Study reveals bycatch risk for dolphins and porpoises in global small-scale fisheries
A new study by Newcastle University shows that the risk of dolphins and porpoises being caught in small-scale (artisanal) fisheries is highest in low- and middle-income regions around the tropics and sub-tropics
2021-06-15
(Press-News.org) A new study by Newcastle University shows that the risk of dolphins and porpoises being caught in small-scale (artisanal) fisheries is highest in low- and middle-income regions around the tropics and sub-tropics.
Marine scientists assessed the risk posed by small-scale fisheries to all 72 species of toothed whales found throughout the world's oceans. They found that this risk was highest in the Central Indo-Pacific, Temperate Northern Pacific, Temperate South America and the Western Indo-Pacific.
Publishing their findings in the journal Fish and Fisheries, the authors argue that addressing the bycatch risks posed by small-scale fisheries in the high-risk regions is especially challenging and must be considered a global priority for toothed whale conservation.
They warn that immediate management and conservation actions are required to reduce and ideally eliminate small-scale fisheries bycatch to prevent species extinctions.
Dr Andrew Temple, Research Associate at the School of Natural and Environmental Sciences and Senior Consultant at MRAG Ltd said: "Fisheries are the greatest threat to the survival of dolphins, porpoises and other toothed whales worldwide. This is the first study to take a global perspective on the threat to these species from small-scale fisheries."
Professor Per Berggren, of Newcastle University's School of Natural and Environmental Sciences, continued: "Small-scale fisheries are a particular threat to species found in coastal shallow waters where dolphin and porpoise distribution overlaps with gillnets use. Our results suggest that some of the most at-risk species are the four species of humpback dolphins, Irrawaddy dolphin, Australian snubfin dolphin, Franciscana dolphin, Guiana dolphin, Indo-Pacific finless porpoise, and the likely soon to be extinct vaquita."
Dr Andrew Temple added: "Our results highlight a "wicked problem" for toothed whale bycatch in small-scale fisheries. Small-scale fisheries are vital to the food, nutritional, and economic security of many communities in low- and middle-income nations. Managers of these fisheries therefore have to carefully balance the actions required to save these species against the risks that these actions might result in unintentional harm to fishing communities that rely on the oceans for their livelihoods. Solving this "wicked problem" is made even more challenging because funds available to fisheries managers are generally more limited in these high-risk regions, making effective fisheries management extremely difficult."
The study authors recognise that conservation actions need to be realistic and will certainly require international collaboration and cooperation. They call for mitigation actions that are tailored to the specific local economic and social contexts, and balance species and human needs.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-15
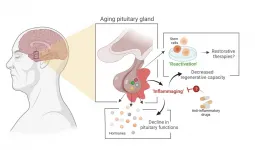
Stem cell biologist Hugo Vankelecom (KU Leuven) and his colleagues have discovered that the pituitary gland in mice ages as the result of an age-related form of chronic inflammation. It may be possible to slow down this process or even partially repair it. The researchers have published their findings in PNAS.
The pituitary gland is a small, globular gland located underneath the brain that plays a major role in the hormonal system, explains Professor Hugo Vankelecom from the Department of Development and Regeneration at KU Leuven. "My research group discovered that the pituitary gland ages as a result of a form of chronic inflammation that affects tissue and even the organism as a whole. This natural process usually goes unnoticed ...
2021-06-15
The inclusion of biological uncertainty and the latest case data can significantly improve the prediction accuracy of standard epidemiological models of virus transmission, new research led by KAUST and the Kuwait College of Science and Technology (KCST) has shown.
Modern mathematical epidemic models have been tested like never before during the COVID-19 pandemic. These models use mathematics to describe the various biological and transmission processes involved in an epidemic. However, when such factors are highly uncertain, such as during the emergence of a new virus like COVID-19, the predictions ...
2021-06-15
Local rice varieties in Vietnam could be used to help breed improved crops with higher resilience to climate change, according to a new study published in Rice.
Earlham Institute researchers are part of an international collaboration with genebanks and rice breeders in Vietnam - championed by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) to help abolish world poverty and hunger - are aiming to identify varieties that can survive an increasingly unpredictable climate.
