(Press-News.org) From 1980 to 2016, grain production in Brazil increased more than fourfold, and the country now stands as the world's largest soybean exporter and the second largest exporter of corn. The two main drivers of this increase in food production were cropland expansion and double-cropping, harvesting two crops, such as corn and soybeans, from the same field in a single year.
While cropland expansion has long been recognized as one of the drivers behind the increase in Brazil's agricultural output, a new study published in Nature Food quantifies for the first time the impact that double-cropping also had on helping Brazil achieve its national grain boom.
Jing Gao, assistant professor of Geospatial Data Science in the University of Delaware's College of Earth, Ocean and Environment (CEOE) and Data Science Institute (DSI), was a co-author on the study that included collaborators from institutions in China and Brazil.
Gao contributed to the team efforts by examining agriculture census-related data gathered from the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), and identifying spatial patterns and changes that occurred over time in three key agricultural regions with regards to food production: the Centre-West, Southeast-South, and Matopiba regions in Brazil.
"You don't know what is happening until you analyze data," said Gao. "This was the first time this unique dataset was analyzed from this angle to show how the system worked. Understanding how the boost in Brazil's grain productivity was achieved in the recent past provides insight for developing sustainable food production in the future."
These three regions covered 36% of Brazil's territory and accounted for 79% of the national soybean production and 85% of the country's corn production in 2016. The Centre-West area showed the biggest increases in production as well as cropland expansion. As such, the Centre-West displaced the Southeast-South as the dominant grain producer in the country, producing 46% of the nation's grain compared to 29% for the Southeast-South.
The increase in grain production in the Centre-West can be attributed to cropland expansion as well as double-cropping.
Contributions from double-cropping in the Centre-West increased from 19% to 33% from 2003 to 2016. While the increase in soybean production was largely due to cropland expansion -- soybean fields account for more than one-third of Brazil's cropland -- the increase in corn production could be linked to the practice of double-cropping. In the Centre-West, the agricultural area for second season corn -- or the corn grown after the first season soybean is harvested -- increased from 26.3% to 66.6% from 2003 to 2016, and in 2012, the second season corn crop surpassed the corn grown during the first season as the main source of corn nationwide.
Tao Lin, from the College of Biosystems Engineering and Food Science at Zhejiang University in China and the corresponding author of the paper, said that it was interesting to see the agricultural developments in these regions had different approaches to agricultural expansion and double-cropping.
"The Centre-West region has experienced a rapid cropland expansion in the last few decades, and after the new cropland was created, farmers then decided to also increase the double-cropping area a lot," said Lin. "Meanwhile, the contribution of double-cropping in the Southeast-South region is over 50%, which has had a much higher impact than cropland expansion in recent times, because there is not much arable land remaining for further expansion in this commercial agricultural region."
The researchers also found that the strongest driver behind this rapid increase in grain production has been the rising demand for corn and soybean exports from Brazil on a global scale.
It is important to understand how double-cropping has helped a country like Brazil, which plays a critical role in the global food supply chain, increase its agricultural productivity while limiting the conversion of natural land for agricultural use and possibly helping offset some of the negative environmental impacts that might result from cropland expansion.
From 2003 to 2016, double-cropping in Brazil offset the equivalent of about 76.7 million hectares of arable land for corn production, that is, more than twice the annual harvested area of corn in the United States.
While not every country is growing food in an area of the world that is conducive or even possible for double-cropping, for other grain-growing pantropical countries, double-cropping could be a solution to increase grain production without expanding cropland over natural landscapes.
INFORMATION:
The fairy circles of the Namib are one of nature's greatest mysteries. Millions of these circular barren patches extend over vast areas along the margins of the desert in Namibia. In 1979, G.K. Theron published the first research about their origin. His hypothesis was that poisonous substances from Euphorbia damarana leaves induced fairy circles. As part of a new study, scientists from the University of Göttingen and the Gobabeb Namib Research Institute located the original euphorbia plants that were part of Theron's study. Four decades later, the researchers are now able to conclusively disprove Theron's original hypothesis. Their results were published in the journal BMC Ecology and Evolution.
In the late 1970s, South African botanist Theron noticed ...
A University of Oklahoma doctoral student, graduate and undergraduate research assistants, and an associate professor in the Homer L. Dodge Department of Physics and Astronomy in the University of Oklahoma College of Arts and Sciences are lead authors on a paper describing a "changing-look" blazar - a powerful active galactic nucleus powered by supermassive blackhole at the center of a galaxy. The paper is published in The Astrophysical Journal.
