More sustainable mortars and concrete with optimal thermal and mechanical efficiency
The University of the Basque Country-UPV/EHU is researching mortars and concrete manufactured from industrial by-products, within the circular economy approach
2021-06-10
(Press-News.org) The consumption of raw materials has increased notably in industry in general, and in the construction industry in particular, amidst growing concerns over sustainability issues. Concrete and mortar are the most commonly used materials in construction, and many studies are currently under way to try and reduce the harmful effects of their manufacture. Concrete and mortar are made by mixing water, sand, cement and aggregates.
"The main problem is the amount of cement used to produce this type of material; cement manufacturing uses a huge amount of energy and natural resources, which implies a high level of CO2 emissions. Diverse studies are under way aimed at reducing the quantity of cement required. We are working to replace cement and aggregates (sand or gravel) with non-natural materials, in order to reduce the use of natural resources and optimise the mechanical and thermal properties of the materials produced,"explains Roque Borinaga Treviño, a researcher at the UPV/EHU's Department of Mechanical Engineering.
To this end, the research team is analysing by-products from different industrial processes, which enable the mortars and concretes produced to be used for different functions, depending on the mechanical and thermal properties they acquire: 'the aim is to reduce as much as possible the volume of industrial by-products that end up in landfill sites, and to reuse these products in accordance with the dictates of the circular economy,' claims Dr Borinaga. Recently, the research team has explored three different by-products in three different areas.
Specific cases
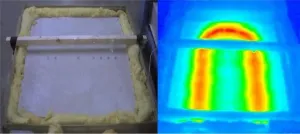
Firstly, they have studied the possibility of using industrial metal waste as a reinforcement in concrete or mortar, analysing mortars reinforced with brass fibres from electrical discharge machining. Secondly, and linked to this avenue of research aimed at reducing the amount of cement required, they have explored the use of lime mud waste from the paper industry, obtaining good results in terms of thermal conductivity and finding that the resulting material is adequate for use in radiant floor heating systems. And finally, they have used furnace slag as an aggregate: 'the thermal conductivity of sand extracted from electric arc furnaces is low, making it a good option for insulation purposes,' explains Dr Borinaga.
Although they are studying many different types of materials, what they are doing is basic research: 'ours is the first step in researching these materials. Industrial by-products and waste are not particularly homogeneous, meaning that they vary greatly in accordance with their origin. Therefore, the first step is to analyse the properties bestowed by each specific type of waste. It is important to conduct these analyses with a large amount of waste with different origins, and to compare the results in order to determine whether or not the materials are suitable for use in manufacturing,' he concludes.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-10
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (06/10/2021) -- New findings from the University of Minnesota Medical School are helping uncover why some people are more likely to be overweight and develop Type 2 diabetes -- and it starts in the womb.
Previous association studies have shown that low birthweight among infants is a strong determinant for eventual obesity and Type 2 diabetes. The placenta of infants with a low birthweight have reduced levels of mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin), and the placenta of bigger infants have increased levels of mTOR. Building off of that research, a U of M Medical ...
2021-06-10
Genova (Italy) 10 June, 2021 - The U-Vip (Unit for Visually Impaired People) research team led by Monica Gori at the IIT- Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology) has recently published a study which shows for the first time how children aged from 3 to 5 years old have problems in recognising the emotions of people wearing surgical masks. This collateral effect of the preventive measures linked to the Covid-19 health emergency could influence the correct development of children's capabilities of social interaction. The research paper has been published in Frontiers in Psychology.
The use of facemasks for children ...
2021-06-10
Actively restoring oyster reefs--beyond simply protecting them from harvest--can create big payoffs for habitat quality and the other species that flock to them. A new study from the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center (SERC), published June 3 in the journal Marine Ecology Progress Series, compared restored, protected and harvested areas using photos and video footage from roughly 200 sites.
Roughly a quarter of Maryland's oyster habitat lies protected in oyster sanctuaries. But only a small fraction of those sanctuaries have undergone full-scale restorations, with reconstructed reefs and new live oyster plantings. ...