The new genomic data they have generated will significantly support efforts to ...
2021-06-15
Pesticides safeguard agricultural yields by controlling harmful insects, fungi, and weeds. However, they also enter neighbouring streams and damage the aquatic communities, which are crucial for maintaining biodiversity, are part of the food web and support the self-purification of water. In a nationwide monitoring programme, a consortium of scientists led by the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) has shown that the governmental thresholds for pesticides are generally too high and that even these excessively high levels are still exceeded in over 80% of water bodies. As they published in the scientific journal Water Research the loss of biodiversity can only be halted if the environmental risk assessment ...
2021-06-15
New research led by the University of Kent has found that there is no link between bed sharing, infant-mother attachment, and infant behavioural outcomes.
Contrary to previous beliefs that bed sharing is beneficial (or even required) for babies to develop a secure attachment style and for mothers to develop a strong bond to their baby, researchers have found that it is neither associated with positive or negative outcomes related to infant attachment and maternal bonding.
There is a lot of controversial debate about bed sharing by parents and the infant sleep literature, in particular. Notably, researchers and practitioners recommend against bed sharing, particularly before four months of age due to the increased risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS).
In reality, ...
2021-06-15
The influx of warmer water masses from the North Atlantic into the European marginal seas plays a significant role in the marked decrease in sea-ice growth, especially in winter. Sea-ice physicists from the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) together with researchers from the US and Russia, now present evidence for this in two new studies, which show that heat from the Atlantic has hindered ice growth in the Barents and Kara Seas for years. Furthermore, they demonstrate that the invasion of warm Atlantic water masses further east, ...
2021-06-15
The research - published ahead of World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought on 17 June 2021 - examines recent and projected climate change impacts on water security across the world's drylands up to the year 2100.
It concludes that more efficient water management, technology and infrastructure, and better demand and supply management can offer more equitable access to water resources and help to achieve development goals.
Lead author, Professor Lindsay Stringer from the Department of Environment and Geography at the University of York said "People in dryland areas are already adapting to climate changes, but they need to be supported with coherent system-oriented policies and institutions that put water security at their core."
Globally, water scarcity already affects ...
2021-06-15
Below please find link(s) to new coronavirus-related content published today in Annals of Internal Medicine. All coronavirus-related content published in Annals of Internal Medicine is free to the public. A complete collection is available at https://annals.org/aim/pages/coronavirus-content.
1. NFL employee and player surveillance program enabled early detection of COVID-19, even among those who were asymptomatic
Free full text: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-0319
Frequent, routine testing within the National Football League (NFL) enabled early detection of COVID-19 infection among players and ...
2021-06-15
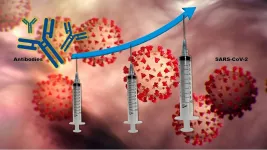
In a study published today in the Annals of Internal Medicine, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they believe that, for the first time, there is evidence to show that three doses of vaccine increase antibody levels against SARS-CoV-2 -- the virus that causes COVID 19 -- more than the standard two-dose regimen for people who have received solid organ transplants.
"Our findings suggest clinical trials are warranted to determine if transplant recipients should receive COVID-19 vaccine booster doses as standard clinical practice, similar to what ...
2021-06-15
Sometimes photos cannot truly capture a scene. How much more epic would that vacation photo of Niagara Falls be if the water were moving?
Researchers at the University of Washington have developed a deep learning method that can do just that: If given a single photo of a waterfall, the system creates a video showing that water cascading down. All that's missing is the roar of the water and the feeling of the spray on your face.
The team's method can animate any flowing material, including smoke and clouds. This technique produces a short video that loops seamlessly, giving the impression of endless movement. The researchers will present this approach June 22 at the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
"A ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study reveals bycatch risk for dolphins and porpoises in global small-scale fisheries
A new study by Newcastle University shows that the risk of dolphins and porpoises being caught in small-scale (artisanal) fisheries is highest in low- and middle-income regions around the tropics and sub-tropics