A frozen leap forward
Novel cryopreservation methods enable long-term storage and worldwide distribution of a cellular therapy for age-related macular degeneration
2021-06-14
(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, Calif.) -- Scientists at UC Santa Barbara, University of Southern California (USC), and the biotechnology company Regenerative Patch Technologies LLC (RPT) have reported new methodology for preservation of RPT's stem cell-based therapy for age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
The new research, recently published in Scientific Reports, optimizes the conditions to cryopreserve, or freeze, an implant consisting of a single layer of ocular cells generated from human embryonic stem cells supported by a flexible scaffold about 3x6 mm in size. This implant is currently in clinical trial for the treatment of AMD, the leading cause of blindness in aging populations. The results demonstrate that the implant can be frozen, stored for long periods and distributed in frozen form to clinical sites where it is designed to be thawed and immediately implanted into the eyes of patients with macular degeneration. The capacity to cryopreserve this and other cell-based therapeutics will extend shelf life and enable on-demand distribution to distant clinical sites, increasing the number of patients able to benefit from such treatments.
The report published by lead author Britney Pennington and colleagues achieves a milestone that brings ocular implants one step closer to the clinic. "This is the first published report that demonstrates high viability and function of adherent ocular cells following cryopreservation, even after long-term frozen storage," said Pennington, head of process development at RPT and assistant project scientist at UC Santa Barbara.
The study demonstrates that cryopreserved implants are comparable to their non-cryopreserved counterparts in appearance, gene expression and cellular function. "It's a major advance in the development of cell therapies using a sheet of cells, or a monolayer of cells, because you can freeze them as the final product and ship them all over the world," said UCSB professor and senior author Dennis O. Clegg,
The implant used in the study consists of clinical-grade retinal pigmented epithelial (RPE) cells derived from human embryonic stem cells by collaborators at cancer hospital City of Hope, and a synthetic scaffold made of ultrathin parylene designed by engineers at California Institute of Technology and manufactured by LEAP Biomed Innovators. The resulting implant consists of cells attached to the scaffold, which permits the targeted delivery of therapeutic cells to the diseased region within the eye. A non-cryopreserved formulation of this cellular therapy is being employed in an ongoing Phase I/IIa clinical trial sponsored by RPT. The cryopreserved formulation enabled by the work of Pennington and colleagues will facilitate anticipated Phase IIb and Phase III clinical trials as well as ultimate commercialization and clinical application of the product.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by funding from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), the William K. Bowes Foundation, and Santen Ventures. Further information about Regenerative Patch Technologies can be found at http://www.regenerativepatch.com.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-14
When lithium ions flow in and out of a battery electrode during charging and discharging, a tiny bit of oxygen seeps out and the battery's voltage - a measure of how much energy it delivers - fades an equally tiny bit. The losses mount over time, and can eventually sap the battery's energy storage capacity by 10-15%.
Now researchers have measured this super-slow process with unprecedented detail, showing how the holes, or vacancies, left by escaping oxygen atoms change the electrode's structure and chemistry and gradually reduce how much energy it can store.
The results contradict some of the assumptions scientists had made about this process and could suggest new ways of engineering electrodes to prevent it.
The research team from the Department of Energy's ...
2021-06-14
MISSOULA - Those in love with the outdoors can spend their entire lives chasing that perfect campsite. New University of Montana research suggests what they are trying to find.
Will Rice, a UM assistant professor of outdoor recreation and wildland management, used big data to study the 179 extremely popular campsites of Watchman Campground in Utah's Zion National Park. Campers use an online system to reserve a wide variety of sites with different amenities, and people book the sites an average of 51 to 142 days in advance, providing hard data about demand.
Along with colleague Soyoung Park of Florida Atlantic University, Rice sifted through nearly 23,000 reservations. The researchers found that price and availability of electricity were the largest drivers of demand. Proximity ...
2021-06-14
Albeit very small, with a carapace width of only 3 cm, the Atlantic mangrove fiddler crab Leptuca thayeri can be a great help to scientists seeking to understand more about the effects of global climate change. In a study published in the journal Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, Brazilian researchers supported by São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP show how the ocean warming and acidification forecast by the end of the century could affect the lifecycle of these crustaceans.
Embryos of L. thayeri were exposed to a temperature rise of 4 °C and a pH reduction of 0.7 against the average for their habitat, growing faster as a result. However, a larger number of ...
