(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. - As soon as an ear of corn is taken off its stalk or a potato is pulled from the ground, it travels anywhere from a few miles to across continents and sometimes undergoes processes that transform it into the food we consume.
These miles and processes contribute to what's known as the food value chain (FVC), along which, as one might expect, the value of the product increases. However, most of the research and attention thus far paid to FVCs occurs at the ends of the chain - inside the farm gate and at the consumer's plate.
Less is understood about all of the other links in the FVC, in part due to a lack of standardized data and methods that can be applied universally. Many studies have been done on individual commodities, or in a single country, but coming up with an international method of analyzing FVCs has been elusive until now.
A team of researchers - led by Chris Barrett and Miguel Gómez, Cornell University professors in the Charles H. Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management - has developed the "Global Food Dollar" method, which distributes the consumer's net purchasing dollar across all farm and post-farmgate activities.
"The key insight, from my perspective, is that the overwhelming majority of the value addition is happening after the farm gate," Barrett said. "People fall into thinking of food issues as being farm issues. And farm issues are important, but they're comparatively less important than most people realize. And they're becoming steadily less important over time."
Their methodology expands on the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Economic Research Service (ERS), "food dollar series," published annually since 1947 but updated by Patrick Canning in 2011 to include modern inputs.
"People really don't understand how consumer dollars get apportioned, either between owners of land and intellectual property and workers, or between actors in different stages along the value chain," Barrett said. "And they don't know how that differs across countries. ... How much are you likely to get if you're a Sysco and you're thinking of entering a market to mediate wholesale food delivery?"
"We have lots of data on food production and food consumption," Gómez said, "but not much in between. And it's important, because 80% to 85% of the value is created beyond the farm."
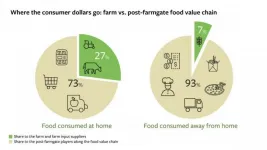
For this research, the team used data collected from 2005-15 from 61 countries, representing 90% of the global economy. They found that farmers receive, on average, 27% of consumer expenditure on foods consumed at home, and a far lower percentage, just 7%, on food consumed away from home (in restaurants, for instance). And as countries' income goes up, the share goes down.
One of the main takeaways, Barrett said, is that more research is needed on all the links in the middle of the value chain.
"The big economic players in the food we consume aren't actually the primary producers on farms," Barrett said. "So when we think about food issues ... maybe we need to spend a little bit more time thinking about what's happening in that post-farmgate value chain, with the processors, manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers and restaurants."
INFORMATION:
"The Overlooked Magnitude of Post-Farmgate Food Value Chains," published in Nature Food, was written, and the method developed, as part of a partnership with the ERS, led by Canning, a co-author on the study.
Oncotarget published "Landscape of somatic mutations in breast cancer: new opportunities for targeted therapies in Saudi Arabian patients" which reported that the association between genetic polymorphisms in tumor suppressor genes and the risk of BCa has been studied in many ethnic populations with conflicting conclusions while Arab females and Saudi Arabian studies are still lacking.
The authors screened a cohort of Saudi BCa patients by NGS using a bespoke gene panel to clarify the genetic landscape of this population, correlating and assessing genetic ...
In the quest for healthy aging and longer lifespan, Danish researchers at the University of Southern Denmark have collaborated with Swedish researchers at Karolinska Institutet to explore the anti-aging effects of football and team handball training in women.
In a current study published in Scientific Reports, the researchers investigated the effects of lifelong regular exercise on two of the central hallmarks of aging combined and showed that football and team handball have a positive effect on telomere length and mitochondrial function in women.
"Our legacy consists of DNA that is packed in chromosomes. When cells divide, the inheritance is copied, but with each cell division the ends of the DNA threads get shorter. The so-called telomeres are shortened, which causes us to age. ...
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is the leading modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular diseases and premature death worldwide. And key to treating patients with conditions ranging from chest pain to stroke is understanding the intricacies of how the cells around arteries and other blood vessels work to control blood pressure. While the importance of metals like potassium and calcium in this process are known, a new discovery about a critical and underappreciated role of another metal - zinc - offers a potential new pathway for therapies to treat hypertension.
