(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA--(June 7, 2021) Type 1 diabetes, which arises when the pancreas doesn't create enough insulin to control levels of glucose in the blood, is a disease that currently has no cure and is difficult for most patients to manage. Scientists at the Salk Institute are developing a promising approach for treating it: using stem cells to create insulin-producing cells (called beta cells) that could replace nonfunctional pancreatic cells.
In a study published on June 7, 2021, in the journal Nature Communications, the investigators reported that they have developed a new way to create beta cells that is much more efficient than previous methods. Additionally, when these beta cells were tested in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes, the animals' blood sugar was brought under control within about two weeks.
"Stem cells are an extremely promising approach for developing many cell therapies, including better treatments for type 1 diabetes," says Salk Professor Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte, the paper's senior author. "This method for manufacturing large numbers of safe and functional beta cells is an important step forward."
In the current work, the investigators started with human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs). These cells, which can be derived from adult tissues (most often the skin), have the potential to become any kind of cell found in the adult body. Using various growth factors and chemicals, the investigators coaxed hPSCs into beta cells in a stepwise fashion that mimicked pancreatic development.
Producing beta cells from hPSCs in the lab is not new, but in the past the yields of these precious cells have been low. With existing methods, only about 10 to 40 percent of cells become beta cells. By comparison, techniques used to create nerve cells from hPSCs have yields of about 80 percent. Another issue is that if undifferentiated cells are left in the mix, they could eventually turn into another kind cell that would be unwanted.
"In order for beta cell-based treatments to eventually become a viable option for patients, it's important to make these cells easier to manufacture," says co-first author Haisong Liu, a former member of the Belmonte lab. "We need to find a way to optimize the process."
To address the problem, the researchers took a stepwise approach to create beta cells. They identified several chemicals that are important for inducing hPSCs to become more specialized cells. They ultimately identified several cocktails of chemicals that resulted in beta cell yields of up to 80 percent.
They also looked at the ways in which these cells are grown in the lab. "Normally cells are grown on a flat plate, but we allowed them to grow in three dimensions," says co-first author Ronghui Li, a postdoctoral fellow in the Belmonte lab. Growing the cells in this way creates more shared surface area between the cells and allows them to influence each other, just as they would during human development.
After the cells were created, they were transplanted into a mouse model of type 1 diabetes, The model mice had a modified immune system that would not reject transplanted human cells. "We found that within two weeks these mice had a reduction of their high blood sugar level into normal range," says co-first author Hsin-Kai Liao, a staff researcher in the Belmonte lab. "The transplanted hPSC-derived beta cells were biologically functional."
The researchers will continue to study this technique in the lab to further optimize the production of beta cells. More research is needed to assess safety issues before clinical trials can be initiated in humans. The investigators say the methods reported in this paper may also be useful for developing specialized cells to treat other diseases.
INFORMATION:
Other authors included Chao Wang, Yang Yu, Lei Shi, and Jiameng Dan of Salk; Zheying Min of Peking University; Alberto Hayek of the University of California San Diego; and Llanos Martinez Martinez and Estrella Nuñez Delicado of Universidad Católica San Antonio de Murcia, in Spain.
This work was funded by Universidad Cato?lica San Antonio de Murcia, Primafrio, The Larry L. Hillblom Foundation, The Moxie Foundation, and Diabetes Research Connection (Project Number: 15; Institution Project Number: Liu-DRC-2019).
About the Salk Institute for Biological Studies:
Every cure has a starting point. The Salk Institute embodies Jonas Salk's mission to dare to make dreams into reality. Its internationally renowned and award-winning scientists explore the very foundations of life, seeking new understandings in neuroscience, genetics, immunology, plant biology and more. The Institute is an independent nonprofit organization and architectural landmark: small by choice, intimate by nature and fearless in the face of any challenge. Be it cancer or Alzheimer's, aging or diabetes, Salk is where cures begin. Learn more at: salk.edu.
WHAT:
New findings published in JAMA Neurology suggest there is no difference in cognitive outcomes at age 2 among children of healthy women and children of women with epilepsy who took antiseizure medication during pregnancy. The findings are part of the large research project Maternal Outcomes and Neurodevelopmental Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs (MONEAD), which is a prospective, long-term study looking at outcomes in pregnant women with epilepsy and their children. The study was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), part of the National Institutes of Health. ...
Youth brain activation data from the largest longitudinal neuroimaging study to date provides valuable new information on the cognitive processes and brain systems that underlie adolescent development and might contribute to mental and physical health challenges in adulthood. The study published today online in END ...
Artificial intelligence natural language computer applications are becoming increasingly sophisticated, raising the possibility that they could assume a greater role in health care, including interacting with patients. But before these applications enter the clinic, their potential and pitfalls need thoughtful exploration, states a new article in NPJ Digital Medicine.
The authors are Diane M. Korngiebel, a Hastings Center research scholar, and Sean D. Mooney, chief research information officer at University of Washington Medicine.
"There is compelling promise and serious hype in AI applications that generate natural language" Korngiebel and Mooney write, referring to OpenAI's Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3) ...
LEBANON, NH - Previous work by a team of researchers led by Steven N. Fiering, PhD, Immunology and Cancer Immunotherapy researcher at Dartmouth's and Dartmouth-Hitchcock's Norris Cotton Cancer Center and Nicole Steinmetz, PhD, Jacobs School of Engineering and Moores Cancer Center, University of California San Diego, showed that a plant virus that does not infect mammals, cowpea mosaic plant virus (CPMV), when injected into cancerous tumors, strongly stimulated the immune system to attack and often eliminate the tumor. However, very little was understood about immune recognition of plant viruses and how and why CPMV is exceptionally immuno-stimulating. In a new study, the team identifies ...
Extreme risk protection orders (ERPOs), also known as gun violence restraining orders, are civil court orders that grant temporary restrictions on purchasing and possessing firearms for individuals determined by a civil court judge to be at extreme risk of committing violence against themselves or others. A new study examined ERPO use in Oregon in the first 15 months after it was adopted. The study found that while ERPOs are commonly considered as a tool to remove guns from dangerous individuals, they should also be considered as a tool to prevent gun purchases by dangerous individuals.
The study was conducted by researchers at Michigan State University (MSU), Columbia University, the University of Michigan, and Johns Hopkins University. It appears in ...
The threat of antibiotic resistance rises as bacteria continue to evolve to foil even the most powerful modern drug treatments. By 2050, antibiotic resistant-bacteria threaten to claim more than 10 million lives as existing therapies prove ineffective.
Bacteriophage, or "phage," have become a new source of hope against growing antibiotic resistance. Ignored for decades by western science, phages have become the subject of increasing research attention due to their capability to infect and kill bacterial threats.
A new project led by University of California San Diego Biological Sciences graduate ...
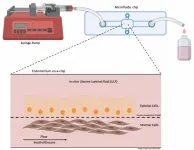
To investigate factors that can jeopardize pregnancy success in cattle, researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil used a kind of chip to mimic the environment of the endometrium, the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus.
The study was conducted by biologist Tiago Henrique Camara de Bem, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of São Paulo's School of Animal Science and Food Engineering (FZEA-USP), in collaboration with four researchers at the University of Leeds in the UK. Their findings are reported in an article in the journal Endocrinology.
The researchers focused on analyzing alterations in levels of insulin and glucose in maternal ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- About 60 percent of drugs on the market have hydrophobic molecules as their active ingredients. These drugs, which are not soluble in water, can be difficult to formulate into tablets because they need to be broken down into very small crystals in order to be absorbed by the human body.
A team of MIT chemical engineers has now devised a simpler process for incorporating hydrophobic drugs into tablets or other drug formulations such as capsules and thin films. Their technique, which involves creating an emulsion of the drug and then crystallizing it, allows for a more powerful dose to be loaded per tablet.
"This is very important because if we can achieve high drug loading, it means that we can ...
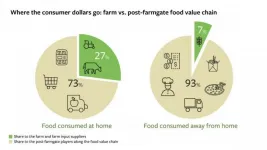
ITHACA, N.Y. - As soon as an ear of corn is taken off its stalk or a potato is pulled from the ground, it travels anywhere from a few miles to across continents and sometimes undergoes processes that transform it into the food we consume.
These miles and processes contribute to what's known as the food value chain (FVC), along which, as one might expect, the value of the product increases. However, most of the research and attention thus far paid to FVCs occurs at the ends of the chain - inside the farm gate and at the consumer's plate.
Less is understood about all of the other links in the FVC, in part due to a lack of ...
Oncotarget published "Landscape of somatic mutations in breast cancer: new opportunities for targeted therapies in Saudi Arabian patients" which reported that the association between genetic polymorphisms in tumor suppressor genes and the risk of BCa has been studied in many ethnic populations with conflicting conclusions while Arab females and Saudi Arabian studies are still lacking.
The authors screened a cohort of Saudi BCa patients by NGS using a bespoke gene panel to clarify the genetic landscape of this population, correlating and assessing genetic ...