecular Plant.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.03.019
Plants get a faster start to their day than we think
2021-06-07
(Press-News.org) To describe something as slow and boring we say it's "like watching grass grow", but scientists studying the early morning activity of plants have found they make a rapid start to their day - within minutes of dawn.
Just as sunrise stimulates the dawn chorus of birds, so too does sunrise stimulate a dawn burst of activity in plants.
Early morning is an important time for plants. The arrival of light at the start of the day plays a vital role in coordinating growth processes in plants and is the major cue that keeps the inner clock of plants in rhythm with day-night cycles.
This inner circadian clock helps plants prepare for the day such as when to make the best use of sunlight, the best time to open flowers for pollinators and release pollen and when to get ready to respond to drought conditions.
There is a peak of gene activity within an hour of dawn; many of these genes code for transcription factors - proteins that regulate expression of a host of downstream genes - with roles related to light, stress and growth hormones, but the detail of how this peak is controlled is not understood.
Researchers at the Sainsbury Laboratory Cambridge University (SLCU) and University of York set out to investigate this burst of activity so as to better understand what happens at the genetic level by sampling thale cress, Arabidopsis thaliana, every two minutes from dawn to measure gene activity.
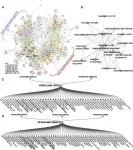
"We set out to characterise 'dawn burst' dynamics in more detail, focussing on the expression of transcription factor genes. We found three distinct gene expression waves within two hours after dawn. The first of these occurs just 16 minutes after dawn and lasts only 8 minutes." said Dr Martin Balcerowicz, researcher at SLCU and first author of the research published in Molecular Plant.
"Many of these genes are known to be sensitive to light and temperature, but we wanted to find out specifically how the transcription of these genes is coordinated. Interfering in photoreceptor signalling, the circadian clock and chloroplast derived light signals did cause problems in some genes' expression, but there was a large proportion of genes still unaffected. This indicated to us that some of the upstream pathways are redundant and that additional regulators are in play."
The team integrated their data with already published transcription factor-DNA binding data and identified a gene regulatory network at dawn, with two key regulators of light signalling - HY5 and BBX31 - at its core. These transcription factors are known to jointly control de-etiolation, which is the developmental switch a seedling undergoes when it emerges from the soil, experiencing light for the first time, and starts greening and unfolding its leaves. It appears that these genes also play a central role during the dark-to-light transition at dawn.
"In fact, multiple BBX genes form part of the dawn burst alongside BBX31, HY5 and its homologue HYH," says Dr Balcerowicz. "These genes include both positive and negative regulators of the light response. We found that they act downstream of phytochrome and cryptochrome photoreceptors to control a light-induced subset of dawn burst genes, with HY5 and BBX31 having largely antagonistic roles. This observation strengthens the idea that HY5 and BBX genes act in concert to fine-tune light responses in the context of the day-night cycle."
Dr Daphne Ezer, lecturer in Computational Biology at the University of York and senior author of the study, investigates gene-environment interactions through analysis of gene networks. "By studying gene networks we can interpret how plants integrate light and temperature signals in the early morning to entrain the circadian clock. Taken together, our results show that phytochrome and cryptochrome signalling is required for fine-tuning the dawn transcriptional response to light, but separate pathways can robustly activate much of the programme in their absence."
"Characterising the peak we see in gene expression that results from the onset of light is useful in helping us to understand how plants respond to light and, in particular, for crops grown under artificial lighting, how this dawn burst impacts longer term on growth."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mandating vaccination could reduce voluntary compliance
2021-06-07
Citizen opposition to COVID-19 vaccination has emerged across the globe, prompting pushes for mandatory vaccination policies. But a new study based on evidence from Germany and on a model of the dynamic nature of people's resistance to COVID-19 vaccination sounds an alarm: mandating vaccination could have a substantial negative impact on voluntary compliance.
Majorities in many countries now favor mandatory vaccination. In March, the government of Galicia in Spain made vaccinations mandatory for adults, subjecting violators to substantial fines. Italy has made vaccinations mandatory for care workers. The University of California and California State University systems announced in late April that vaccination ...
Darkened windows save migrating birds
2021-06-07
ITHACA, N.Y. - Building lights are a deadly lure for the billions of birds that migrate at night, disrupting their natural navigation cues and leading to deadly collisions. But even if you can't turn out all the lights in a building, darkening even some windows at night during bird migration periods could be a major lifesaver for birds.
Research published this week in PNAS found that over the course of 21 years, one building sustained 11 times fewer nighttime bird collisions during spring migration and 6 times fewer collisions during fall migration when only half of the building's windows were illuminated, compared ...
Correcting misperceptions about, and increasing empathy for, migrants
2021-06-07
Many mainstream depictions of immigration at the southern border of the United States paint a dark picture, eliciting imagery of violent gang members and child trafficking. But how many undocumented immigrants are really involved in this kind of activity? Many people may be surprised to learn the answer is far fewer than they think.
