Preliminary genetic link to developmental coordination disorder, dyspraxia identified
2021-06-09
(Press-News.org) New research by scientists at Oxford Brookes University has identified specific genes which could provide vital information about the biology of developmental coordination disorder (DCD), also known as dyspraxia. Dyspraxia is a common motor coordination condition which is estimated to affect at least one child in every classroom.
DCD can impact a child's handwriting and coordination skills such as tying a shoelace or catching a ball. The condition can limit school achievement, impact cognitive development, constrain career opportunities and increase children's risk of developing mental health issues.
Despite the condition affecting five per cent of children, as common as dyslexia or autism, very little is known about why some children struggle with motor coordination.
Genetic data research is first step in understanding causes of DCD
Scientists examined genetic data from over 4,000 participants in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children who had their motor coordination tested when they were seven years old. These data were used to link common genetic variants with motor coordination difficulties, allowing them to better understand the genetic and cellular processes that are involved in DCD.
The researchers say that this is the first step in understanding the causes of DCD.
"If we can identify genes, we can use this information to understand why some children develop DCD," says Dr Hayley Mountford, Research Fellow in the Department of Biological and Medical Sciences at Oxford Brookes University and lead author of the study.
Clear potential to unravel the biology of DCD
Many children with motor coordination difficulties remain undiagnosed and coupled with a lack of research, this has a vast impact on the visibility of DCD in both the public and the medical community.
"Although this is a preliminary study, these findings show a clear potential for genetics studies to unravel the underlying biology of DCD," adds Dr Mountford. "We need to replicate these findings in larger datasets to uncover the reasons why some children are at a higher risk. This will lead to developments in the diagnosis of DCD, improving the lives of affected families."
INFORMATION:
The paper, Genome Wide Association Study of Motor Coordination, is published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-09
Therapy based on the Nintendo® Wii Balance Board can help improve balance in children with cerebral palsy, according to an analysis published in END ...
2021-06-09
Advanced age is often considered a contraindication for heart transplantation, but a new study published in the END ...
2021-06-09
It all started, when Patrice Cani, FNRS researcher at University of Louvain (UCLouvain), and his team repeatedly observed that a bacterium (called Subdoligranulum) is almost absent in obese and diabetic people, while it is systematically present in healthy people. So, they decided to take a closer look at this "family" of bacteria.
There is as yet only one cultivated strain of this family available in the world (the only known member of a large family) and, no luck, it is not the strain that was observed to be decreased in sick people. This is not unusual: nearly 70% of bacteria in the intestine have not yet been identified (this is called the dark matter of the ...
2021-06-09
It's incumbent upon counselors to initiate or respond to clients' concerns about racial, ethnic, and cultural issues, but guidelines lack specific instructions. An article published in the Journal of Counseling & Development provides counselors with strategies for broaching and discussing topics of race, ethnicity, and culture with clients.
The article describes a model for broaching these issues and explains a series of steps--joining, assessment, preparation, and delivery--involved in using it.
"This and other articles serve as the foundation for the next phase in our research on counselor implementation of broaching and its impact on client mental health outcomes," the authors wrote.
INFORMATION: ...
2021-06-09
A study published in Career Development Quarterly has looked at whether beliefs and attitudes influence career aspirations of college students with different genders and sexual orientations.
Among 1,129 college students at a midwestern urban university, stronger self-efficacy beliefs--or perceptions about whether a person has the ability to achieve a desired outcome--led both male and lesbian, gay, bisexual, queer, intersex, and questioning (LGBQIQ) students to seek out leadership positions within their chosen career field. Stronger feminist attitudes were associated with an increase in achievement efforts for LGBQIQ college students, but not for heterosexual students.
"The results of the study not only demonstrate that beliefs and attitudes influence ...
2021-06-09
New research reveals that only a minority of U.S. Medicare beneficiaries with knee osteoarthritis in 2005-2010 used non-surgical care such as physical therapy and knee injections, and few were treated by rheumatologists, physiatrists, or pain specialists. The study, which is published in END ...
2021-06-09
Oncotarget published "Differential expression of Vitamin D binding protein in thyroid cancer health disparities" which reported that thyroid cancer incidence, recurrence, and death rates are higher among Filipino Americans than European Americans.
In this study, the authors determined the correlation between differential DBP expression in tumor tissues and cancer staging in Filipino Americans versus European Americans.
The majority of Filipino Americans presented with advanced tumor staging. In contrast, European Americans showed early staging and very few advanced tumors.
On the contrary, in the tumor tissues derived from European Americans, moderate to strong DBP staining was detected ...
2021-06-09
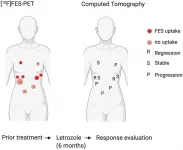
Oncotarget published "[18F]FDG and [18F]FES positron emission tomography for disease monitoring and assessment of anti-hormonal treatment eligibility in granulosa cell tumors of the ovary" which reported that the authors evaluated 22 PET/CTs from recurrent Anti-hormonal granulosa cell tumors (AGCT) patients to determine tumor FDG and FES uptake by qualitative and quantitative analysis.
They included all consecutive patients from two tertiary hospitals between 2003-2020.
Expression of ERα and ERβ and mitoses per 2 mm2 were determined by immunohistochemistry and compared to FES and FDG uptake, respectively.
Qualitative assessment showed low-to-moderate FDG uptake in most patients, and intense uptake in ...
2021-06-09
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Women's mental health likely has a higher association with dietary factors than men's, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
Lina Begdache, assistant professor of health and wellness studies at Binghamton University, had previously published research on diet and mood that suggests that a high-quality diet improves mental health. She wanted to test whether customization of diet improves mood among men and women ages 30 or older.
Along with research assistant Cara M. Patrissy, Begdache dissected the different food groups that are associated with mental distress in men and women ages 30 years and older, as well as studied ...
2021-06-09
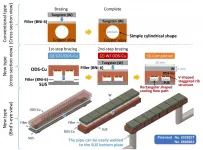
The oxide dispersion strengthened copper alloy (ODS-Cu) is superior in thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, heat resistance and friction tolerance, etc. Although the ODS-Cu can be expected to have various industrial applications, its joint with other materials is extremely difficult because of its intrinsic poor weldability. The research group of Dr. Masayuki Tokitani in the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS) has developed an extremely novel joint technique that enables us to fabricate any component made of ODS-Cu. This technique highly contributes to producing the efficient heat removal component for the fusion reactor.
Copper ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Preliminary genetic link to developmental coordination disorder, dyspraxia identified