Ibuprofen and other NSAIDs superior to codeine for managing outpatient postoperative pain
2021-06-14
(Press-News.org) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen provide better pain control and have fewer adverse effects than codeine, a commonly prescribed opioid, when prescribed after outpatient surgery, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.201915.
"In all surgery types, subgroups and outcome time points, NSAIDs were equal or superior to codeine for postoperative pain," writes Dr. Matthew Choi, Associate Professor of Surgery, McMaster University, with coauthors.
The researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 high-quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving more than 5100 adults to compare pain levels and safety of medications containing codeine, such as Tylenol #3, with NSAIDs. Patients who took NSAIDs had lower pain scores at 6 and 12 hours after treatment than patients taking codeine.
"We found that patients randomized to NSAIDs following outpatient surgical procedures reported better pain scores, better global assessment scores, fewer adverse effects and no difference in bleeding events, compared with those receiving codeine," write the authors.
Codeine is widely used for postoperative pain management and is the most commonly prescribed opioid in Canada. However, codeine is associated with a range of adverse effects and potential misuse or addiction. Alternatives such as NSAIDs can help reduce opioid use in patients after dental and surgical procedures.
Given the range of procedures and dosage combinations included in the high-quality RCTs, the authors suggest that their results have wide clinical application.
"These findings are of general importance to any clinician performing painful medical procedures. The various trials in our meta-analysis evaluated a range of procedures, different NSAID types and various degrees of acetaminophen administration."
The authors conclude that their findings "strengthen existing evidence and are broadly generalizable to patients across surgical disciplines."
INFORMATION:
"Managing postoperative pain in adult outpatients: a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing codeine with NSAIDs" is published June 14, 2021.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-14
The raucous calls of tree hyraxes -- small, herbivorous mammals -- reverberate through the night in the forests of West and Central Africa, but their sound differs depending on the location.
Tree hyraxes living between the Volta and Niger rivers make a barking call that is distinct from the shrieking vocalizations of hyraxes inhabiting other regions of the African forest zone.
A new study in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society co-authored by Yale anthropologist Eric Sargis finds that the barking hyraxes are a separate species from their shrieking neighbors. The newly described species, Dendrohyrax interfluvialis, ...
2021-06-14
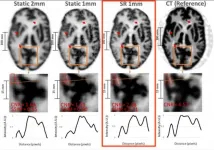
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 5:00 p.m. EDT, Sunday, June 13, 2021) - A new imaging technique has the potential to detect neurological disorders--such as Alzheimer's disease--at their earliest stages, enabling physicians to diagnose and treat patients more quickly. Termed super-resolution, the imaging methodology combines position emission tomography (PET) with an external motion tracking device to create highly detailed images of the brain. This research was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging's 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting.
In brain PET imaging, the quality of the images ...
2021-06-12
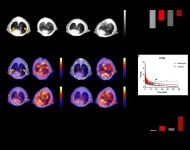
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 4:30 p.m. EDT, Saturday, June 12, 2021)--Positron emission tomography (PET) using a 68Ga-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) can noninvasively identify and monitor pulmonary fibrosis, according to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting. By binding to activated fibroblasts present in affected lungs, FAPI-PET allows for direct imaging of the disease process.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) causes substantial scarring to the lungs, making it difficult for ...
2021-06-12
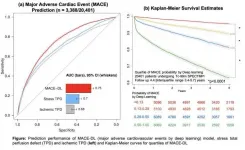
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 6:15 p.m. EDT, Friday, June 11, 2021)--An advanced artificial intelligence technique known as deep learning can predict major adverse cardiac events more accurately than current standard imaging protocols, according to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting. Utilizing data from a registry of more than 20,000 patients, researchers developed a novel deep learning network that has the potential to provide patients with an individualized prediction of their annualized risk for adverse events such as heart attack or death.
Deep learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that mimics the workings of the human brain to process ...
2021-06-11
For decades, the ice shelf helping to hold back one of the fastest-moving glaciers in Antarctica has gradually thinned. Analysis of satellite images reveals a more dramatic process in recent years: From 2017 to 2020, large icebergs at the ice shelf's edge broke off, and the glacier sped up.
Since floating ice shelves help to hold back the larger grounded mass of the glacier, the recent speedup due to the weakening edge could shorten the timeline for Pine Island Glacier's eventual collapse into the sea. The study from researchers at the University of Washington and British Antarctic Survey was published June 11 in the open-access journal Science Advances.
"We may not have the luxury of waiting for slow changes on Pine Island; things could actually go much quicker than expected," ...
2021-06-11
PHILADELPHIA - Cells contain machinery that duplicates DNA into a new set that goes into a newly formed cell. That same class of machines, called polymerases, also build RNA messages, which are like notes copied from the central DNA repository of recipes, so they can be read more efficiently into proteins. But polymerases were thought to only work in one direction DNA into DNA or RNA. This prevents RNA messages from being rewritten back into the master recipe book of genomic DNA. Now, Thomas Jefferson University researchers provide the first evidence that RNA segments can be written back into DNA, which potentially challenges the central dogma in biology and could have wide implications ...
2021-06-11
BOSTON - Vitamin D deficiency strongly exaggerates the craving for and effects of opioids, potentially increasing the risk for dependence and addiction, according to a new study led by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). These findings, published in Science Advances, suggest that addressing the common problem of vitamin D deficiency with inexpensive supplements could play a part in combating the ongoing scourge of opioid addiction.
Earlier work by David E. Fisher, MD, PhD, director of the Mass General Cancer Center's Melanoma Program and director of MGH's Cutaneous Biology Research Center (CBRC), laid the foundation for the current study. In 2007, Fisher and his team found something unexpected: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays ...
2021-06-11
For centuries, scientists, aeronautic designers and adventure-seekers have sought to replicate the qualities that allow birds to fly, namely wing-structure and balance. However, without an external mechanism such as a hot air balloon or airplane, humans have remained earth-bound, unable to use their own bodies to propel themselves into the stratosphere.
While researchers have long-focused on structural factors, like wings, that define the category of bird, a recent study published Science Advances by Professor Avihu Klar at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem's Faculty of Medicine and Prof. Claudio Mello from Oregon Health and Science University found that there are specific molecular characteristics that distinguish birds from animals, and these differences allow birds to flap their ...
2021-06-11
The enormous potential of Big Data has already been demonstrated in areas such as financial services and telecommunications. An international team of researchers led by the IPK Leibniz Institute has now tapped the potential of big data for the first time on a large scale for plant research. To this end, data from three projects were used to increase the predictive accuracy for yield in hybrid varieties of wheat.
"We were able to draw on the largest dataset published to date, which contains information from almost a decade of wheat research and development," says Prof. Dr. Jochen Reif, Head of the Breeding Research Department at IPK. ...
2021-06-11
What The Study Did: Editorial team composition by gender, race, ethnicity and sexual orientation was assessed at 25 leading medical and scientific journals in this survey study.
Authors: James W. Salazar, M.D., M.A.S., of the University of California San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.2363)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ibuprofen and other NSAIDs superior to codeine for managing outpatient postoperative pain