Largest-ever pre-adolescent brain activation study reveals cognitive function maps
Data from largest study of its kind will clarify risk factors for mental health challenges
2021-06-07
(Press-News.org) Youth brain activation data from the largest longitudinal neuroimaging study to date provides valuable new information on the cognitive processes and brain systems that underlie adolescent development and might contribute to mental and physical health challenges in adulthood. The study published today online in END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Considering the potential and pitfalls of "Dr. GPT-3" in a clinic near you
2021-06-07
Artificial intelligence natural language computer applications are becoming increasingly sophisticated, raising the possibility that they could assume a greater role in health care, including interacting with patients. But before these applications enter the clinic, their potential and pitfalls need thoughtful exploration, states a new article in NPJ Digital Medicine.
The authors are Diane M. Korngiebel, a Hastings Center research scholar, and Sean D. Mooney, chief research information officer at University of Washington Medicine.
"There is compelling promise and serious hype in AI applications that generate natural language" Korngiebel and Mooney write, referring to OpenAI's Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3) ...
Researchers discover how cowpea mosaic plant virus activates immune system against cancer
2021-06-07
LEBANON, NH - Previous work by a team of researchers led by Steven N. Fiering, PhD, Immunology and Cancer Immunotherapy researcher at Dartmouth's and Dartmouth-Hitchcock's Norris Cotton Cancer Center and Nicole Steinmetz, PhD, Jacobs School of Engineering and Moores Cancer Center, University of California San Diego, showed that a plant virus that does not infect mammals, cowpea mosaic plant virus (CPMV), when injected into cancerous tumors, strongly stimulated the immune system to attack and often eliminate the tumor. However, very little was understood about immune recognition of plant viruses and how and why CPMV is exceptionally immuno-stimulating. In a new study, the team identifies ...
In Oregon, new gun violence restraining orders appear to be used as intended, but could be used more proactively
2021-06-07
Extreme risk protection orders (ERPOs), also known as gun violence restraining orders, are civil court orders that grant temporary restrictions on purchasing and possessing firearms for individuals determined by a civil court judge to be at extreme risk of committing violence against themselves or others. A new study examined ERPO use in Oregon in the first 15 months after it was adopted. The study found that while ERPOs are commonly considered as a tool to remove guns from dangerous individuals, they should also be considered as a tool to prevent gun purchases by dangerous individuals.
The study was conducted by researchers at Michigan State University (MSU), Columbia University, the University of Michigan, and Johns Hopkins University. It appears in ...
Trained viruses prove more effective at fighting antibiotic resistance
2021-06-07
The threat of antibiotic resistance rises as bacteria continue to evolve to foil even the most powerful modern drug treatments. By 2050, antibiotic resistant-bacteria threaten to claim more than 10 million lives as existing therapies prove ineffective.
Bacteriophage, or "phage," have become a new source of hope against growing antibiotic resistance. Ignored for decades by western science, phages have become the subject of increasing research attention due to their capability to infect and kill bacterial threats.
A new project led by University of California San Diego Biological Sciences graduate ...
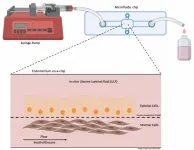
Chip mimicking bovine endometrium used in study of factors that can jeopardize pregnancy
2021-06-07
To investigate factors that can jeopardize pregnancy success in cattle, researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil used a kind of chip to mimic the environment of the endometrium, the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus.
The study was conducted by biologist Tiago Henrique Camara de Bem, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of São Paulo's School of Animal Science and Food Engineering (FZEA-USP), in collaboration with four researchers at the University of Leeds in the UK. Their findings are reported in an article in the journal Endocrinology.
The researchers focused on analyzing alterations in levels of insulin and glucose in maternal ...
New drug-formulation method may lead to smaller pills
2021-06-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- About 60 percent of drugs on the market have hydrophobic molecules as their active ingredients. These drugs, which are not soluble in water, can be difficult to formulate into tablets because they need to be broken down into very small crystals in order to be absorbed by the human body.
A team of MIT chemical engineers has now devised a simpler process for incorporating hydrophobic drugs into tablets or other drug formulations such as capsules and thin films. Their technique, which involves creating an emulsion of the drug and then crystallizing it, allows for a more powerful dose to be loaded per tablet.
"This is very important because if we can achieve high drug loading, it means that we can ...
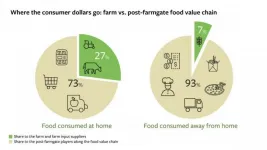
From farm to plate: Where do global consumer dollars flow?
2021-06-07
ITHACA, N.Y. - As soon as an ear of corn is taken off its stalk or a potato is pulled from the ground, it travels anywhere from a few miles to across continents and sometimes undergoes processes that transform it into the food we consume.
These miles and processes contribute to what's known as the food value chain (FVC), along which, as one might expect, the value of the product increases. However, most of the research and attention thus far paid to FVCs occurs at the ends of the chain - inside the farm gate and at the consumer's plate.
Less is understood about all of the other links in the FVC, in part due to a lack of ...
Saudi Arabians: Somatic mutations in breast cancer: New opportunities
2021-06-07
Oncotarget published "Landscape of somatic mutations in breast cancer: new opportunities for targeted therapies in Saudi Arabian patients" which reported that the association between genetic polymorphisms in tumor suppressor genes and the risk of BCa has been studied in many ethnic populations with conflicting conclusions while Arab females and Saudi Arabian studies are still lacking.
The authors screened a cohort of Saudi BCa patients by NGS using a bespoke gene panel to clarify the genetic landscape of this population, correlating and assessing genetic ...
Football and team handball training may increase health span and, ultimately, lifespan
2021-06-07
In the quest for healthy aging and longer lifespan, Danish researchers at the University of Southern Denmark have collaborated with Swedish researchers at Karolinska Institutet to explore the anti-aging effects of football and team handball training in women.
In a current study published in Scientific Reports, the researchers investigated the effects of lifelong regular exercise on two of the central hallmarks of aging combined and showed that football and team handball have a positive effect on telomere length and mitochondrial function in women.
"Our legacy consists of DNA that is packed in chromosomes. When cells divide, the inheritance is copied, but with each cell division the ends of the DNA threads get shorter. The so-called telomeres are shortened, which causes us to age. ...
Unexpected discovery opens a new way to regulate blood pressure
2021-06-07
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is the leading modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular diseases and premature death worldwide. And key to treating patients with conditions ranging from chest pain to stroke is understanding the intricacies of how the cells around arteries and other blood vessels work to control blood pressure. While the importance of metals like potassium and calcium in this process are known, a new discovery about a critical and underappreciated role of another metal - zinc - offers a potential new pathway for therapies to treat hypertension.
The study results were published recently in Nature Communications.
All the body's functions depend on arteries channeling oxygen-rich ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Largest-ever pre-adolescent brain activation study reveals cognitive function mapsData from largest study of its kind will clarify risk factors for mental health challenges