AI could soon tell you, how often to see the eye doctor
2021-06-08
(Press-News.org) Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the most common cause of vision loss in people over 50. Up to 12 percent of those over 80 have the chronic disease. An estimated 16.4 million adults are affected by retinal vein occlusion (RVO) worldwide, a condition caused by a thrombosis of a retinal vein. It is the second most common cause of blindness from retinal vascular disease after diabetic retinopathy (DR). DR in turn is the leading cause of blindness in developed countries and affects up to 80 percent of people with more than 20 years of diabetes. It can lead to a swelling of the macula (diabetic macular edema, DME), which may cause partial or complete vision loss.
All three conditions are treated by injections of a so-called anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) into the eye at intervals to slow down disease progress and prevent blindness. Because with eyesight a central human sense is in jeopardy, patients are eager to know that they are being treated often enough to avoid rapid worsening. And doctors want to make sure they see each patient frequently enough not to miss important developments.
The challenge
With the ageing population, cases of AMD, RVO or DME are globally on the rise, making it hard for specialized eye clinics to keep up with the growing demand for regular treatments. "As doctors, we want to give each patient the necessary attention and treatment frequency that they need", says Sebastian Wolf, Head of the Ophthalmology Department of the Inselspital that currently sees 6000 patients with AMD, RVO and DR. "But it is also an organizational challenge to meet all patients' needs and be able to study all relevant eye imaging data to assess individual disease progression and take treatment decisions in the short time given."
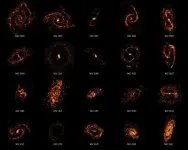
To monitor progression of the chronic eye conditions, Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), an imaging tool that generates 3D images of the eye at extremely high resolution, is usually applied. In collaboration with the ARTORG Center for Biomedical Engineering Research, the Inselspital has developed automated OCT analysis tools based on artificial intelligence, which can assist eye doctors in the assessment of a whole patient OCT-set in just a few seconds. Together with RetinAI, a startup specialized in AI-based eye care technologies, they now have conducted a retrospective study of patients to assess how well AI can predict anti-VEGF treatment demand from the start.
The setup
The study looked at OCT-data from 340 patients with AMD and 285 patients with RVO or DME, treated with anti-VEGF at the Inselspital between 2014 and 2018. Based on morphological features automatically extracted from the OCT volumes at baseline and after two consecutive visits, as well as patient demographic information, two machine learning models were trained to predict the probability of the long-term treatment frequency demand of a new patient (one for AMD and one for RVO and DME).
Based on the first three visits, it was possible to predict if a patient had a low or a high treatment demand for both the AMD and the RVO & DME groups with similar high accuracy. More importantly, the study revealed that it is possible to predict reasonably well at the initial visit and even before the first injection if a patient will less often require injections.
Three advantages
"We have shown that machine learning classifiers can predict treatment demand when a patient is first diagnosed with a chronic eye disease," says Mathias Gallardo, postdoctoral researcher the ARTORG AI in Medical Imaging (AIMI) lab and member of the new Center for Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (CAIM). "Hence, artificial intelligence may assist in establishing patient-specific treatment plans for the most common chronic eye conditions in the near future."
Planning the ideal treatment frequency for each patient has multiple benefits. Firstly, patients can be sure their disease is being treated in the best way possible without subjecting them to too frequent visits and unpleasant injections into the eye. Secondly, individualized planning can help clinics cope with ever growing patient numbers allowing for the highest possible capacity utilization of specialized medical skills and infrastructure. Thirdly, objectivized on-demand planning helps avoid overprovision and can lead to improved cost-efficiency and less healthcare expenditures.
High-yield confluence of clinical, data science, and industrial research
This study illustrates once more the proven eye-level collaboration between clinicians and data scientists of the Inselspital and the ARTORG Center, which produces technology solutions suitable for everyday use because they were designed directly as a response to clinical needs. A further important aspect to provide a roadmap for the clinical implementation of such technology was the startup RetinAI. "We are extremely happy to apply the EU funding we received to build patient-focused solutions in ophthalmology, making sure that technology can be transformed into products that can really benefit patients and improve treatment at scale," says RetinAI CEO Carlos Ciller. With its headquarters at sitem-insel the startup also is spatially located exactly at the interface between clinic and science. This unique Bernese environment for clinically driven AI technologies will be further capitalized by the new Center for Artifical Intelligence in Medicine (CAIM), combining the best of the three worlds of healthcare, science, and industry for the benefit of patients.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-08
A defining characteristic of all life is its ability to evolve. However, the fact that biologically engineered systems will evolve when used has, to date, mostly been ignored. This has resulted in biotechnologies with a limited functional shelf-life that fail to make use of the powerful evolutionary capabilities inherent to all biology.
Sim Castle, first author of the research, published in Nature Communications, and a PhD student in the School of Biological Sciences at Bristol, explained the motivation for the work: "The thing that has always fascinated me about biology is that it changes, it is chaotic, it adapts, it evolves. Bioengineers therefore do not just design static artefacts - they design living populations that ...
