RUDN University chemist proposed eco-friendly synthesis of fluorescent compounds for medicine
2021-06-10
(Press-News.org) RUDN and Shahid Beheshti University(SBU) chemist proposed an eco-friendly method for the synthesis of pyrrole and pyrazole derivatives with a wide range of applications in medicine: from antidepressants to anticancer. Moreover, the synthesized compounds possess interesting fluorescence features, and the bioactive scaffolds might attract great interest in the fields of clinical diagnostics and biomedical research in the future. The results are published in the Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry.
Heterocyclic compounds expose remarkable chemistry with significant applications in medicinal and organic chemistry, industry, and pharmaceutical. These compounds are widely found in many natural products such as vitamins, hormones, antibiotics, alkaloids, herbicides, pigments, and dyes. Besides, a wide variety of heterocyclic rings is originated from the scaffolds of various drugs and bioactive molecules. Among them, pyrrole and pyrazole are heterocycles with a wide biological activity. They are part of drugs for the treatment of cancer, headaches and depression, relieving inflammation and a number of other diseases. Some of them demonstrate fluorescent properties, and therefore they can be used for clinical diagnosis, for example, cancer. However, the synthesis of compounds with these heterocycles remains non eco-friendly and expensive. It needs high temperatures and hazardous compounds. The RUDN and SBU chemist and his colleagues from Tehran-Iran suggested a safer and cheaper way to create pyrrole and pyrazole derivatives.
"Pyrroles and pyrazoles represent one of the most active classes of compounds, possessing a wide range of biological activities. It includes anti-inflammatory, antidepressant, antitubercular activity, they are also active against microbes, fungi and bacteria. That is not the complete list. Still, it is a powerful challenge to design an ideal synthetic protocol for this type of biologically active compound using environmentally friendly and step-economic methods and less hazardous reagents under mild reaction conditions", Dr. Ahmad Shaabani from RUDN and SBU.
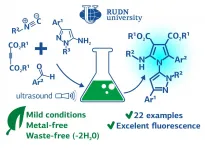
The chemists have obtained compounds of pyrazole and pyrrole derivatives by the "one-pot" method, when all the stages of synthesis take place in a single reactor. Thus, scientists do not need to waste time and reagents on the isolation and purification of intermediate compounds. In total, four types of substances participate in the reaction: aminopyrazole, aldehyde, dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate, isocyanide. They convert in a domino reaction, when all the steps occur one after the other without additional compounds. The reaction occurs at a low temperature -- 45? -- under ultrasound irradiation in the presence of p-toluenesulfonic acid as a catalyst.
By changing the combinations of the four reactants, the chemists obtained 22 compounds. It turned out that most of them have fluorescent features -- they glow blue under the ultraviolet light. The most intense fluorescence was associated with the presence of bromine derivatives in the cyclic fragments of the obtained substances.
"This eco-friendly, mild condition and atom-economical process generated two C-N and two C-C bonds and formed two five-membered heterocycles connected to each other. We believe that these new classes of fluorescent compounds may be of excellent interest in biomedical applications and clinical diagnostics in the future".
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-10
Wine grape growers in California and elsewhere face increasing labor costs and severe labor shortages, making it difficult to manage and harvest a vineyard while maintaining profitability. Growers are increasingly turning to machines for pruning, canopy management and harvesting, but how well these practices are executed can substantially affect yield and quality. A new review by researchers at the University of California, Davis, published in the journal Catalyst, provides guidelines for growers to make the best use of machines.
"Wine grape laborers have been virtually nonexistent. People don't want to work in vineyards anymore because it's remote, tough work," said Kaan Kurtural, professor of viticulture and enology and extension ...
2021-06-10
BONN, 10 June - Unprecedented changes in climate and biodiversity, driven by human activities, have combined and increasingly threaten nature, human lives, livelihoods and well-being around the world. Biodiversity loss and climate change are both driven by human economic activities and mutually reinforce each other. Neither will be successfully resolved unless both are tackled together.
This is the message of a workshop report, published today by 50 of the world's leading biodiversity and climate experts.
The peer-reviewed workshop report is the product of a four-day virtual workshop between ...
2021-06-10
Kanazawa, Japan - Fungal diseases in cereal crops cause major economic losses and also threaten human and livestock health, because some fungi produce powerful toxins that might enter the food chain. Farmers use fungicides to control crop diseases, such as wheat head blight. Although agrochemicals are rigorously tested for safety, there can be concerns over chemical residues in food.
