INFORMATION:
Both of these studies were carried out as part of the National Science Foundation-funded Shelfbreak Productivity Interdisciplinary Research Operation at the Pioneer Array involving partners at WHOI, University of Massachusetts Dartmouth, Massachusetts Division of Marine Fisheries, Virginia Institute of Marine Science, Wellesley College, and Old Dominion University. Additional support has been provided by the Dalio Explorer Fund.
For more information, see the video "Life at the Edge: Plankton Growth at the Shelf Break Front," produced by ScienceMedia.nl for WHOI.
About Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is a private, non-profit organization on Cape Cod, Massachusetts, dedicated to marine research, engineering, and higher education. Established in 1930, its primary mission is to understand the ocean and its interaction with the Earth as a whole, and to communicate an understanding of the ocean's role in the changing global environment. WHOI's pioneering discoveries stem from an ideal combination of science and engineering--one that has made it one of the most trusted and technically advanced leaders in basic and applied ocean research and exploration anywhere. WHOI is known for its multidisciplinary approach, superior ship operations, and unparalleled deep-sea robotics capabilities. We play a leading role in ocean observation and operate the most extensive suite of data-gathering platforms in the world. Top scientists, engineers, and students collaborate on more than 800 concurrent projects worldwide--both above and below the waves--pushing the boundaries of knowledge and possibility. For more information, please visit http://www.whoi.edu
A Regional, Early Spring Bloom of Phaeocystis pouchetii on the New England Continental Shelf
Authors: Walker O. Smith Jr.1,2*, Weifeng G. Zhang3, Andrew Hirzel3, Rachel M. Stanley4, Meredith G. Meyer1, Heidi Sosik3, Philip Alatalo3, Hilde Oliver3, Zoe Sandwith3, E. Taylor Crockford3 , Emily E. Peacock3, Arshia Mehta4 , and Dennis J. McGillicuddy Jr.3
Affiliations:
1 Virginia Institute of Marine Science, William & Mary, Gloucester Pt., VA, USA
2 School of Oceanography, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
3 Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MA, USA
4 Department of Chemistry, Wellesley College, Wellesley, MA, USA
*Corresponding author
Diatom Hotspots Driven by Western Boundary Current Instability
Authors: Hilde Oliver1*, Weifeng G. Zhang1, Walker O. Smith, Jr.,2,3, Philip Alatalo1, P. Dreux Chappell4, Andrew Hirzel1, Corday R. Selden4, Heidi M. Sosik1, Rachel H. R. Stanley5, Yifan Zhu4, and Dennis J. McGillicuddy, Jr.1
Affiliations:
1Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MA, USA
2Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William & Mary, Gloucester Point, VA, USA
3School of Oceanography, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, People's Republic of China
4Department of Ocean and Earth Sciences, Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA USA
5Department of Chemistry, Wellesley College, Wellesley, MA, USA
*Corresponding author
Papers explore massive plankton blooms with very different ecosystem impacts
2021-06-07
(Press-News.org) "The big mystery about plankton is what controls its distribution and abundance, and what conditions lead to big plankton blooms," said Dennis McGillicuddy, Senior Scientist and Department Chair in Applied Ocean Physics and Engineering at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI).
Two new papers explore this question and provide examples of conditions that lead to massive plankton blooms with vastly different potential impacts on the ecosystem, according to McGillicuddy, co-author of both papers. Both papers also point to the importance of using advanced technology--including Video Plankton Recorders, autonomous underwater vehicles, and the Ocean Observatories Initiative's Coastal Pioneer Array--to find and monitor these blooms.
In one paper, Diatom Hotspots Driven by Western Boundary Current Instability, published in Geophysical Research Letters (GRL), scientists found unexpectedly productive subsurface hotspot blooms of diatom phytoplankton.
In the GRL paper, researchers investigated the dynamics controlling primary productivity in a region of the Mid-Atlantic Bight (MAB), one of the world's most productive marine ecosystems. In 2019, they observed unexpected diatom hotspots in the slope region of the bight's euphotic zone, the ocean layer that receives enough light for photosynthesis to occur. Phytoplankton are photosynthetic microorganisms that are the foundation of the aquatic food web.
It was surprising to the researchers that the hotspots occurred in high-salinity water intruding from the Gulf Stream. "While these intrusions of low?nutrient Gulf Stream water have been thought to potentially diminish biological productivity, we present evidence of an unexpectedly productive subsurface diatom bloom resulting from the direct intrusion of a Gulf Stream meander towards the continental shelf," the authors note. They hypothesize that the hotspots were not fueled by Gulf Stream surface water, which is typically low in nutrients and chlorophyll, but rather that the hotspots were fueled by nutrients upwelled into the sunlight zone from deeper Gulf Stream water.
