Solving mystery of the four-headed echidna penis
Scientists explain why echidna penis is 'weird'
2021-06-09
(Press-News.org) Scientists from the University of Melbourne and University of Queensland have revealed the mystery behind the unique reproductive parts of the much-loved echidna.
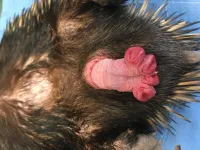
In the paper, "The Unique Penile Morphology of the Short-Beaked Echidna, Tachyglossus aculeatus", the team detail how the male monotreme's testes never descend, have no scrotum, and when not in use, their penis is stored internally.
They also detail how the echidna penis has four heads, which are actually rosette-like glans at the end. Just two of the four glans ever become functional during erection and which glans are functional appears to alternate between subsequent erections.
INFORMATION:
The research is a collaborative project involving scientists from the University of Melbourne, University of Queensland and Monash University, and the Currumbin Wildlife Sanctuary on the Gold Coast, which has established a small breeding colony of echidnas.
The research is now published in the journal Sexual Development.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-09
Led by Professor Andreas Hartmann, from the University of Freiburg (Germany), the researchers analyzed the presence of several pollutants in water from many karst aquifers of Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East, relating fast infiltration processes to an increased concentration of these substances. The findings of this research are published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
This way, they warn that during rainfall events -when aquifers recharge, especially during autumn rainfall- the concentration of pollutants and pathogenic microorganisms can significantly exceed the safe levels, causing serious consequences for human consumption.
"About one quarter of the ...
2021-06-09
Obesity is generally linked to poor eating habits and the availability of tasty, high-calorie foods. However, a new study led by researchers from the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Research Unit in the Department of Radiology at Hospital del Mar and the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has found that more elements are involved. Thanks to images obtained by functional magnetic resonance imaging, the researchers found that certain parts of the brains of obese children show alterations with respect to normal-weight or overweight children of the same age. ...
2021-06-09
At the heart of almost every sufficiently massive galaxy there is a black hole whose gravitational field, although very intense, affects only a small region around the centre of the galaxy. Even though these objects are thousands of millions of times smaller than their host galaxies our current view is that the Universe can be understood only if the evolution of galaxies is regulated by the activity of these black holes, because without them the observed properties of the galaxies cannot be explained.
Theoretical predictions suggest that as these black holes grow they generate sufficient energy to heat ...
2021-06-09
New research has revealed that people with the ability to visualise vividly have a stronger connection between their visual network and the regions of the brain linked to decision-making. The study also sheds light on memory and personality differences between those with strong visual imagery and those who cannot hold a picture in their mind's eye.
The research, from the University of Exeter, published in Cerebral Cortex Communications, casts new light on why an estimated one-three per cent of the population lack the ability to visualise. This phenomenon was named "aphantasia" by the University of Exeter's Professor Adam Zeman in 2015 Professor Zeman called those with highly ...
2021-06-09
Homocysteine (HCY) is a sulfur-containing aminoacid, which attract more and more attention as the increase of homocysteine level associates with a number of pathological conditions. Hyperhomocysteinemia (hHCY) is an elevation of HCY level in plasma and develops due to genetic mutations of enzymes involved in regulation of HCY metabolism, nutritional deficiencies of vitamins B12, B6 and folate; chronic renal failure; alcoholism, smoking, excess coffee consumption, hypothyroidism; taking a number of medications like antiepileptic drugs and LDOPA; and aging. hHcy is a well-known ...
2021-06-09
The movement of electrons can have a significantly greater influence on spintronic effects than previously assumed. This discovery was made by an international team of researchers led by physicists from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU). Until now, a calculation of these effects took, above all, the spin of electrons into consideration. The study was published in the journal "Physical Review Research" and offers a new approach in developing spintronic components.
Many technical devices are based on conventional semiconductor electronics. Charge currents are used to store and process information in these components. However, this electric current generates heat and energy is lost. To get around this problem, ...
2021-06-09
BOSTON - In the three months since Johnson & Johnson's COVID-19 vaccine received emergency use authorization from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, more than 10 million Americans have received the vaccine, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The single-shot viral vector vaccine -- developed in collaboration with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) immunologist Dan Barouch, MD, PhD -- was authorized for use based on clinical trial data showing strong clinical efficacy against symptomatic COVID-19 in the United States, Latin ...
2021-06-09
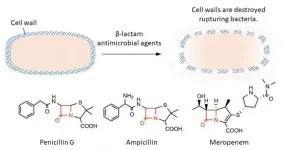
A joint research project based in Kumamoto University, Japan has developed a new, highly sensitive analytical method that can detect degraded β-lactam antibacterial agents used in the treatment of bacterial infections. With this method, researchers found that reactive sulfur species produced by bacteria degrade and inactivate β-lactam antibiotics.
Bacteria are different from animal cells in that their outer layer is covered with a rigid structure called a cell wall. β-lactam antimicrobial agents interfere with the processes that form the cell wall. This results in bacteria no longer being able to withstand their own internal pressure so they rupture and die. β-lactam antimicrobial agents are very potent ...
2021-06-09
For nearly half a century, astrophysicists and organic chemists have been on the hunt for the origins of C6H6, the benzene ring - an elegant, hexagonal molecule comprised of 6 carbon and 6 hydrogen atoms.
Astrophysicists say that the benzene ring could be the fundamental building block of polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons or PAHs, the most basic materials formed from the explosion of dying, carbon-rich stars. That swirling mass of matter would eventually give shape to the earliest forms of carbon - precursors to molecules some scientists say are connected to ...
2021-06-09
New research shows transmission of the virus behind COVID-19 varies seasonally, but warmer conditions are not enough to prevent transmission.
The study, led by Imperial College London researchers and published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is the first to incorporate environmental data into epidemiological models of the transmission of SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19.
The team show that temperature and population density are the most important factors determining how easily the virus spreads, but only in the absence of mobility-restricting measures, such as lockdowns.
First author of the study Dr Tom Smith, from the Department of Life Sciences at Imperial, said: "Our results ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Solving mystery of the four-headed echidna penis
Scientists explain why echidna penis is 'weird'