(Press-News.org) Oncotarget published "Mutually exclusive lymphangiogenesis or perineural infiltration in human skin squamous-cell carcinoma" which reported that although tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis correlates with metastasis and poor prognosis in several cancers, it also supports T cell infiltration into the tumor and predicts favorable outcome to immunotherapy.
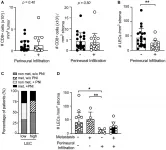
Using quantitative multiplex immunohistochemistry, the authors analyzed skin squamous-cell carcinoma (sSCC) sections from 36 patients.
CD8 T cell infiltration showed great differences between patients, whereby these cells were mainly excluded from the tumor mass. Similar to our data in melanoma, sSCC with high density of lymphatic endothelial cells showed increased CD8 T cell density in tumor areas.
An entirely new observation is that sSCC with perineural infiltration but without metastasis was characterized by low lymphatic endothelial cell density.
Since both metastasis and perineural infiltration are known to affect tumor progression and patients' prognosis, it is important to identify the molecular drivers, opening future options for therapeutic targeting. This Oncotarget data suggest that the mechanisms underlying perineural infiltration may be linked with the biology of lymphatic vessels and thus stroma.
Dr. Karin Schaeuble from The University Hospital Lausanne said, "Over the last few years, oncology research is increasingly focused on the understanding of mutual interactions between cancer, stromal and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment."
"Over the last few years, oncology research is increasingly focused on the understanding of mutual interactions between cancer, stromal and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment."
Specific growth factors like vascular endothelial growth factor -C and -D secreted by tumor cells and/or immune cells stimulate lymphangiogenesis in the vicinity of the tumor.
Lymphatic vessels offer a route for cancer cells to disseminate, enhanced by secretion of different chemokines such as CCL21 that actively supports tumor cell invasion into lymphatic vessels and promotes lymph node metastases.
Investigations into the immune cell composition showed the presence of various immune cells in sSCC.
On the other hand, the presence of lymphatic vessels in the tumour immune microenvironment (TME) has also been shown to support adaptive anti-tumoral immune responses by carrying immune cells and antigens to the draining LNs.
For further investigation of possible associations of lymphatic vessels with stroma and T cells, they performed a comprehensive analysis of the abundance and localization of lymphatic vessels in 36 patients with sSCC.
The Schaeuble Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Output that an entirely new observation is that perineural infiltrated sSCC in absence of metastases are characterized by low LVD compared to tumors without PNI.
Since both are known to affect tumor progression and patients' prognosis, it may be particularly important to identify the underlying mechanisms triggering either lymphangiogenesis or PNI, thus opening future options for therapeutic targeting.
INFORMATION:
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27915
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/27915/text/
Correspondence to - Karin Schaeuble - karin.schauble@unil.ch
Keywords - lymphatic vessel, CD8+ T cell, perineural infiltration, skin squamous-cell carcinoma, tumor immunology
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a bi-weekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
18009220957x105
Copyright © 2021 Impact Journals, LLC
Impact Journals is a registered trademark of Impact Journals, LLC
ADELPHI, Md. -- Army researchers developed a pioneering framework that provides a baseline for the development of collaborative multi-agent systems.
The framework is detailed in the survey paper Survey of recent multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithms utilizing centralized training, which is featured in the SPIE Digital Library. Researchers said the work will support research in reinforcement learning approaches for developing collaborative multi-agent systems such as teams of robots that could work side-by-side with future Soldiers.
"We propose that the underlying information sharing mechanism plays a critical role in centralized learning for multi-agent systems, ...
WASHINGTON -- For more than 25 years, Burmese pythons have been living and breeding in the Florida Everglades where they prey on native wildlife and disrupt the region's delicate ecosystems. A new study shows that infrared cameras could make it easier to spot these invasive snakes in the Florida foliage, providing a new tool in the effort to remove them.
In the Optical Society (OSA) journal Applied Optics, researchers led by Dr. Kyle Renshaw from the University of Central Florida College of Optics and Photonics report that a near infrared camera helped people detect Burmese pythons at distances up to 1.3 times farther away than was possible using a traditional visible-wavelength ...