With changing stability of the Gulf Stream, intrusions from the Gulf Stream had become more frequent in recent decades, according to the researchers. "These results suggest that changing large?scale circulation has consequences for regional productivity that are not detectable by satellites by virtue of their occurrence well below the surface," the authors note.
"In this particular case, changing climate has led to an increase in productivity in this particular region, by virtue of a subtle and somewhat unexpected interaction between the physics and biology of the ocean. That same dynamic may not necessarily hold elsewhere in the ocean, and it's quite likely that other areas of the ocean will become less productive over time. That's of great concern," said McGillicuddy. "There are going to be regional differences in the way the ocean responds to climate change. And society needs to be able to intelligently manage from a regional perspective, not just on a global perspective."
The research finding demonstrated "a cool, counterintuitive biological impact of this changing large scale circulation," said the GRL paper's lead author, Hilde Oliver, a postdoctoral scholar in Applied Ocean Physics and Engineering at WHOI. She recalled watching the instrument data come in. With typical summertime values of about 1-1.5 micrograms of chlorophyll per liter of seawater, researchers recorded "unheard of concentrations for chlorophyll in this region in summer," as high as 12 or 13 micrograms per liter, Oliver said.
Oliver, whose Ph.D. focused on modeling, said the cruise helped her to look at phytoplankton blooms from more than a theoretical sense. "To go out into the ocean and see how the physics of the ocean can manifest these blooms in the real world was eye opening to me," she said.
Another paper, A Regional, Early Spring Bloom of Phaeocystis pouchetii on the New England Continental Shelf, published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans (JGR: Oceans), also was eye opening. Researchers investigating the biological dynamics of the New England continental shelf in 2018 discovered a huge bloom of the haptophyte phytoplankton Phaeocystis pouchetii.
However, unlike the diatom hotspots described in the GRL paper, Phaeocystis is "unpalatable to a lot of different organisms and disrupts the entire food web," said Walker Smith, retired professor at the Virginia Institute of Marine Science William and Mary, who is the lead author on the JGR: Oceans paper. The phytoplankton form gelatinous colonies that are millimeters in diameter.
When Phaeocystis blooms, it utilizes nutrients just like any other form of phytoplankton would. However, unlike the diatoms noted in the GRL paper, Phaeocystis converts biomass into something that doesn't tend to get passed up the rest of the food chain, said McGillicuddy.
"Understanding the physical-biological interactions in the coastal system provides a basis for predicting these blooms of potentially harmful algae and may lead to a better prediction of their impacts on coastal systems," the authors stated.
Massive blooms of the colonial stage of this and similar species have been reported in many systems in different parts of the world, which Smith has studied. These types of blooms probably occur about every three years in the New England continental shelf and probably have a fairly strong impact on New England waters, food webs, and fisheries, said Smith. Coastal managers need to know about these blooms because they can have economic impacts on aquaculture in coastal areas, he said.
"Despite the fact that the Mid-Atlantic Bight has been well-studied and extensively sampled, there are things that are going on that we still don't really appreciate," said Smith. "One example are these Phaeocystis blooms that are deep in the water and that you are never going to see unless you are there because satellites can't show them. So, the more we look, the more we find out."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Do customer loyalty programs really help sellers make money?
2021-06-07
Key Takeaways:
Study finds non-tiered customer loyalty programs create a more sustainable customer base.
Non-tiered customer loyalty programs are not as likely to generate increases in spending per transaction or accelerate transactions.
CATONSVILLE, MD, June 7, 2021 - Customer loyalty programs have been around for decades and are used to help businesses, marketers and sellers build a sustainable relationship with their customers. But do they work? A recent study sought to find out and researchers learned that while yes, customer loyalty programs do work, perhaps not in ways most may assume.
There are two basic ...
Research advances one step closer to stem cell therapy for type 1 diabetes
2021-06-07
LA JOLLA--(June 7, 2021) Type 1 diabetes, which arises when the pancreas doesn't create enough insulin to control levels of glucose in the blood, is a disease that currently has no cure and is difficult for most patients to manage. Scientists at the Salk Institute are developing a promising approach for treating it: using stem cells to create insulin-producing cells (called beta cells) that could replace nonfunctional pancreatic cells.
In a study published on June 7, 2021, in the journal Nature Communications, the investigators reported that they have developed a new way to create beta cells that is much more efficient than previous methods. Additionally, when these beta cells were tested in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes, ...