2021-06-14
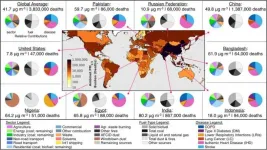
An interdisciplinary group of researchers from across the globe has comprehensively examined the sources and health effects of air pollution -- not just on a global scale, but also individually for more than 200 countries.
They found that worldwide, more than one million deaths were attributable to the burning of fossil fuels in 2017. More than half of those deaths were attributable to coal.
Findings and access to their data, which have been made public, were published today in the journal Nature Communications.
Pollution is at once a global crisis and a devastatingly personal problem. It is analyzed by satellites, but PM2.5 -- tiny particles that can infiltrate a person's lungs -- can also sicken a person who cooks dinner nightly on a cookstove.
"PM2.5 ...
2021-06-14
Treatment options for a deadly liver cancer, fibrolamellar carcinoma, are severely lacking. Drugs that work on other liver cancers are not effective, and although progress has been made in identifying the specific genes involved in driving the growth of fibrolamellar tumors, these findings have yet to translate into any treatment. For now, surgery is the only option for those affected--mostly children and young adults with no prior liver conditions.
Sanford M. Simon and his group understood that patients dying of fibrolamellar could not afford to wait. "There are people who need therapy now," he says. So his group threw the kitchen sink at the problem and tested over 5,000 compounds, either already approved for other clinical uses or in clinical ...
2021-06-14
DALLAS - June 14, 2021 - Overweight cancer patients receiving immunotherapy treatments live more than twice as long as lighter patients, but only when dosing is weight-based, according to a study by cancer researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center.
The findings, published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer, run counter to current practice trends, which favor fixed dosing, in which patients are given the same dose regardless of weight. The study included data on nearly 300 patients with melanoma, lung, kidney, and head and neck cancers ...
2021-06-14
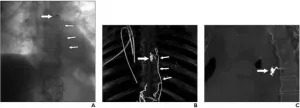
Leesburg, VA, June 14, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), high-dose intranodal lymphangiography (INL) with ethiodized oil is a safe and effective procedure for treating high-output postsurgical chylothorax with chest tube removal in 83% of patients.
"To our knowledge," wrote corresponding author Geert Maleux of University Hospitals in Leuven, Belgium, "no data are available on the safety or potential beneficial effect of injecting higher doses of ethiodized oil to treat patients with refractory postoperative chylothorax."
All 18 patients (mean, 67 years; range, ...
2021-06-14
A team of scientists from Kaunas University of Technology and Lithuanian Energy Institute proposed a method to convert lint-microfibers found in clothes dryers into energy. They not only constructed a pilot pyrolysis plant but also developed a mathematical model to calculate possible economic and environmental outcomes of the technology. Researchers estimate that by converting lint microfibers produced by 1 million people, almost 14 tons of oil, 21.5 tons of gas and nearly 10 tons of char could be produced.
Each year, the global population consumes approximately 80 billion pieces of clothing and approximately €140 million worth of it goes into landfill. This is accompanied by large amounts of emissions, causing serious environmental and health problems. One of the ways to lessen ...
2021-06-14
A new study found higher education students are more engaged and motivated when they are taught using playful pedagogy rather than the traditional lecture-based method. The study was conducted by University of Colorado Denver counseling researcher Lisa Forbes and was published in the Journal of Teaching and Learning.
While many educators in higher education believe play is a method that is solely used for elementary education, Forbes argues that play is important in post-secondary education to enhance student learning outcomes.
Throughout the spring 2020 semester, Forbes observed students who were enrolled in three of her courses between the ages of 23-43. To introduce playful pedagogy, Forbes included games and play, not always tied to the ...
2021-06-14
Solar flares jetting out from the sun and thunderstorms generated on Earth impact the planet's ionosphere in different ways, which have implications for the ability to conduct long range communications.
A team of researchers working with data collected by the Incoherent Scatter Radar (ISR) at the Arecibo Observatory, satellites, and lightning detectors in Puerto Rico have for the first time examined the simultaneous impacts of thunderstorms and solar flares on the ionospheric D-region (often referred to as the edge of space).
In the first of its kind analysis, the team determined that solar flares ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A frozen leap forward
Novel cryopreservation methods enable long-term storage and worldwide distribution of a cellular therapy for age-related macular degeneration