Now, researchers at Kanazawa University, in collaboration with colleagues at Ehime University and Nagoya University, have shown that the natural substance nicotinamide (NIM - a vitamin found in food and used as a dietary supplement) can help stimulate ...
2021-06-10
Curtin University researchers have helped uncover the four billion year old story of a lunar sample brought from the Moon to Earth, by the manned Apollo 17 mission more than 50 years ago.
The global research collaboration, involving scientists from the UK, Canada, Sweden and Australia, aimed to analyse the ancient rock sample through a modern lens to find out its age, which crater it came from and its geological trajectory.
That modern lens was provided, in part, by both Curtin's Geoscience Atom Probe Facility* and Space Science and Technology Centre* (SSTC) where the research team was ...
2021-06-10
With the onset of the 4th industrial revolution, artificial intelligence has recently been utilized in smartphone cameras, providing functions such as auto-focusing, face recognition, and 100x zoom, to dramatically improve our daily life. It has also been applied to research and development of new materials.
A joint research team from POSTECH and Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS) has applied deep learning to the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) system to develop a technique that can detect and improve the quality of SEM images without human oversight. The EMS is an essential material analysis equipment used for developing new materials. The findings from this research were recently published ...
2021-06-10
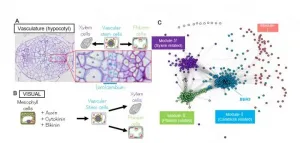
An inter-university research group has succeeded in constructing the gene expression network behind the vascular development process in plants. They achieved this by performing bioinformatics analysis using the 'VISUAL' (*1) tissue culture platform, which generates vascular stem cells (*2) from leaf cells. In this network, they also discovered a new BES/BZR transcription factor (*3), BEH3, which regulates vascular stem cells. In addition, they illuminated a novel vascular cell maintenance system whereby BEH3 competes with other transcription factors from the same BES/BZR family in order to stabilize vascular stem ...
2021-06-10
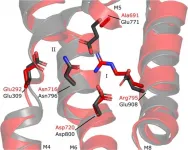
Cell viability require that a variety of functions at the cell membrane are maintained properly. P-type ATPases translocate substrates across the membrane, and they have evolved into different types taking care of specific substrates within a diverse range. Now, key structural aspects have been described on how two different types of P-type ATPases - a Ca2+ transporting Ca2+ -ATPase and a lipid transporting P4-ATPase - have adapted to different substrates and physical environments.
Many bacteria export intracellular calcium using active transporters homologous to the well-described ...
2021-06-10
Researchers from Tel Aviv University took part in a new international study proposing an amendment to the widely accepted theory on the extinction of animal species - by moving the focus from the animal's body size to its reproductive capacity. The researchers found gaps and incompatibilities between mammals and amphibians in the relation between body size and extinction risk: Whereas large mammals bear a smaller number of offspring per birth, leading to higher risk of extinction, larger amphibian females lay more eggs, reducing the threat to the species.
The researchers analyzed data from databases on both extinction risks and reproductive capacities of various species of amphibians (e.g., frogs and salamanders). Contributors to the ...
2021-06-10
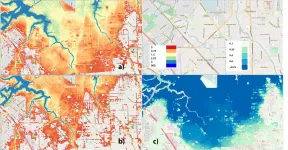
How much do the effects of climate change contribute to extreme weather events? It's hard to say--the variables involved are plentiful, each event is unique, and we can only do so much to investigate what didn't happen. But a new paper from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) climate scientist Michael Wehner investigates the question for one particular element of one significant storm and makes the results available to those who lived through it.
In the paper, "Attributable human-induced changes in the magnitude of flooding in the Houston, Texas region during Hurricane Harvey," published May 19 in Climatic Change, Wehner and Christopher Sampson from Fathom Bristol used a hydraulic ...
2021-06-10
Even on a good day, DNA is constantly getting damaged.
Nicks, scratches, breaks: the delicate strands that carry life's genetic code take a beating as they jumble about in the course of their work. If left untreated, errors accumulate, with fatal consequences -- such as cancerous tumors -- for the cell and the organism.
This is where two key proteins come to the rescue: PARP -- or poly ADP ribose polymerase -- acts as a marker for a trouble spot, allowing XRCC1 -- or X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1 -- to zoom in and begin a repair.
This much has been known for some time and was even recognized in the 2015 Nobel prizes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] RUDN University chemist proposed eco-friendly synthesis of fluorescent compounds for medicine