Study suggests no link between antiseizure drugs used in pregnancy and cognitive problems in babies
2021-06-07
WHAT:
New findings published in JAMA Neurology suggest there is no difference in cognitive outcomes at age 2 among children of healthy women and children of women with epilepsy who took antiseizure medication during pregnancy. The findings are part of the large research project Maternal Outcomes and Neurodevelopmental Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs (MONEAD), which is a prospective, long-term study looking at outcomes in pregnant women with epilepsy and their children. The study was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), part of the National Institutes of Health. ...
Largest-ever pre-adolescent brain activation study reveals cognitive function maps
2021-06-07
Youth brain activation data from the largest longitudinal neuroimaging study to date provides valuable new information on the cognitive processes and brain systems that underlie adolescent development and might contribute to mental and physical health challenges in adulthood. The study published today online in END ...
Considering the potential and pitfalls of "Dr. GPT-3" in a clinic near you
2021-06-07
Artificial intelligence natural language computer applications are becoming increasingly sophisticated, raising the possibility that they could assume a greater role in health care, including interacting with patients. But before these applications enter the clinic, their potential and pitfalls need thoughtful exploration, states a new article in NPJ Digital Medicine.
The authors are Diane M. Korngiebel, a Hastings Center research scholar, and Sean D. Mooney, chief research information officer at University of Washington Medicine.
"There is compelling promise and serious hype in AI applications that generate natural language" Korngiebel and Mooney write, referring to OpenAI's Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3) ...
Researchers discover how cowpea mosaic plant virus activates immune system against cancer
2021-06-07
LEBANON, NH - Previous work by a team of researchers led by Steven N. Fiering, PhD, Immunology and Cancer Immunotherapy researcher at Dartmouth's and Dartmouth-Hitchcock's Norris Cotton Cancer Center and Nicole Steinmetz, PhD, Jacobs School of Engineering and Moores Cancer Center, University of California San Diego, showed that a plant virus that does not infect mammals, cowpea mosaic plant virus (CPMV), when injected into cancerous tumors, strongly stimulated the immune system to attack and often eliminate the tumor. However, very little was understood about immune recognition of plant viruses and how and why CPMV is exceptionally immuno-stimulating. In a new study, the team identifies ...
In Oregon, new gun violence restraining orders appear to be used as intended, but could be used more proactively
2021-06-07
Extreme risk protection orders (ERPOs), also known as gun violence restraining orders, are civil court orders that grant temporary restrictions on purchasing and possessing firearms for individuals determined by a civil court judge to be at extreme risk of committing violence against themselves or others. A new study examined ERPO use in Oregon in the first 15 months after it was adopted. The study found that while ERPOs are commonly considered as a tool to remove guns from dangerous individuals, they should also be considered as a tool to prevent gun purchases by dangerous individuals.
The study was conducted by researchers at Michigan State University (MSU), Columbia University, the University of Michigan, and Johns Hopkins University. It appears in ...
Trained viruses prove more effective at fighting antibiotic resistance
2021-06-07
The threat of antibiotic resistance rises as bacteria continue to evolve to foil even the most powerful modern drug treatments. By 2050, antibiotic resistant-bacteria threaten to claim more than 10 million lives as existing therapies prove ineffective.
Bacteriophage, or "phage," have become a new source of hope against growing antibiotic resistance. Ignored for decades by western science, phages have become the subject of increasing research attention due to their capability to infect and kill bacterial threats.
A new project led by University of California San Diego Biological Sciences graduate ...
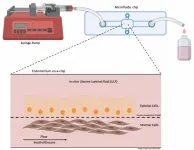
Chip mimicking bovine endometrium used in study of factors that can jeopardize pregnancy
2021-06-07
To investigate factors that can jeopardize pregnancy success in cattle, researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil used a kind of chip to mimic the environment of the endometrium, the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus.
The study was conducted by biologist Tiago Henrique Camara de Bem, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of São Paulo's School of Animal Science and Food Engineering (FZEA-USP), in collaboration with four researchers at the University of Leeds in the UK. Their findings are reported in an article in the journal Endocrinology.
The researchers focused on analyzing alterations in levels of insulin and glucose in maternal ...
New drug-formulation method may lead to smaller pills
2021-06-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- About 60 percent of drugs on the market have hydrophobic molecules as their active ingredients. These drugs, which are not soluble in water, can be difficult to formulate into tablets because they need to be broken down into very small crystals in order to be absorbed by the human body.
A team of MIT chemical engineers has now devised a simpler process for incorporating hydrophobic drugs into tablets or other drug formulations such as capsules and thin films. Their technique, which involves creating an emulsion of the drug and then crystallizing it, allows for a more powerful dose to be loaded per tablet.
"This is very important because if we can achieve high drug loading, it means that we can ...