AMES, Iowa - Scientists have invested great time and effort into making connections between a plant's genotype, or its genetic makeup, and its phenotype, or the plant's observable traits. Understanding a plant's genome helps plant biologists predict how that plant will perform in the real world, which can be useful for breeding crop varieties that will produce high yields or resist stress.
But environmental conditions play a role as well. Plants with the same genotype will perform differently when grown in different environments. A new study led by an Iowa State University scientist uses advanced data analytics to help scientists understand ...
A study conducted by a group of Brazilian researchers contributes to a deeper understanding of the molecular basis for schizophrenia, and potentially to the development of more specific and effective treatments for the disease. The medications currently available on the market act generically on the brain and can have severe adverse side effects.
Treatment of post-mortem samples from the hippocampus of schizophrenic patients with an NMDA receptor antagonist pointed to biological processes associated with the disease that are specific to neurons and oligodendrocytes. NMDA receptors are neurotransmitter receptors located in the postsynaptic ...
In those with fatty liver disease, a person's fat goes to their liver instead of their fat tissue, either because of an absence of fat depots, which is seen in the rare genetic disease lipodystrophy, or because the depots are too full, which is seen in people with obesity.
One third of these people will go on to develop nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH - an advanced form of fatty liver disease brought on by progressive inflammation and scarring in the organ.
In 2002, Michigan Medicine endocrinologist Elif Oral, M.D., who had just moved from the National Institutes of Health at the time, published her discovery that patients with severe lipodystrophy lack leptin, a hormone that helps curb appetite and control weight gain. When given ...
BOSTON - Automated emails and letters that provide personalized feedback related to cafeteria purchases at work may help employees make healthier food choices. That's the conclusion of a new study that was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and is published in END ...
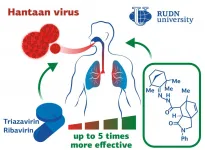
RUDN University chemists and their colleagues from Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk Institute of Organic Chemistry and The State Research Center of Virology and Biotechnology VECTOR have obtained a new class of compounds that inhibit the replication of the deadly Hantaan virus that affects blood vessels and internal organs of humans. The resulting substances were 5 times more effective than existing antiviral drugs. The results have been published Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters.
The Hantaan virus causes acute haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). The disease ...
Microgravity in space perturbs human physiology and is detrimental for astronaut health, a fact first realized during early Apollo missions when astronauts experienced inner ear disturbances, heart arrhythmia, low blood pressure, dehydration, and loss of calcium from their bones after their missions.
One of the most striking observations from Apollo missions was that just over half of astronauts became sick with colds or other infections within a week of returning to Earth. Some astronauts have even experienced re-activation of dormant viruses, such as the chickenpox virus. These findings stimulated studies on the effects of weak gravity, or ...
A new study from researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and colleagues suggests a slowdown in the use of convalescent plasma to treat hospitalized COVID-19 patients led to a higher COVID-19 mortality during a critical period during this past winter's surge.
U.S. hospitals began treating COVID-19 patients with convalescent plasma therapy--which uses antibody-rich blood from recovered COVID-19 patients--in the summer of 2020 when doctors were looking to identify treatments for the emerging disease. By the spring of 2021, doctors in the United States had treated over 500,000 COVID-19 patients with convalescent plasma. The use ...
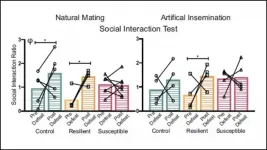
Male mice more susceptible to stress can pass down their behaviors to offspring via changes in their sperm's genetic code, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Stressful experiences alter gene expression, which parents can pass down to their offspring. But it was unclear if sperm itself transmits this information, or if behavioral cues between the parents play a larger role.
Cunningham et al. tracked the stress response of male mice after ten days of chronic stress and sorted them into resilient and susceptible groups, based on the severity of their response. The offspring of resilient and control mice showed decreased stress behaviors ...