The study results were published recently in Nature Communications.
All the body's functions depend on arteries channeling oxygen-rich ...
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to disrupt and end lives around the world, and public health officials worldwide have recognized vaccines as the critical tools required for controlling the COVID-19 death toll and achieving a return to normal life. Several vaccines against COVID-19 are already in use, but the limited supplies of these vaccines and the possibility of safety and efficacy issues of the existing vaccines mean that it is important for scientists to develop more (and even better) vaccines. In fact, as of February 2021, 69 different vaccines are in various phases of clinical development.
One type of vaccine that could prove quite useful is the inactivated vaccine, which contains an inactivated form of the virus. The inactivated virus cannot harm the recipient, but ...
A new study published in the journal Diversity and Distributions predicts massive range declines of Africa's great apes - gorillas, chimpanzees and bonobos - due to the impacts of climate change, land-use changes and human population growth.
For their analysis, the authors compiled information on African ape occurrence held in the IUCN SSC A.P.E.S. database, a repository that includes a remarkable amount of information on population status, threats and conservation for several hundred sites, collected over 20 years.
The first-of-its-kind study quantifies the joint effects of climate, land-use, and human population changes across African ape ranges for the year ...
Oncotarget published "Effect of cell microenvironment on the drug sensitivity of hepatocellular cancer cells" which reported that this study aimed to investigate whether Hepatocellular Cancer (HCC) cells cultured in more native conditions have an altered phenotype and drug sensitivity compared to those cultured in standard conditions.
Six HCC cell lines were cultured in "standard" or more "native" conditions.
HCC cells cultured in native conditions had slower doubling times, increased HK2 and GLUT, lower PHDA and ATP levels, and mutations in mitochondrial DNA.
From 90 comparisons of drug sensitivity, increased resistance ...
Oncotarget published "Mutually exclusive lymphangiogenesis or perineural infiltration in human skin squamous-cell carcinoma" which reported that although tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis correlates with metastasis and poor prognosis in several cancers, it also supports T cell infiltration into the tumor and predicts favorable outcome to immunotherapy.
Using quantitative multiplex immunohistochemistry, the authors analyzed skin squamous-cell carcinoma (sSCC) sections from 36 patients.
CD8 T cell infiltration showed great differences between patients, whereby these ...
ADELPHI, Md. -- Army researchers developed a pioneering framework that provides a baseline for the development of collaborative multi-agent systems.
The framework is detailed in the survey paper Survey of recent multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithms utilizing centralized training, which is featured in the SPIE Digital Library. Researchers said the work will support research in reinforcement learning approaches for developing collaborative multi-agent systems such as teams of robots that could work side-by-side with future Soldiers.
"We propose that the underlying information sharing mechanism plays a critical role in centralized learning for multi-agent systems, ...
WASHINGTON -- For more than 25 years, Burmese pythons have been living and breeding in the Florida Everglades where they prey on native wildlife and disrupt the region's delicate ecosystems. A new study shows that infrared cameras could make it easier to spot these invasive snakes in the Florida foliage, providing a new tool in the effort to remove them.
In the Optical Society (OSA) journal Applied Optics, researchers led by Dr. Kyle Renshaw from the University of Central Florida College of Optics and Photonics report that a near infrared camera helped people detect Burmese pythons at distances up to 1.3 times farther away than was possible using a traditional visible-wavelength ...
AMES, Iowa - Scientists have invested great time and effort into making connections between a plant's genotype, or its genetic makeup, and its phenotype, or the plant's observable traits. Understanding a plant's genome helps plant biologists predict how that plant will perform in the real world, which can be useful for breeding crop varieties that will produce high yields or resist stress.
But environmental conditions play a role as well. Plants with the same genotype will perform differently when grown in different environments. A new study led by an Iowa State University scientist uses advanced data analytics to help scientists understand ...