Study: Important contribution to spintronics has received little consideration until now
2021-06-09
(Press-News.org) The movement of electrons can have a significantly greater influence on spintronic effects than previously assumed. This discovery was made by an international team of researchers led by physicists from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU). Until now, a calculation of these effects took, above all, the spin of electrons into consideration. The study was published in the journal "Physical Review Research" and offers a new approach in developing spintronic components.
Many technical devices are based on conventional semiconductor electronics. Charge currents are used to store and process information in these components. However, this electric current generates heat and energy is lost. To get around this problem, spintronics uses a fundamental property of electrons known as spin. "This is an intrinsic angular momentum, which can be imagined as a rotational movement of the electron around its own axis," explains Dr Annika Johansson, a physicist at MLU. The spin is linked to a magnetic moment that, in addition to the charge of the electrons, could be used in a new generation of fast and energy-efficient components.
Achieving this requires an efficient conversion between charge and spin currents. This conversion is made possible by the Edelstein effect: by applying an electric field, a charge current is generated in an originally non-magnetic material. In addition, the electron spins align, and the material becomes magnetic. "Previous papers on the Edelstein effect primarily focused on how electron spin contributes to magnetisation, but electrons can also carry an orbital moment that also contributes to magnetisation. If the spin is the intrinsic rotation of the electron, then the orbital moment is the motion around the nucleus of the atom," says Johansson. This is similar to the earth, which rotates both on its own axis and around the sun. Like spin, this orbital moment generates a magnetic moment.
In this latest study, the researchers used simulations to investigate the interface between two oxide materials commonly used in spintronics. "Although both materials are insulators, a metallic electron gas is present at their interface which is known for its efficient charge-to-spin conversion," says Johansson. The team also factored the orbital moment into the calculation of the Edelstein effect and found that its contribution to the Edelstein effect is at least one order of magnitude greater than that of spin. These findings could help to increase the efficiency of spintronic components.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation, DFG), the European Research Council and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation.
About the study: Johansson A., Göbel B., Henk J., Bibes M., Mertig I. Spin and orbital Edelstein effects in a two-dimensional electron gas: Theory and application to SrTiO3 interfaces. Physical Review Research (2021). Doi: 10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.013275
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.013275
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-09
BOSTON - In the three months since Johnson & Johnson's COVID-19 vaccine received emergency use authorization from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, more than 10 million Americans have received the vaccine, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The single-shot viral vector vaccine -- developed in collaboration with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) immunologist Dan Barouch, MD, PhD -- was authorized for use based on clinical trial data showing strong clinical efficacy against symptomatic COVID-19 in the United States, Latin ...
2021-06-09
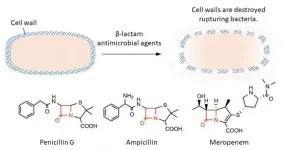
A joint research project based in Kumamoto University, Japan has developed a new, highly sensitive analytical method that can detect degraded β-lactam antibacterial agents used in the treatment of bacterial infections. With this method, researchers found that reactive sulfur species produced by bacteria degrade and inactivate β-lactam antibiotics.
Bacteria are different from animal cells in that their outer layer is covered with a rigid structure called a cell wall. β-lactam antimicrobial agents interfere with the processes that form the cell wall. This results in bacteria no longer being able to withstand their own internal pressure so they rupture and die. β-lactam antimicrobial agents are very potent ...
2021-06-09
For nearly half a century, astrophysicists and organic chemists have been on the hunt for the origins of C6H6, the benzene ring - an elegant, hexagonal molecule comprised of 6 carbon and 6 hydrogen atoms.
Astrophysicists say that the benzene ring could be the fundamental building block of polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons or PAHs, the most basic materials formed from the explosion of dying, carbon-rich stars. That swirling mass of matter would eventually give shape to the earliest forms of carbon - precursors to molecules some scientists say are connected to ...
2021-06-09
New research shows transmission of the virus behind COVID-19 varies seasonally, but warmer conditions are not enough to prevent transmission.
The study, led by Imperial College London researchers and published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is the first to incorporate environmental data into epidemiological models of the transmission of SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19.
The team show that temperature and population density are the most important factors determining how easily the virus spreads, but only in the absence of mobility-restricting measures, such as lockdowns.
First author of the study Dr Tom Smith, from the Department of Life Sciences at Imperial, said: "Our results ...
2021-06-09
KINSHASA, Democratic Republic of Congo (June 9, 2021) - A new study led by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) has updated the global population estimate for the Critically Endangered Grauer's gorillas (Gorilla beringei graueri) - the world's largest gorilla subspecies- to 6,800 individuals from a previous global estimate of 3,800 individuals. This revised estimate comes from recent field surveys conducted in one of this animal's largest remaining strongholds, in areas that were previously inaccessible for surveys. However, these gorillas continue to be heavily impacted by ongoing insecurity, and by human incursion into their remaining habitat in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo.
Publishing in the American Journal of Primatology, ...
2021-06-09
Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) have identified a common mechanism underlying a spectrum of epilepsy syndromes and neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism, that are caused by variations in a gene encoding a vital transporter protein in the brain.
Their findings, reported last month in the journal Brain, suggest that boosting transporter function via genetic or pharmacological means could be beneficial in treating brain disorders linked to these genetic variations.
"This points (to) a clear direction of treating a wide spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders, from various epilepsy syndromes (and) autism to neurodevelopmental delay and intellectual ...
2021-06-09
June 9, 2021 - The first analysis of medical evidence on domestic mass shooters in the U.S. finds that a large majority of perpetrators have psychiatric disorders for which they have received no medication or other treatment, reports a study in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Without losing sight of the larger perspective that most who are violent are not mentally ill, and most of the mentally ill are not violent, our message is that mental health providers, lawyers, and the public should be made aware that some unmedicated patients do pose an increased risk of violence," according to the report by Ira D. Glick, MD, of Stanford University School of Medicine and colleagues.
In-depth analysis of ...
2021-06-09
Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute scientists are one step closer to understanding why some corals can weather climate change better than others, and the secret could be in a specific protein that produces a natural sunscreen. As their name implies, Hawaiian blue rice corals sport a deep blue pigment, which is created by chromoprotein and filters out harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Although UV damage may produce long-term impacts to reproduction in many coral species--including brown rice coral--it may not have the same effect on blue rice coral. The findings of this study were published June 9 in ...
2021-06-09
From 1980 to 2016, grain production in Brazil increased more than fourfold, and the country now stands as the world's largest soybean exporter and the second largest exporter of corn. The two main drivers of this increase in food production were cropland expansion and double-cropping, harvesting two crops, such as corn and soybeans, from the same field in a single year.
While cropland expansion has long been recognized as one of the drivers behind the increase in Brazil's agricultural output, a new study published in Nature Food quantifies for the first time the impact that double-cropping also ...
2021-06-09
The fairy circles of the Namib are one of nature's greatest mysteries. Millions of these circular barren patches extend over vast areas along the margins of the desert in Namibia. In 1979, G.K. Theron published the first research about their origin. His hypothesis was that poisonous substances from Euphorbia damarana leaves induced fairy circles. As part of a new study, scientists from the University of Göttingen and the Gobabeb Namib Research Institute located the original euphorbia plants that were part of Theron's study. Four decades later, the researchers are now able to conclusively disprove Theron's original hypothesis. Their results were published in the journal BMC Ecology and Evolution.
In the late 1970s, South African botanist Theron noticed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study: Important contribution to spintronics has received little consideration until now