2021-06-10
A new study reports that birds across the continental U.S. tend to avoid backyard feeders in louder areas. When light and noise pollution were both present, even more species stayed away.
The study, published in Global Change Biology, used data from the community science program Program FeederWatch. The research team analyzed more than 3.4 million observations of 140 different bird species across the continental U.S.
"Broadly speaking, we are just starting to dive into the consequences of light and noise for animals," said Ashley Wilson, a graduate student at California Polytechnic State University who led the study. "Most studies focus on a single species' responses to noise or light pollution. As such, our study involving 140 species provides the most comprehensive assessment ...
2021-06-10
Humans have been plagued by a myriad of deadly cancers since ages. Parallelly, they have also been attempting different permutations and combinations of treatments to cure the disease. Part of these attempts involving biomolecular targets have come to the fore in recent years. Like a broad-spectrum antibiotic that can attack and eliminate several microbes at a time, some of these biomolecular targets, when manipulated appropriately, can alleviate different cancers. One such biomolecular target of interest is LIM domain only 1 gene (LMO1).
LMO1 codes for a protein 'connector' that helps in the assembly ...
2021-06-10
Increasing evidence shows that physical activity and exercise training may delay or prevent the onset of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In aging humans, aerobic exercise training increases gray and white matter volume, enhances blood flow, and improves memory function. The ability to measure the effects of exercise on systemic biomarkers associated with risk for AD and relating them to key metabolomic alterations may further prevention, monitoring, and treatment efforts. However, systemic biomarkers that can measure exercise effects on brain function and that link to relevant metabolic responses are lacking.
To address this issue, Henriette van Praag, Ph.D., from Florida Atlantic University's ...
2021-06-10
Highly dispersed platinum catalysts provide new possibilities for industrial processes, such as the flameless combustion of methane, propane, or carbon monoxide, which has fewer emissions and is more resource efficient and consistent than conventional combustion. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a team of researchers reports on which platinum species are active in high-temperature oxidations and what changes they can undergo in the course of the process--important prerequisites for the optimization of catalysts.
Individual metal atoms and clusters consisting of only a few metal atoms have interesting catalytic properties determined by the exact nature of the active metal species. Usually, these are highly dispersed and deposited on ...
2021-06-10
Black people have a higher risk of colorectal cancer than white people, but this risk is likely not due to genetics. Data from a recent study by researchers from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine adds more data to the existing evidence.
"The next step is determining what is behind this increased risk," said lead author Thomas Imperiale, M.D., Regenstrief Institute research scientist, VA investigator and professor of gastroenterology and hepatology at IU School of Medicine. "Lifestyle and healthcare-related behaviors may explain some of the difference." ...
2021-06-10
Washington, D.C. - June 9, 2021 - The Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine is protective against several SARS-CoV-2 variants that have emerged, according to new research presented in the journal mBio, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology. While this is good news, the study also found that the only approved monoclonal antibody therapy for SARS-CoV-2 might be less effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants in laboratory experiments.
"The vaccines provide very strong protection against the earlier forms of the virus as well as the newer variants. This is an important point because I have heard people say that they don't think there is a reason to get vaccinated, because the vaccine isn't going to ...
2021-06-10
Scientists say naked mole rats - a rodent native to West Africa - may hold the key to new treatments for degenerative diseases such as cancer and dementia.
The reclusive animals have a lifespan far in excess of other rodents - for example, mice and rats live about two years, whereas naked mole rats can live for 40 or 50 years.
Researchers at the University of Bradford say the animals have a unique DNA repair mechanism that enables them to prevent cancers and other degenerative conditions, including dementia.
Cancer resistant
Professor Sherif El-Khamisy, Director of the Institute of Cancer Therapeutics at the University, said: "Naked mole rats are fascinating ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] More sustainable mortars and concrete with optimal thermal and mechanical efficiency
The University of the Basque Country-UPV/EHU is researching mortars and concrete manufactured from industrial by-products, within the circular economy approach