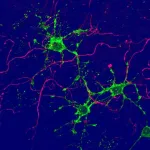
(Press-News.org) Like amyloid plaque, the genetic variant APOE4 has long been associated with Alzheimer's disease, but still little is known about the role the gene plays in the disease process.
Now, a new study published in END
USC study reveals potential new treatment target for Alzheimer's disease
Researchers at Keck School of Medicine of USC identify a novel target related to the blood-brain barrier and a potential therapy that offers hope for slowing progression of Alzheimer's disease in people with the APOE4 gene
2021-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Touchless technology could enable early detection and treatment of eye diseases that cause blindness
2021-06-14
A non-contact laser imaging system could help doctors diagnose and treat eye diseases that cause blindness much earlier than is now possible.
The new technology, developed by engineering researchers at the University of Waterloo, is designed to detect telltale signs of major blinding diseases in retinal blood and tissue that typically go unseen until it is too late.
With current testing methods, diseases such as age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma--which have no symptoms in their early stages--are usually diagnosed only after vision is irreversibly affected.
"We're optimistic that our technology, by providing functional details of the eye such as oxygen saturation and oxygen metabolism, may be able to play a critical role in early ...
Consumers will pay more for ready-to-eat meals made with fewer ingredients
2021-06-14
PULLMAN, Wash. - Most consumers care about the technology and the ingredients used to make their microwavable dinners and other shelf ready meals, according to a new study led by Washington State University researchers. The study found that many consumers are willing to pay a premium for ready-to-eat meals with a 'clean label' showing few ingredients.
They are also more willing to fork out their hard-earned cash when they know their processed foods are made with a new technology that helps limit the number of additives and preservatives commonly found in most ...
NUS engineers devise novel approach to wirelessly power wearable devices
2021-06-14
Advancements in wearable technology are reshaping the way we live, work and play, and also how healthcare is delivered and received. Wearables that have weaved their way into everyday life include smart watches and wireless earphones, while in the healthcare setting, common devices include wearable injectors, electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring patches, listening aids, and more.
A major pain point facing the use of these wearables is the issue of keeping these devices properly and conveniently powered. As the number of wearables one uses increases, the need to charge multiple ...
New glial cells discovered in the brain: Implications for brain repair
2021-06-14
Neurons, nerve cells in the brain, are central players in brain function. However, a key role for glia, long considered support cells, is emerging. A research group at the University of Basel has now discovered two new types of glial cells in the brain, by unleashing adult stem cells from their quiescent state. These new types of glia may play an important role in brain plasticity and repair.
The brain is malleable well into adulthood. Brain plasticity is not only due to the formation of new nerve connections. Stem cells present in the adult brain also ...
What happens in brain cells affected by Alzheimer's disease?
2021-06-14
Moreover, they identified a correlation between the progression of the disease and certain corpuscles in the cell nuclei. They published their report in the journal Acta Neuropathological Communications on 13 April 2021.
Aggregates seem to have a function
Affecting over 50 million people, Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia and primarily occurs in people over the age of 65. The pathology of the disease in the brain is mainly characterised by two factors: beta-amyloid plaques outside the nerve cells and tau proteins. The tau protein stabilises tube-like structures (microtubules) inside cells, which are relevant ...
Bionic reconstruction: New foot for 'Mia' the bearded vulture
2021-06-14
With Oskar Aszmann and his team at the Department of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery, MedUni Vienna has long been regarded as a world leader in bionic limb reconstruction. It was only last year that the world's first fully integrated bionic arm prosthesis was developed at MedUni Vienna. This is ready-to-use and is described as "Plug and Play". Although all bionic aids have so far been used in humans, the technique known as osseointegration (direct skeletal attachment) has now been used for the very first time in a bearded vulture - the creature was given a new foot. A paper on this ground-breaking procedure has been published today (Friday) in the prestigious Journal Scientific Reports.
In large birds such as vultures, the loss of limbs results in the ...
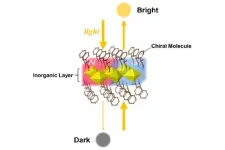
Novel magnet design with magic mirror-like properties
2021-06-14
Researchers at Tohoku University have demonstrated the designability of novel magnets with magic mirror-like characteristics in organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite (OIHP)-type compounds.
OIHP-type compounds, a type of material used to construct solar cells, possess exceptional optical properties and have recently attracted worldwide interest. Researchers are keen to harness their structural diversity.
Although the superior optical properties of OIHPs have been mainly studied for their photoelectric characteristics, several OIHP-type compounds are known to function as magnets that transmit light. Combining the excellent optical ...
The sun's clock
2021-06-14
Not only the very concise 11-year cycle, but also all other periodic solar activity fluctuations can be clocked by planetary attractive forces. This is the conclusion drawn by Dr. Frank Stefani and his colleagues from the Institute of Fluid Dynamics at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) and from the Institute of Continuous Media Mechanics in Perm, Russia. With new model calculations, they are proposing a comprehensive explanation of all important known sun cycles for the first time. They also reveal the longest fluctuations in activity over thousands of years as a chaotic process. ...
Earliest memories can start from the age of two-and-a-half, new study shows
2021-06-14
On average the earliest memories that people can recall point back to when they were just two-and-a-half years old, a new study suggests.
The findings, published in peer-reviewed journal Memory, pushes back the previous conclusions of the average age of earliest memories by a whole year.
They are presented in a new 21-year study, which followed on from a review of already-existing data.
"When one's earliest memory occurs, it is a moving target rather than being a single static memory," explains childhood amnesia expert and lead author Dr Carole Peterson, from Memorial University of Newfoundland.
"Thus, what many people provide when asked for their earliest memory is not a boundary or watershed beginning, before which there are no memories. Rather, ...
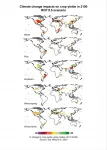
A quarter of global harvests at risk if agriculture does not adapt to climate change
2021-06-14
Shifts in weather patterns induced by climate change will increase extreme heat and reduce rainfall across major crop growing regions, with impacts on agricultural production. Will this trigger a decline in the supply of calories needed to sustain the world's growing population?
According to a study published in the Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, global calorie supplies are subject to continuing or even increasing vulnerability to climate change. Climate change could reduce global crop yields by 10% by mid-century and 25% by century's end, under a vigorous warming scenario, if farmers cannot adapt better than they did historically. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] USC study reveals potential new treatment target for Alzheimer's diseaseResearchers at Keck School of Medicine of USC identify a novel target related to the blood-brain barrier and a potential therapy that offers hope for slowing progression of Alzheimer's disease in people with the APOE4 gene