(Press-News.org) Ethiopia, Nigeria, Colombia, Myanmar and Syria are just a handful of the places around the world currently engaged in ongoing civil wars. Even when peace agreements can be negotiated to end civil wars, maintaining stability is incredibly challenging. In these fragile post-conflict areas, a small communal dispute can easily escalate and unravel peace deals.
Peacekeepers can help contain the spread of violence and promote peaceful interactions between groups, but how? And in what situations can peacekeepers be most effective? New research from Washington University in St. Louis answers these important questions.
The research, conducted by William Nomikos, assistant professor of political science in Arts & Sciences, demonstrates that peacekeeping patrols make individuals more optimistic in their perceptions of the risks of engagement and about the likelihood that members of outgroups will reciprocate attempts at cooperation. That confidence makes individuals more willing to cooperate with members of other groups.
And that's important because intergroup cooperation limits communal violence, promotes economic development and bolsters social trust, Nomikos said.
"Peacekeepers do what domestic security institutions are unable or unwilling to do -- draw a clear line between violence used in intergroup interactions and the punishment of such violence," Nomikos said.
"Peacekeepers interact with civilians, learn about ongoing disputes in a locality and attempt to stop such disputes from escalating," he added. "Even when disputes are far from violent, the presence of peacekeepers discourages aggression that may lead to bloodshed. They lay the foundation for intergroup cooperation at the local level."
But not all peacekeeping arrangements work. Nomikos' research, in the Journal of Politics, explains why and offers valuable insight for the international community on how to reduce the fragility of post-conflict settings, including between Israel and Gaza.
Conducting research in the field
To test the effectiveness of peacekeepers, Nomikos conducted a "lab-in-the-field" experiment in Mali, a West African country with an active conflict managed by troops from France and the United Nations, between February and March 2016. At this time, the ethnic conflict between minority Tuareg separatists and the Malian government had receded as a threat to the stability of Mali, replaced instead by pockets of communal violence driven by breakdowns in cooperation.
Nomikos recruited participants to play a trust game. Each participant was given 1,000 West African francs (FCFA) and tasked to donate a portion of the endowment to a fictitious Tuareg partner. They were told that study organizers would double the donation, up to 2,000, and the Tuareg partner would choose how much to send back. In this game, the non-Tuareg's optimal strategy is to cooperate with their Tuareg partners.
Participants were randomly assigned to either a control group or one of two treatment groups, in which they were told that two patrolling officers from either the UN or France would punish any low partner contributions with a fine. For the safety of the research participants, real peacekeepers and Tuareg Malians did not participate in the game.
Some, not all, peacekeeping efforts work
Participants assigned to the control group sent an average of 601 FCFA or about 60% of their initial endowments to their Tuareg partners. Participants assigned to the French peacekeeping group sent an average of 631 FCFA, approximately 5% more than the control group. The difference was statistically insignificant.
Those assigned to UN peacekeeping test group were far more generous, though. On average, they sent 797 FCFA to their Tuareg partners -- an increase of 32.6% compared with the control group.
Follow-up interviews and surveys with study participants show UN peacekeepers were more effective than French peacekeepers at encouraging cooperation because they were viewed as unbiased. Additionally, participants believed UN peacekeepers were more likely to intervene in everyday interactions than French counterparts.
"Individuals trust that unbiased peacekeepers will punish any potential party that transgresses in a social interaction," Nomikos said. "By contrast, biased peacekeepers fail to reassure individuals that they will protect them from being taking advantage of by favored parties."
Research provides blueprint for future success
According to Nomikos, the results imply that residents of post-conflict settings may reject the presence of some international actors more than others, which can impact peacekeeping outcomes.
"Former colonial powers account for the vast majority of unilateral military intervention in existing conflicts in Africa," Nomikos said. "Even if an intervention is conducted by a non-colonial major power such as the United States or a historically neutral power such as Sweden, locals are likely to perceive troops as biased. Countries typically launch military operations in alliance with local ethnic groups. This is especially true in the context of communal disputes at the local level."
Additionally, peacekeeping at the local level is at its most effective when baseline levels of intergroup and social trust are low.
"It is under these conditions that enforcement is needed the most since members of two different social groups will have little reason to trust each other enough to cooperate," Nomikos said.
Peacekeepers deployed with the explicit mandate to enforce peaceful interactions within civilian communities can promote intergroup cooperation, even in weakly institutionalized settings. However, intergroup cooperation will dissipate when peacekeepers withdraw unless there is substantial development of domestic institutional capacity, Nomikos said.
"It is for this reason that most modern UN peace operations have become long, drawn-out affairs, even after nominal peace treaties have been signed," he said.
While this may be a challenging electoral proposition for many countries, Nomikos hopes his research will provide rationale for contributing countries to make further investments in local-level peacekeeping efforts.
"The conditional aspects of the results -- that the UN is more effective in low trust settings and with increased contact -- could also help us understand failures of UN peacekeeping," he said.
The research also offers a potential way forward for Israel and Gaza, where the most recent conflict left more than 200 people dead and ended with an Egyptian-brokered ceasefire. According to Nomikos, the first ever UN peacekeeping operation was deployed to Israel-Palestine in 1948 as part of the UN's mediation efforts with the founding of the state of Israel.
"That mission is still in place, but it is small and non-military -- around 400 civilian staff. It is unlikely that a substantial peacekeeping operation would be deployed to the area to mediate the conflict for political reasons," Nomikos said.