2021-06-08
The presence of amino acids on the prebiotic Earth is widely accepted, either coming from endogenous chemical processes or being delivered by extraterrestrial material. On the other hand, plausibly prebiotic pathways to peptides often rely on different aqueous approaches where condensation of amino acids is thermodynamically unfavorable. Now, chemists from the Ruđer Bošković Institute (RBI), in collaboration with colleagues from Xellia Pharmaceuticals, have shown that solid-state mechanochemical activation of glycine and alanine in combination with mineral surfaces leads to the formation of peptides. ...
2021-06-08
A team of astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) has completed the first census of molecular clouds in the nearby Universe, revealing that contrary to previous scientific opinion, these stellar nurseries do not all look and act the same. In fact, they're as diverse as the people, homes, neighborhoods, and regions that make up our own world.
Stars are formed out of clouds of dust and gas called molecular clouds, or stellar nurseries. Each stellar nursery in the Universe can form thousands or even tens of thousands of new stars during its lifetime. Between 2013 and 2019, astronomers on the PHANGS-- Physics at High Angular Resolution in Nearby GalaxieS-- project conducted the first systematic survey of 100,000 stellar nurseries ...
2021-06-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Astronomers have taken a big step forward in understanding the dark and violent places where stars are born.
Over the past five years, an international team of researchers has conducted the first systematic survey of "stellar nurseries" across our part of the universe, charting the more than 100,000 of these nurseries across more than 90 nearby galaxies and providing new insights into the origins of stars.
"Every star in the sky, including our own sun, was born in one of these stellar nurseries," said Adam Leroy, associate professor of astronomy at The Ohio State University and one of ...
2021-06-08
Researchers from the University of Arizona will present findings from radio-astronomical observations of organic molecules at the 238th Meeting of the American Astronomical Society, or AAS, during a press conference titled "Molecules in Strange Places" at the 238th AAS Meeting on Tuesday, June 8, at 12:15 p.m. EDT.
A team led by Lucy Ziurys at the University of Arizona reports observations of organic molecules in planetary nebulae in unprecedented detail and spatial resolution. Using the Atacama Large Millimeter Array, or ALMA, Ziurys and her team observed radio emissions from hydrogen cyanide (HCN), formyl ion (HCO+) and carbon monoxide (CO) in five planetary nebulae: M2-48, M1-7, M3-28, K3-45 and K3-58.
The ...
2021-06-08
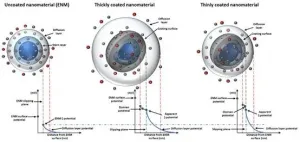
Researchers have developed a 'library of properties' to help identify the environmental impact of nanomaterials faster and more cost effectively.
Whilst nanomaterials have benefited a wide range of industries and revolutionised everyday life, there are concerns over potential adverse effects - including toxic effects following accumulation in different organs and indirect effects from transport of co-pollutants.
The European Union H2020-funded NanoSolveIT project is developing a ground-breaking computer-based Integrated Approach to Testing and Assessment (IATA) for the environmental health and safety of nanomaterials.
Over ...
2021-06-08
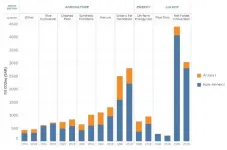
A new global analysis says that greenhouse-gas emissions from food systems have long been systematically underestimated--and points to major opportunities to cut them. The authors estimate that activities connected to food production and consumption produced the equivalent of 16 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide in 2018--one third of the human-produced total, and an 8 percent increase since 1990. A companion policy paper highlights the need to integrate research with efforts to reduce emissions. The papers, developed jointly by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, NASA, New York University and experts at Columbia University, are part of a special issue of Environmental Research Letters on sustainable food systems.
The Center on Global Energy ...
2021-06-08
Stereotypes are knowledge structures integrated in our world representation, which have an influence on our decisions and which are hard to change. A team from the Faculty of Psychology of the University of Barcelona (UB) and the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL), in collaboration with the Èpica Foundation - La Fura dels Baus analysed how a performing experience could have a positive impact in reducing the population's bias against physical illnesses. This performing experience is a pioneer one for it combines scientific training and theatre performance in the same working platform.
The study, published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology, shows that the participation ...
2021-06-08
After looking for just one-twentieth of a second, experts in camouflage breaking can accurately detect not only that something is hidden in a scene, but precisely identify the camouflaged target, a skill set that can mean the difference between life and death in warfare and the wild, investigators report.
They can actually identify a camouflaged target as fast and as well as individuals identifying far more obvious "pop-out" targets, similar to the concept used at a shooting range, but in this case using easy-to-spot scenarios like a black O-shaped target among a crowd of black C shapes.
In fact, the relatively rapid method for training civilian novices to become expert camouflage breakers developed by Medical College of Georgia neuroscientist ...
2021-06-08
Medics training to be GPs reported positive improvement in burnout and resilience after completing a mindfulness course specially designed for doctors
The participants in the study by Warwick Medical School also saw improvements in their wellbeing and stress
By improving the mental wellbeing of trainees the researchers hope to better prepare them for the challenges of general practice and the impact of Covid-19 on the profession
Supports the wider adoption of mindfulness in medical training and the need for larger studies
Medics training to become general practitioners reported a significant positive improvement in their mental wellbeing after participating in a specially-designed mindfulness programme, a study from University of Warwick researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] AI could soon tell you, how often to see the eye doctor