Hora D. Mishra, a Ph.D. student, and faculty member Xinyu Dai are lead authors of the paper, along with Christopher Kochanek and Kris Stanek at the Ohio State University and Ben Shappee at the University of Hawaii. The paper represents the findings of researchers from 12 different institutions who participated ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Holographic displays help add a three-dimensional--and thus more life-like--feel to what would otherwise appear as a two-dimensional image. Now, researchers in Japan have tested how this may work on a supramolecular level; such tests could lead to improved displays.
Commonly, one cannot overlay a certain type of molecular component that underlies helically arranged liquid crystals onto their molecular mirror images, much like a person cannot overlay their two hands and have them match up exactly without flipping one over. Molecules with this property are described as "chiral." Some materials make use of the principle of chirality to rotate light in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the light wave, known as circular ...
Researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) have developed novel techniques, known as Automated Fibre Embedding (AFE), to produce complex fibre and silicone composite structures for soft robotics applications. Their work was published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters.
Many soft robot components, including sensors and actuators, utilise embedded continuous fibres within elastomeric substrates to achieve various functionalities. However, manual embedding of continuous fibres in soft substrates is challenging due to the complexities involved in handling precise layering, and ...
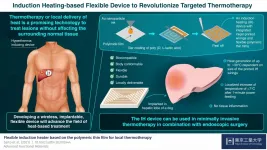
Thermotherapy or heat treatment can help in treating lesions and other tissue injuries. For example, chemotherapy or radiotherapy, when combined with thermotherapy, kills tumorous cells more effectively. Thermotherapy is considered a promising approach for treating internal lesions, but the advancement in the field depends on the availability of patient-friendly heat-inducing devices capable of rapidly increasing the temperature of target tissues.
Current clinical practices around thermotherapy majorly employ heat-generating devices that are probed inside ...
DALLAS - June 9, 2021 - A phenomenon in which an RNA named NORAD drives a protein named Pumilio to form liquid droplets in cells, much like oil in water, appears to tightly regulate the activity of Pumilio. A new study led by UT Southwestern scientists suggests that such RNA-driven "phase separation," in turn, protects against genome instability, premature aging, and neurodegenerative diseases, and may represent a previously unrecognized way for RNAs to regulate cellular processes.
"It's becoming more and more clear that phase separation is an important organizing ...
A research team, led by Professor Kyoung-Duck Park in the Department of Physics at UNIST has succeeded in investigating and controlling the physical properties of naturally-formed nanoscale wrinkles in two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors. This is thanks to their previously-developed hyperspectral adaptive tip-enhanced photoluminescence (a-TEPL) spectroscopy. This will be a major step forward in developing paper-thin, ultra-flexible displays.
Wrinkles are an inevitable structural deformation in 2D semiconductor materials, which gives rise to spatial heterogeneity in material properties, according to the research team. Such structural deformation has long been considered one of the top technical challenges in semiconductor manufacturing, as this would harm the uniformity ...
Young clownfish living closest to shore are dying faster than those further offshore because they are being exposed to artificial lighting, says an international research team.
Working on the reefs around Moorea in French Polynesia, scientists from France, the United Kingdom, Chile and Australia found that nearshore juvenile clownfish living in anemones under lights had higher mortality than juveniles in anemones not exposed to artificial light.
The scientists also found that the surviving clownfish grew 44 per cent more slowly than clownfish under natural lighting conditions.
Professor Stephen Swearer, a marine ecologist, from the University of Melbourne, ...
Scientists have leapt over the emerging problem of publication bias within genetic research by performing a meta-analysis of publicly available databases of 'transcriptomes', or the full range of messenger RNA molecules produced by an organism. Researchers from Hiroshima University applied the technique to their own field--the study of the genes that are activated when an organism experiences low-oxygen conditions--but it should also be applicable in any other fields that make use of the transcriptome, providing a powerful weapon against the threat posed by publication bias.
The meta-analysis technique ...
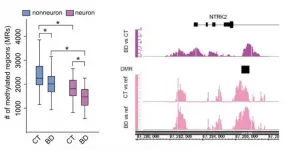
A research collaboration based in Kumamoto University, Japan has revealed the DNA methylation status of gene transcriptional regulatory regions in the frontal lobes of patients with bipolar disorder (BD). The regions with altered DNA methylation status were significantly enriched in genomic regions which were reported to be genetically related to BD. These findings are expected to advance the understanding of the pathogenesis of BD and the development of therapeutic drugs targeting epigenetic conditions.
BD is a mental disorder that affects about 1% of the population and requires long-term treatment. Epidemiological studies have ...