A new study from the Peace and Conflict Neuroscience Lab (PCNL) at the Annenberg School for Communication found that Americans dramatically overestimate the number of migrants affiliated with gangs and children being trafficked, and that this overestimation contributes to dehumanization of migrants, lack of empathy for their suffering, and individuals' views on immigration policy. In addition, the researchers developed and tested interventions to ...
Non-invasive sensor shows correlation between blood pressure and intracranial pressure
2021-06-07
Brazilian researchers have simultaneously demonstrated the mechanism linking high blood pressure to elevated intracranial pressure, validated a non-invasive intracranial pressure monitoring method, and proposed a treatment for high blood pressure that does not affect intracranial hypertension.
The study was supported by FAPESP and involved collaboration between researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) and Brain4care, a startup based in São Carlos. It could result in novel treatments for intracranial hypertension and its complications, including stroke. The main findings are reported in the journal Hypertension.
The researchers monitored blood pressure and intracranial pressure in rats for six weeks. “We set out to investigate ...
Clever biomolecular labelling enables identification of immune cells
2021-06-07
Biomolecules regulate the biological functions inside every living cell. If scientists can understand the molecular mechanisms of such functions, then it is possible to detect the severe dysfunction which can lead to illness. At a molecular level, this can be achieved with fluorescent markers that are specifically incorporated into the respective biomolecules. In the past, this has been achieved by incorporating a marker in the bio-molecule by completely rebuilding it from the beginning, necessitating a large number of steps. Unfortunate-ly, this approach not only takes a lot of time and resources, but also produces unwanted waste products. Researchers at the Universities of Göttingen and Edinburgh have now ...
A new disease called halo blight threatens Michigan hop production
2021-06-07
If you're a beer drinker, you've noticed that hoppy beers have become increasingly popular. Most of the nation's hops come from the Pacific Northwest. However, commercial hop production regions have expanded significantly. In Michigan hop production nearly tripled between 2014 and 2017 and in 2019, Michigan growers harvested around 720 acres of hops.
Michigan hop growers contend with unique challenges as a result of frequent rainfall and high humidity during the growing season. In 2018, growers approached Michigan State University researchers and the Michigan State University's Plant & Pest Diagnostics lab with concerns about a leaf blight ...
Study sheds light on pre-Columbian life in understudied area of SW Amazon
2021-06-07
ORLANDO, June 2021 - A new study co-authored by University of Central Florida researchers shows that pre-Columbian people of a culturally diverse but not well-documented area of the Amazon in South America significantly altered their landscape thousands of years earlier than previously thought.
The findings, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, show evidence of people using fire and improving their landscape for farming and fishing more than 3,500 years ago. This counters the often-held notion of a pristine Amazon during pre-Columbian times before the arrival of Europeans in the late 1400s.
The study, ...
Study shows cities can consider race and income in household energy efficiency programs
2021-06-07
Climate change and social inequality are two pressing issues that often overlap. A new study led by Princeton researchers offers a roadmap for cities to address inequalities in energy use by providing fine-grained methods for measuring both income and racial disparities in energy use intensity. Energy use intensity, the amount of energy used per unit floor area, is often used as a proxy for assessing the efficiency of buildings and the upgrades they receive over time. The work could guide the equitable distribution of rebates and other measures that decrease energy costs and increase efficiency.
Examining inequality in cities has been hampered ...
Papers explore massive plankton blooms with very different ecosystem impacts
2021-06-07
"The big mystery about plankton is what controls its distribution and abundance, and what conditions lead to big plankton blooms," said Dennis McGillicuddy, Senior Scientist and Department Chair in Applied Ocean Physics and Engineering at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI).
Two new papers explore this question and provide examples of conditions that lead to massive plankton blooms with vastly different potential impacts on the ecosystem, according to McGillicuddy, co-author of both papers. Both papers also point to the importance of using advanced technology--including Video Plankton Recorders, autonomous underwater vehicles, and the Ocean Observatories Initiative's Coastal Pioneer Array--to find and monitor these blooms.
In one paper, Diatom Hotspots Driven ...
Do customer loyalty programs really help sellers make money?
2021-06-07
Key Takeaways:
Study finds non-tiered customer loyalty programs create a more sustainable customer base.
Non-tiered customer loyalty programs are not as likely to generate increases in spending per transaction or accelerate transactions.
CATONSVILLE, MD, June 7, 2021 - Customer loyalty programs have been around for decades and are used to help businesses, marketers and sellers build a sustainable relationship with their customers. But do they work? A recent study sought to find out and researchers learned that while yes, customer loyalty programs do work, perhaps not in ways most may assume.
There are two basic ...