"However, my research suggests that there are gains to be made if the international community is willing to get creative and focus on local-level peace rather than bargaining between elites. Secretary of State Antony Blinken, for example, is met with the relevant leadership, but it's unclear how much control these leaders have over their own communities.
"The new frontier of the Israel-Palestine conflict has been so-called intercommunal violence or communal conflict, meaning that there have been outbursts of violence between civilians in mixed ethnicity communities. My research shows that international actors can be effective in small numbers in these areas," he added.
INFORMATION:
Changing your eating habits or altering your circadian clock can impact healthy fat tissue throughout your lifespan, according to a preclinical study published today in Nature by researchers with The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth).
Healthy fat tissue helps provide energy, supports cell growth, protects organs, and keeps the body warm. A good quality diet and one that is consumed in a rhythmic manner (i.e., during our active cycle) is important in maintaining healthy fat, the researchers found.
Adipocyte progenitor cells mature into adipocytes - the healthy fat cells that make up our adipose tissue, which stores energy as fat. Researchers discovered that adipocyte progenitors undergo rhythmic daily proliferation throughout the ...
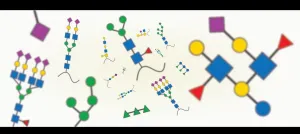
A new model that applies artificial intelligence to carbohydrates improves the understanding of the infection process and could help predict which viruses are likely to spread from animals to humans. This is reported in a recent study led by researchers at the University of Gothenburg.
Carbohydrates participate in nearly all biological processes - yet they are still not well understood. Referred to as glycans, these carbohydrates are crucial to making our body work the way it is supposed to. However, with a frightening frequency, they are also ...
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have developed two rapid diagnostic tests for COVID-19 that are nearly as accurate as the gold-standard test currently used in laboratories. Unlike the gold standard test, which extracts RNA and uses it to amplify the DNA of the virus, these new tests can detect the presence of the virus in as little as five minutes using different methods.
One test is a COVID-19 molecular diagnostic test, called Antisense, that uses electrochemical sensing to detect the presence of the virus. The other uses a simple assay of gold nanoparticles to detect a color change when the virus is present. Both tests were developed by Dipanjan Pan, PhD, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Nuclear Medicine ...
Two new studies have cast unprecedented light on disease processes in tuberculosis, identifying key genetic changes that cause damage in the lungs and a drug treatment that could speed up recovery.
Tuberculosis (TB) is a lung infection that has killed more humans than any other and until last year was the top infectious killer around the world. Globally, an estimated 10 million people develop the disease each year.
The findings are reported in two papers in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
In the first study, a team from the University of Southampton used a new 3D culture system they have developed to observe the changes that occur in cells infected with TB. Unlike the laboratory-standard 2D culture system, where cells are placed ...
This past year has been transformational in terms of not only a global pandemic but a sustained focus on racism and systemic injustice. There has been a widespread circulation of images and videos in the news and online. Just like adults, adolescents are exposed to these images with important consequences for their emotional health and coping. However, few studies have sought to understand the influence of racism experienced online.
According to a qualitative study published in JAMA Network Open adolescents expressed feelings of helplessness when exposed to secondhand racism online. Specifically, adolescents described helplessness stemming from the pervasiveness of racism in our society. This was illustrated by quotes, such as "[racist events are] just another day in the life" referring ...
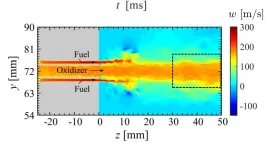
WASHINGTON, June 8, 2021 -- Combustion engines can develop high frequency oscillations, leading to structural damage to the engines and unsafe operating conditions. A detailed understanding of the physical mechanism that causes these oscillations is required but has been lacking until now.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, research from the Tokyo University of Science and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency clarifies the feedback processes that give rise to these oscillations in rocket engines.
The investigators studied simulated combustion events in a computational model of a rocket combustor. Their analysis involved sophisticated techniques, including symbolic ...
For many, the Thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana) is little more than a roadside weed, but this plant has a long history with scientists trying to understand how plants grow and develop. Arabidopsis was first scientifically described as early as the 16th century and the first genetic mutant was identified in the 1800s. Since the 1940s, Arabidopsis has increased in popularity within the scientific community, which continues to use it as a model system to explore plant genetics, development and physiology to this day.
One might expect that after decades of scientific scrutiny the structure of Arabidopsis had been fully documented, but a new study from scientists from The Pennsylvania State University, USA, has revealed that this humble plant still has some surprises. The researchers describe ...
A team of scientists at the Keck School of Medicine of USC has created what could be a key building block for assembling a synthetic kidney. In a new study in Nature Communications, Zhongwei Li and his colleagues describe how they can generate rudimentary kidney structures, known as organoids, that resemble the collecting duct system that helps maintain the body's fluid and pH balance by concentrating and transporting urine.
"Our progress in creating new types of kidney organoids provides powerful tools for not only understanding development and disease, but also finding new treatments and regenerative approaches for patients," said Li, the study's corresponding ...
What The Study Did: In this survey of 1,186 medical, graduate and health professional school faculty, more faculty considered leaving since the COVID-19 pandemic than before. Faculty with children, particularly female faculty with children, were more likely to consider leaving since the pandemic.
Authors: Susan A. Matulevicius, M.D., M.S.C.S., of the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.13539)
Editor's Note: Please ...
What The Study Did: Researchers examined whether a sweetened beverage tax in Philadelphia was associated with sustained changes in beverage prices and purchases of sweetened beverages and high-sugar foods two years after implementation of the tax.
Authors: Christina A. Roberto, Ph.D., of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.13527)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest ...